Abstract
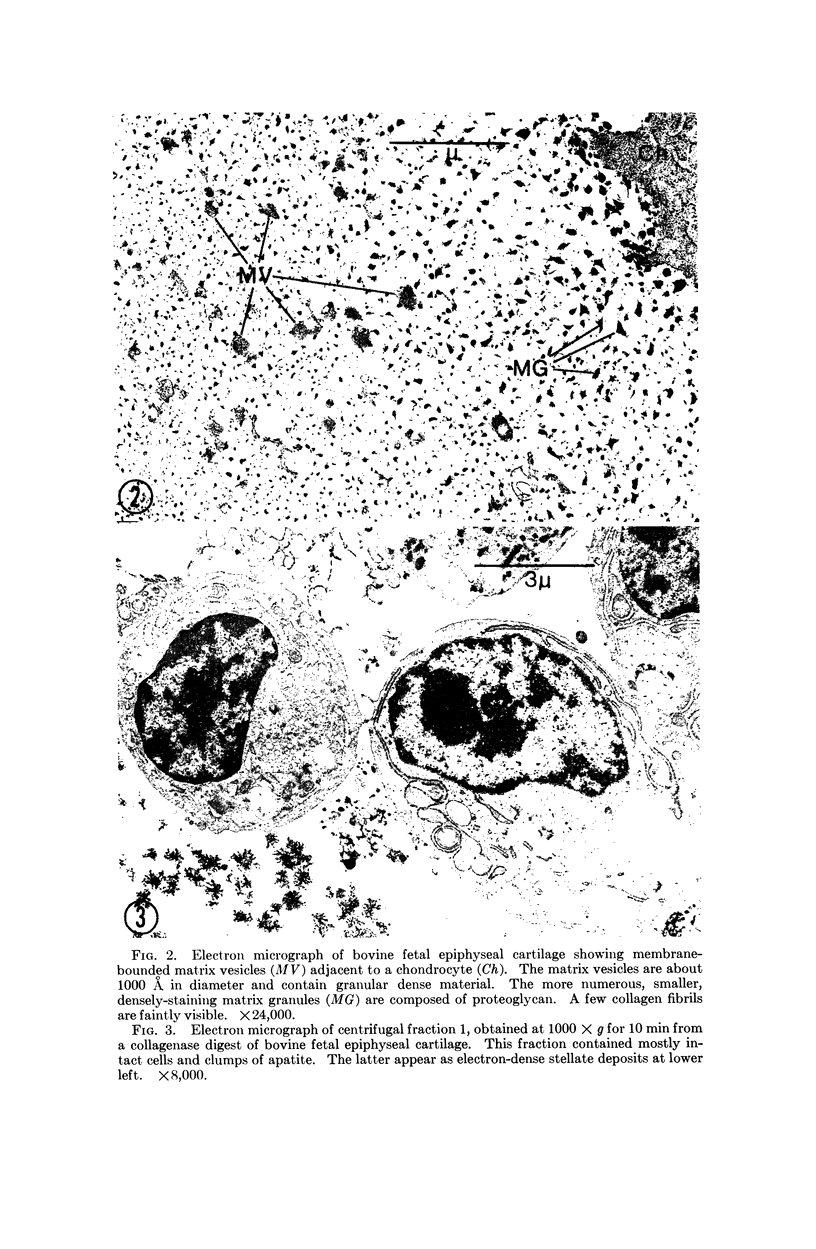
Matrix vesicles, associated with initial calcification in cartilage, have been isolated from bovine fetal epiphyseal cartilage. Cartilage was digested with collagenase, then partitioned into seven fractions by differential centrifugation. The cellular fractions contained over 80% of the DNA in the digest. The extracellular fraction that contained matrix vesicles, in which apatite crystals were often seen on electron microscopy, also displayed the highest specific activity for alkaline phosphatase, pyrophosphatase, ATPase, and 5′-AMPase (EC 3.1.3.1., 3.6.1.1, 3.6.1.3, and 3.1.3.5, respectively). Most of the acid phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.2) activity, on the other hand, was found in the cellular fractions, indicating that matrix vesicles are quite distinct from lysosomes. This appears to be the first instance of isolation of membrane-bounded extracellular particles from any normal tissue.
The matrix vesicles possess enzymes that can increase the local concentration of orthophosphate and thus could lead to the formation of hydroxyapatite. The membrane-bounded matrix vesicles may also provide a mechanism for ATP-dependent transport of calcium or phosphate into the lumen of the vesicles with resultant mineralization.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S. Y., Evans L. Studies on the cathepsins in elastic cartilage. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(4):427–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1120427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson H. C., Matsuzawa T., Sajdera S. W., Ali S. Y. Membranous particles in calcifying cartilage matrix. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1970 May;32(5):619–630. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1970.tb02737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAUFAY H., DE DUVE C., HOLT S. J., UNDERHAY E. Intracellular localization of esterase in rat liver. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Sep 25;2(5):635–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.5.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard G. W., Pease D. C. An electron microscopic study of initial intramembranous osteogenesis. Am J Anat. 1969 Jul;125(3):271–290. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001250303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonucci E. Fine structure and histochemistry of "calcifying globules" in epiphyseal cartilage. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;103(2):192–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00337312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonucci E. Fine structure of early cartilage calcification. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Sep;20(1):33–50. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISH H., NEUMAN W. F. Mechanisms of calcification: role of collagen, polyphosphates, and phosphatase. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1296–1300. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernley H. N., Walker P. G. Studies on alkaline phosphatase. Inhibition by phosphate derivatives and the substrate specificity. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):1011–1018. doi: 10.1042/bj1041011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIANETTO R., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 4. Comparative study of the binding of acid phosphatase, beta-glucuronidase and cathepsin by rat-liver particles. Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):433–438. doi: 10.1042/bj0590433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. Hydrolysis of guanosine 5'-triphosphate associated wh binding of aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5680–5686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSELBACH W., MAKINOSE M. [The calcium pump of the "relaxing granules" of muscle and its dependence on ATP-splitting]. Biochem Z. 1961;333:518–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell D. S., Pita J. C., Marquez J. F., Madruga J. E. Partition of calcium, phosphate, and protein in the fluid phase aspirated at calcifying sites in epiphyseal cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1121–1132. doi: 10.1172/JCI105801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRVING J. T. THE SUDANOPHIL MATERIAL AT SITES OF CALCIFICATION. Arch Oral Biol. 1963 Nov-Dec;8:735–745. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(63)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jibril A. O. Phosphates and phosphatases in preosseous cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 29;141(3):605–613. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman E. M., Palmer R. F., Collins G. H. Calcium ion uptake by crustacean peripheral nerve subcellular particles. Exp Cell Res. 1967 May;46(2):412–418. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison R. The Possible Significance of Hexosephosphoric Esters in Ossification. Biochem J. 1923;17(2):286–293. doi: 10.1042/bj0170286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattiaux-De Coninck S., Wattiaux R. Nucleosidediphosphatase activity in plasma membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 3;183(1):118–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann B. A colorimetric method for alpha-naphthol and its application to assay of hydrolases. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuthier R. E. A zonal analysis of inorganic and organic constituents of the epiphysis during endochondral calcification. Calcif Tissue Res. 1969 Aug 11;4(1):20–38. doi: 10.1007/BF02279103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]