Abstract
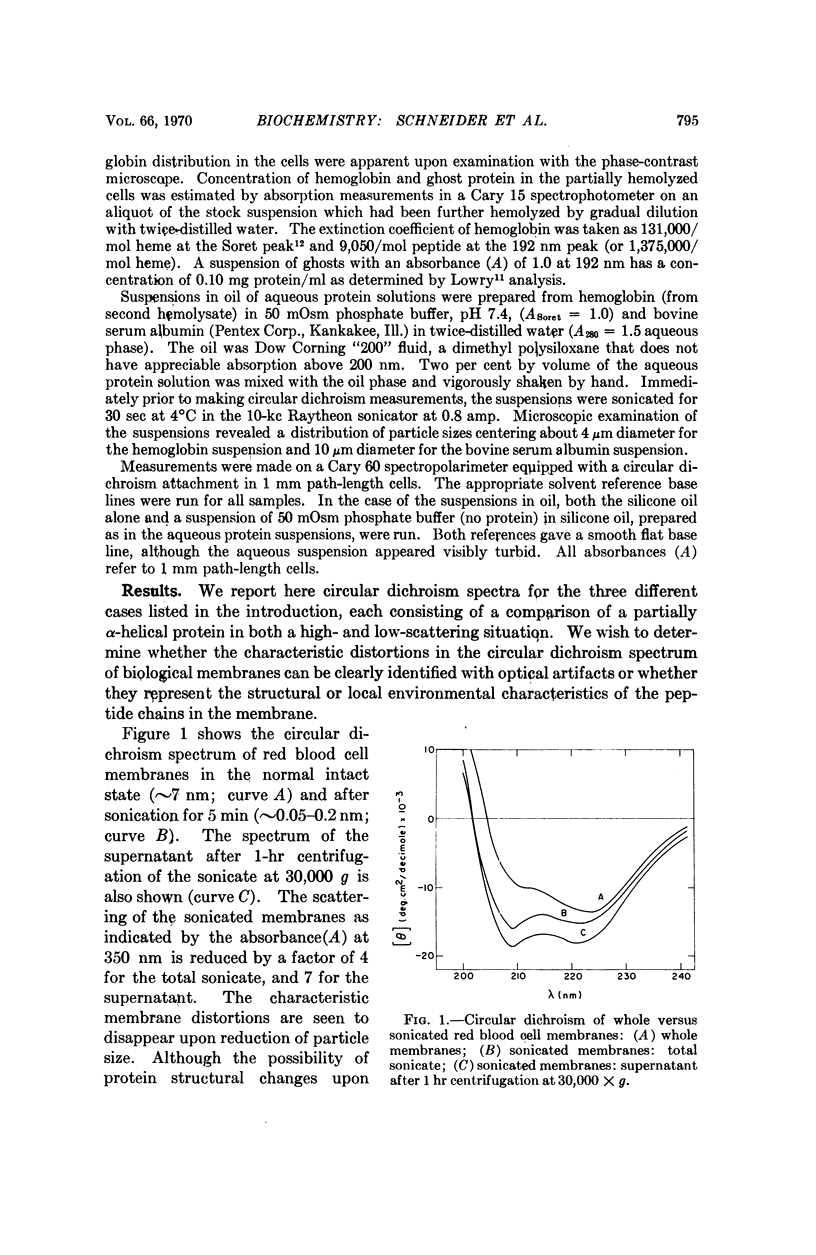
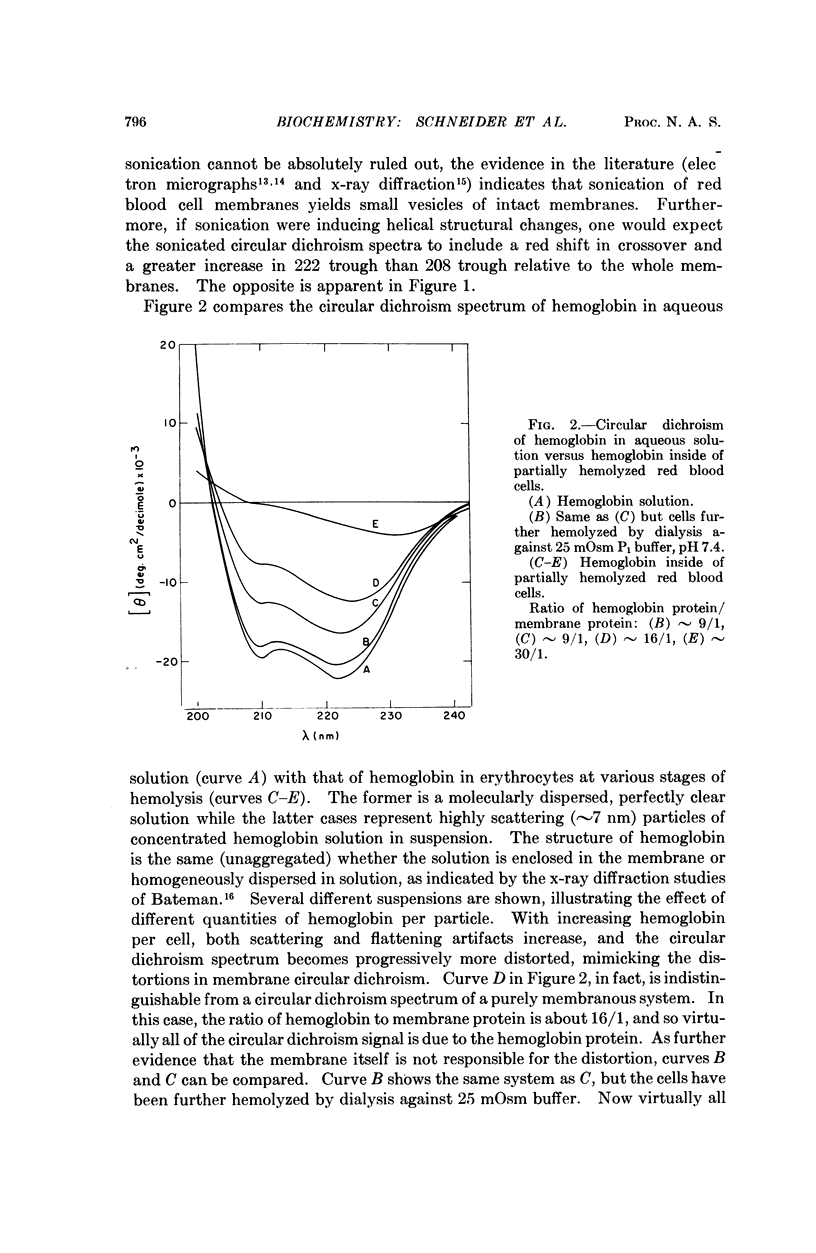
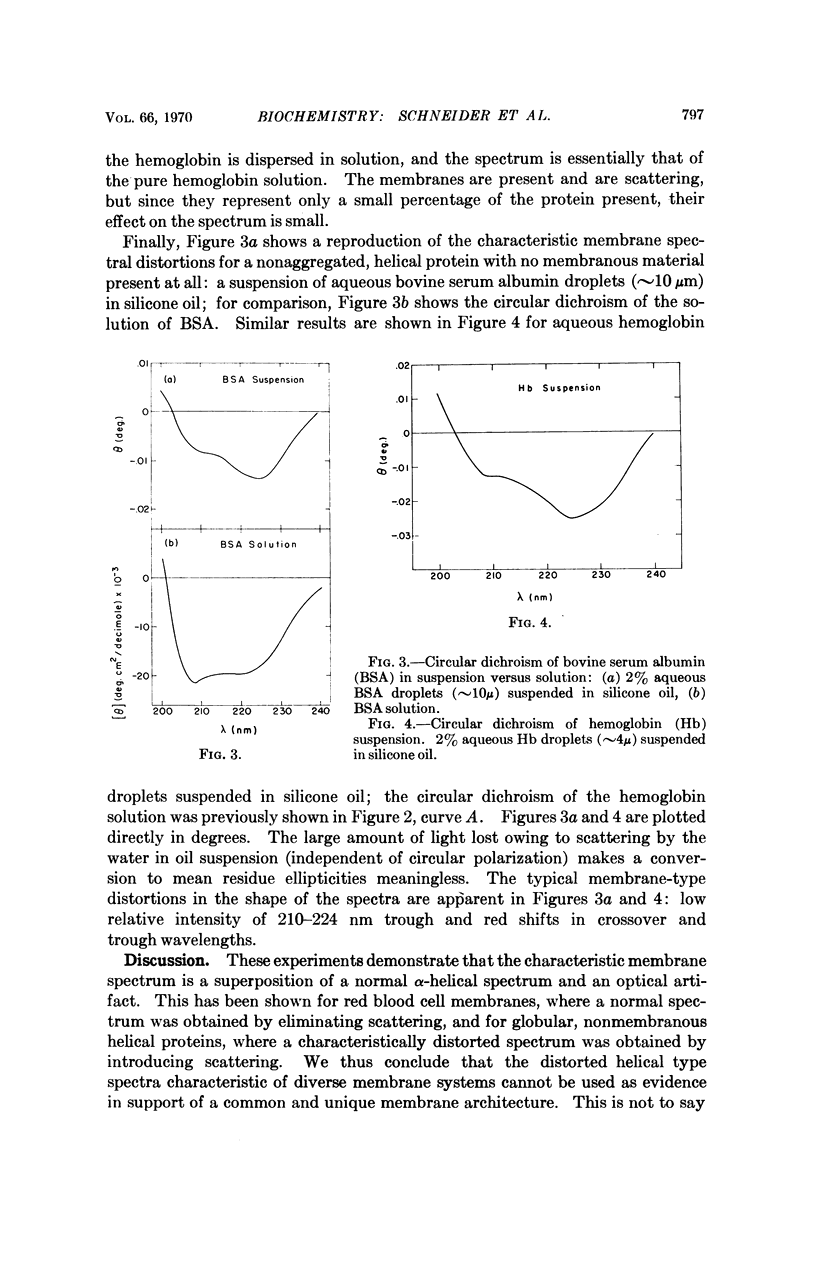
The following question has recently arisen in the literature concerning the interpretation of the optical activity of biological membranes: do the characteristic spectral distortions observed for diverse membrane systems reflect some common and unique aspect of membrane architecture or are they the result of scattering effects owing to the particulate nature of membranous systems? We have confirmed the latter interpretation on the basis of the following experimental observations: (a) red blood cell membranes give a normal circular dichroism spectrum when scattering is reduced and (b) nonaggregated, nonmembranous helical proteins give distorted membranelike spectra when scattering is introduced. An improved estimate of secondary structure on the basis of undistorted spectra results in about 50 per cent α-helix for red blood cell membrane protein. In addition we conclude that the distortions in optical activity spectra offer no evidence in support of various proposed membrane models.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DUYSENS L. N. The flattening of the absorption spectrum of suspensions, as compared to that of solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Jan;19(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finean J. B., Coleman R., Green W. G., Limbrick A. R. Low-angle x-ray diffraction and electron-microscope studies of isolated cell membranes. J Cell Sci. 1966 Sep;1(3):287–296. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1.3.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield N., Fasman G. D. Computed circular dichroism spectra for the evaluation of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4108–4116. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSU S. S., KNUDSEN J. P., YUDOWITCH K. L. Hemoglobin spacing in erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Aug;45(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(53)80017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji T. H., Urry D. W. Correlation of light scattering and absorption flattening effects with distortions in the circular dichroism patterns of mitochondrial membrane fragments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 21;34(4):404–411. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke B. Optical rotatory dispersion of chloroplast-lamellae fragments. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Dec;112(3):554–561. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Singer S. J. Protein conformation in cell membrane preparations as studied by optical rotatory dispersion and circular dichroism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1828–1835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Palade G. E. The localization of Mg-Na-K-activated adenosine triphosphatase on red cell ghost membranes. J Cell Biol. 1967 Nov;35(2):385–404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mommaerts W. F. Conformational studies on the membrane protein of sarcotubular vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2476–2482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., McIntosh J. R. Erythrocyte membranes: effects on sonication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 5;163(3):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steim J. M., Fleischer S. Aggregation-induced red shift of the Cotton effect of mitochondrial structural protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1292–1298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Ji T. H. Distortions in circular dichroism patterns of particulate (or membranous) systems. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Dec;128(3):802–807. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Mednieks M., Bejnarowicz E. Optical rotation of mitochondrial membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1043–1049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. F., Zahler P. H. Protein conformations in cellular membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1552–1559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigglesworth J. M., Packer L. Optical rotary dispersion and circular dichroism studies on mitochondria: correlation of ultrastructure and metabolic state with molecular conformational changes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Dec;128(3):790–801. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


