Abstract
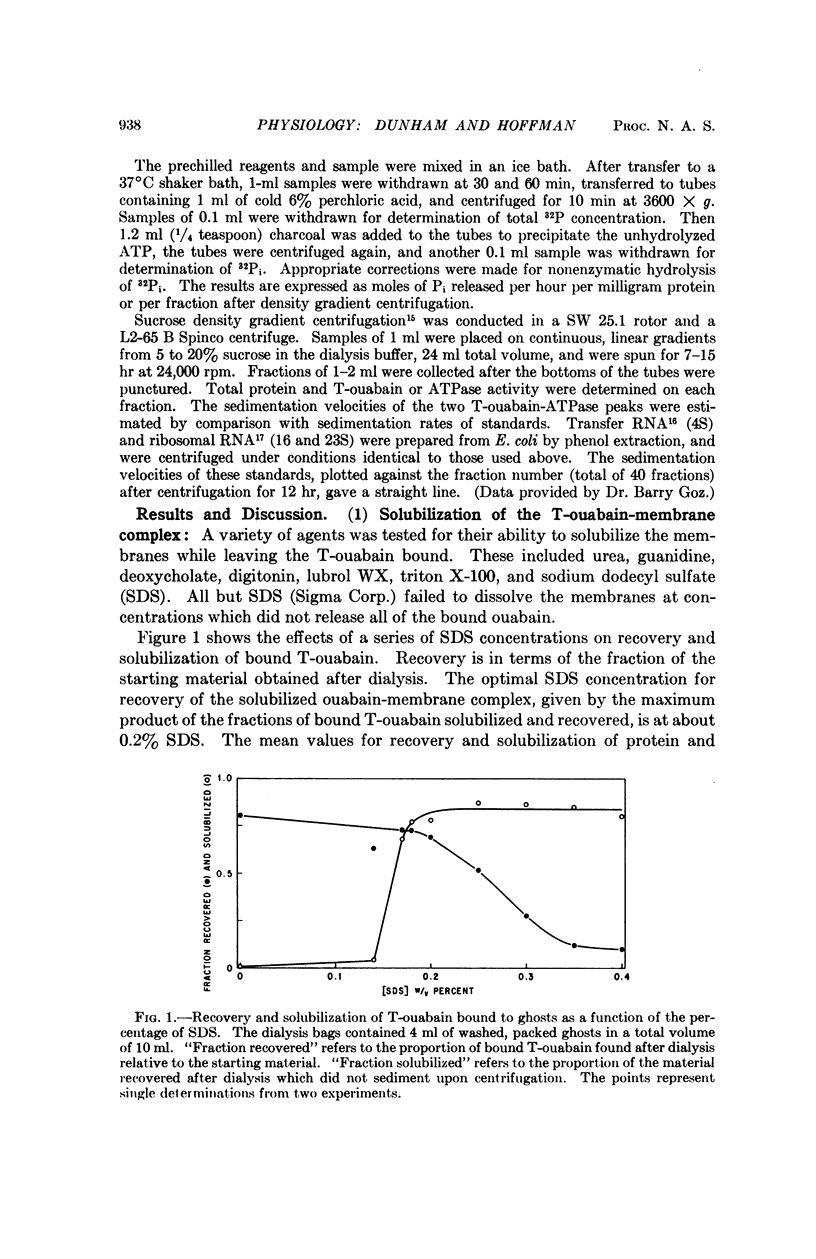
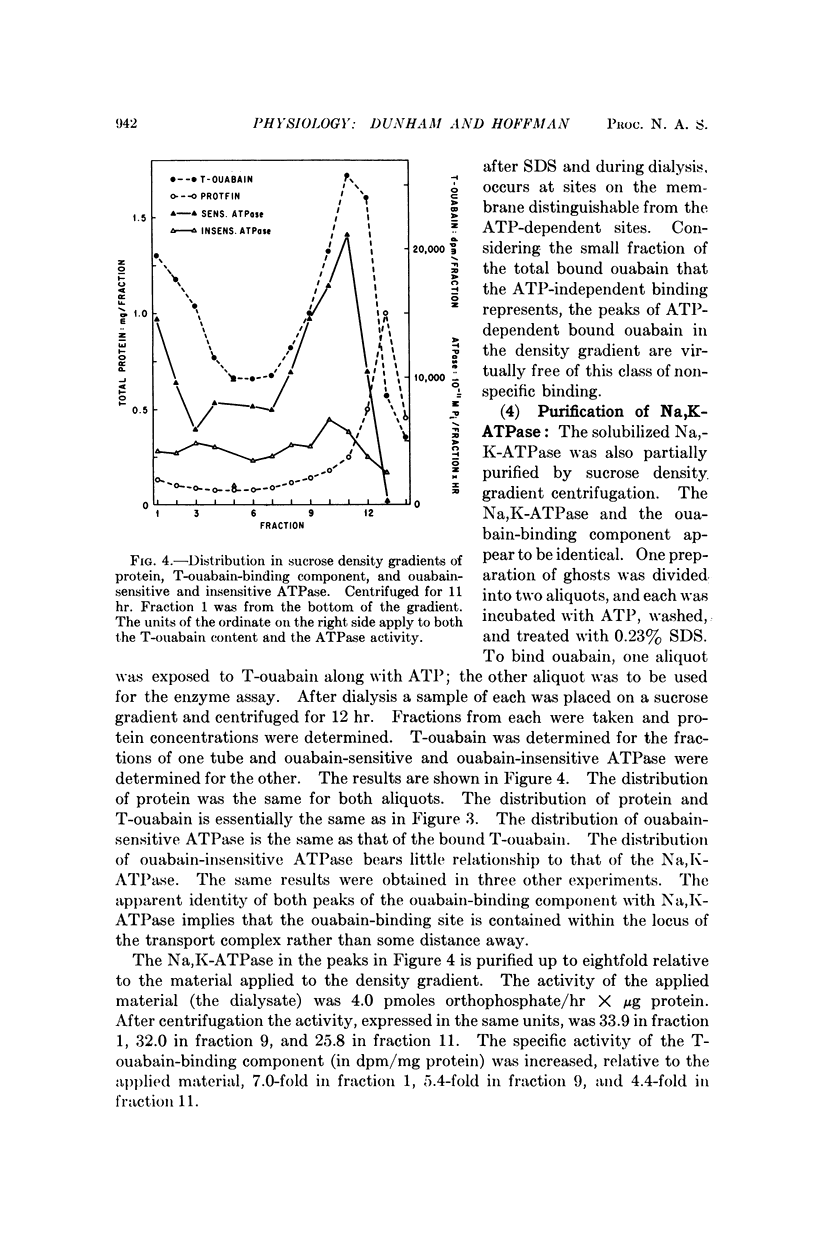
Ghosts of human red cells were incubated with tritiated ouabain in the presence of ATP, Mg, and Na, conditions under which ouabain binds with high specificity to Na:K transport sites. The labeled membranes were solubilized with sodium dodecyl sulfate and dialyzed. Sodium dodecyl sulfate solubilizes most of the membrane protein and leaves most of the tritiated-ouabain bound to a solubilized component. Solubilized Na,K-ATPase could also be obtained after dialysis. The solubilized membranes were centrifuged in a sucrose density gradient. The ouabain-membrane complex and the Na,K-ATPase sedimented faster than the bulk of the protein. The ouabain-membrane complex and the Na,K-ATPase appeared to be identical and were purified about eightfold relative to the starting material. These results represent a step toward the isolation and characterization of the cation transport mechanism in red cell membranes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers R. W., Koval G. J., Siegel Studies on the interaction of ouabain and other cardio-active steroids with sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Jul;4(4):324–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINZ E., HOFFMAN J. F. PHOSPHATE INCORPORATION AND NA, K-ATPASE ACTIVITY IN HUMAN RED BLOOD CELL GHOSTS. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Feb;65:31–43. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030650106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L., Skou J. C. Preparation of highly active (Na+ + K+)-ATPase from the outer medulla of rabbit kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 24;37(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90877-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahlenberg A., Dulak N. C., Dixon J. F., Galsworthy P. R., Hokin L. E. Studies on the characterization of the sodium-potassium transport adenosinetriphosphatase. V. Partial purification of the lubrol-solubilized beef brain enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Apr;131(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepner G. R., Macey R. I. Membrane enzyme systems. Molecular size determinations by radiation inactivation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):188–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Singer S. J. Protein conformation in cell membrane preparations as studied by optical rotatory dispersion and circular dichroism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1828–1835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddy A. H. The chemical organization of the plasma membrane of animal cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1966;20:1–65. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60796-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno N., Nagano K., Nakao T., Tashima Y., Fujita M., Nakao M. Approximation of molecular weight of (Na+ -K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 21;168(2):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Guidotti G. Fractionation of the protein components of human erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5118–5124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


