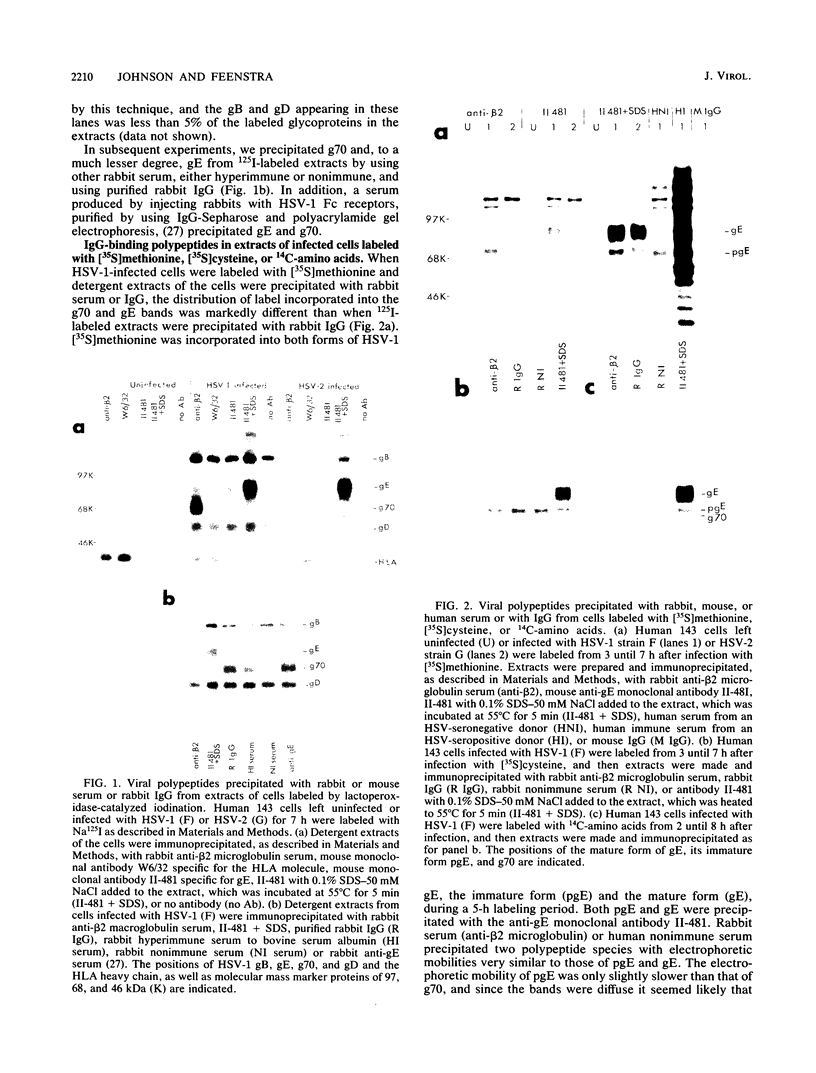
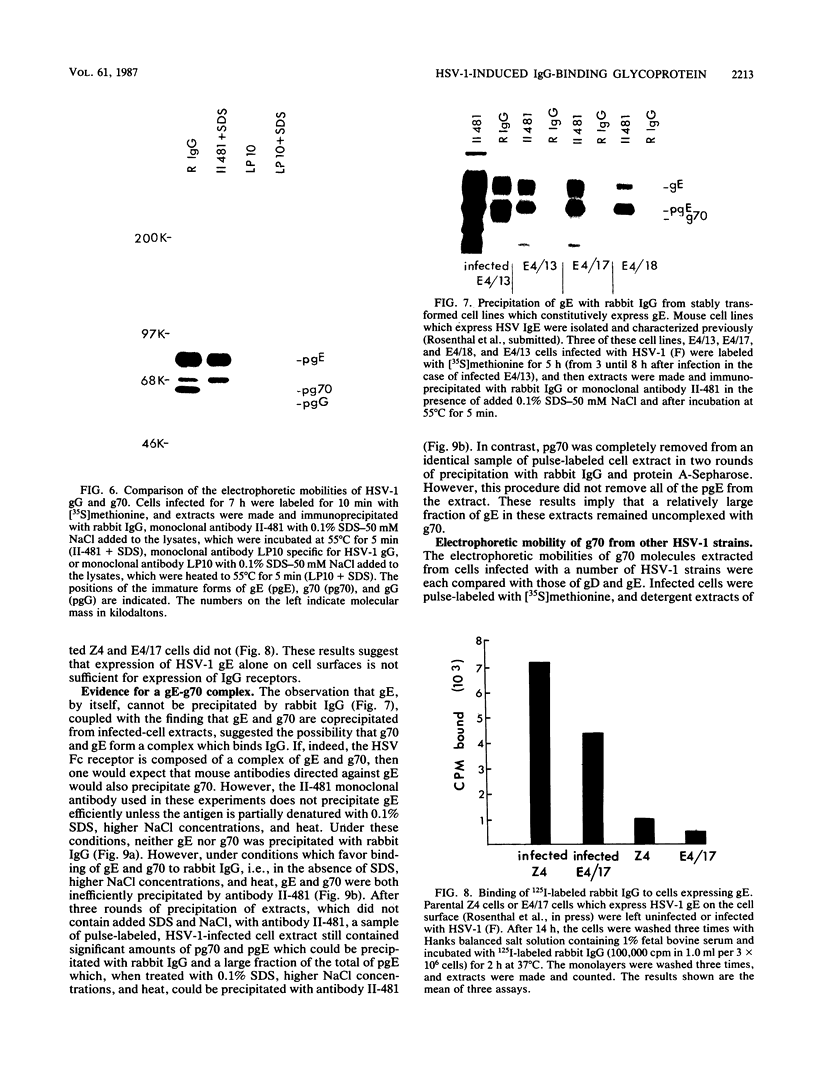
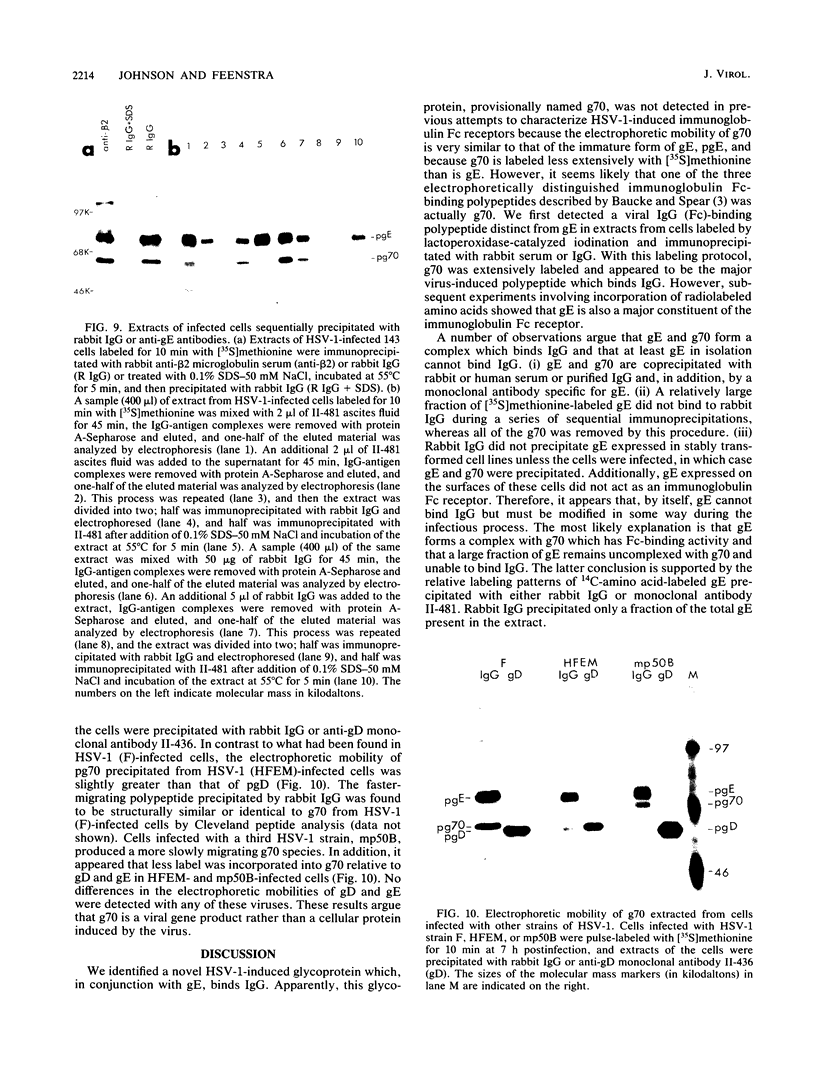
Abstract
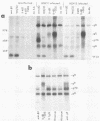
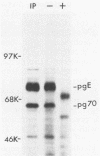
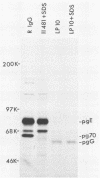
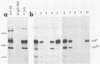
We detected a glycoprotein on the surface of cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) which, in conjunction with gE, binds immunoglobulin G (IgG). The novel glycoprotein, which has an apparent molecular mass of 70 kilodaltons and was provisionally named g70, was first detected in extracts of HSV-1-infected cells labeled by lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination and precipitated with rabbit sera or IgG and protein A-Sepharose. In subsequent experiments, g70 and gE were coprecipitated from extracts of HSV-1-infected cells labeled with [35S]methionine, [35S]cysteine, or 14C-amino acids. We were unable to precipitate a polypeptide analogous to g70 or gE from extracts of HSV-2-infected cells with rabbit IgG and protein A-Sepharose. Partial proteolytic peptide analysis indicated that g70 is structurally distinct from gE and gI). In addition, g70 was electrophoretically distinct from the HSV-1 Us4 glycoprotein gG. HSV-1 gE, expressed in mouse cells transfected with the gE gene, was not precipitated with rabbit IgG, nor could these cells bind radiolabeled IgG, suggesting that gE alone cannot act as an IgG (Fc) receptor. This result, coupled with the findings that gE and g70 are coprecipitated with IgG and with an anti-gE monoclonal antibody, suggests that gE and g70 form a complex which binds IgG. The electrophoretic mobilities of g70 molecules induced by different strains of HSV-1 differed markedly, arguing that g70 is encoded by the virus and is not a cellular protein induced by virus infection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Longnecker R., Roizman B., Pereira L. Identification, properties, and gene location of a novel glycoprotein specified by herpes simplex virus 1. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):207–220. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler R., Glorioso J. C., Cossman J., Levine M. Possible role of Fc receptors on cells infected and transformed by herpesvirus: escape from immune cytolysis. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):442–447. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.442-447.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. V. Identification of an Fc-binding glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa J. C., Rabson A. S. Role of Fc receptors in herpes simplex virus infection. Lancet. 1975 Jan 11;1(7898):77–78. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., McGeoch D. J. Evolutionary comparisons of the S segments in the genomes of herpes simplex virus type 1 and varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):597–611. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feorino P. M., Shore S. L., Reimer C. B. Detection by indirect immunofluorescence of Fc receptors in cells acutely infected with Herpes simplex virus. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;53(3):222–233. doi: 10.1159/000231756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Marsden H. S., McGeoch D. J. Novel herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins identified by antiserum against a synthetic oligopeptide from the predicted product of gene US4. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):745–751. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope R. G., Palfreyman J., Suh M., Marsden H. S. Sulphated glycoproteins induced by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Feb;58(Pt 2):399–415. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-58-2-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. Monensin inhibits the processing of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins, their transport to the cell surface, and the egress of virions from infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1102–1112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1102-1112.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. O-linked oligosaccharides are acquired by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in the Golgi apparatus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90083-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Peitchel R., Goldman J. N., Goldman M. An IgG-Fc receptor induced in cytomegalovirus-infected human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):772–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaThangue N. B., Shriver K., Dawson C., Chan W. L. Herpes simplex virus infection causes the accumulation of a heat-shock protein. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):267–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. T., Para M. F., Spear P. G. Location of the structural genes for glycoproteins gD and gE and for other polypeptides in the S component of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.41-49.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Wilton J. M., Shillitoe E. J. Immunological basis for latency, recurrences and putative oncogenicity of herpes simplex virus. Lancet. 1975 Jul 12;2(7924):60–62. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90499-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Buckmaster A., Palfreyman J. W., Hope R. G., Minson A. C. Characterization of the 92,000-dalton glycoprotein induced by herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):547–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.547-554.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McTaggart S. P., Burns W. H., White D. O., Jackson D. C. Fc receptors induced by herpes simplex virus. I. Biologic and biochemical properties. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):726–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Costa J., Tralka T. S., Yee C. L., Rabson A. S. Properties of the cell surface Fc-receptor induced by herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1128–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Shigeta S. Appearance of immunoglobulin G Fc receptor in cultured human cells infected with varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):770–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.770-774.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr H. T., Lancet D., Robb R. J., Lopez de Castro J. A., Strominger J. L. The heavy chain of human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B7 contains an immunoglobulin-like region. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):266–270. doi: 10.1038/282266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Glycoprotein gE of herpes simplex virus type 1: effects of anti-gE on virion infectivity and on virus-induced fc-binding receptors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):129–136. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.129-136.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Immunoglobulin G(Fc)-binding receptors on virions of herpes simplex virus type 1 and transfer of these receptors to the cell surface by infection. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.512-520.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Goldstein L., Spear P. G. Similarities and differences in the Fc-binding glycoprotein (gE) of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and tentative mapping of the viral gene for this glycoprotein. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.137-144.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Parish M. L., Noble A. G., Spear P. G. Potent neutralizing activity associated with anti-glycoprotein D specificity among monoclonal antibodies selected for binding to herpes simplex virions. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):483–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.483-488.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gA/B: evidence that the infected Vero cell products comap and arise by proteolysis. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):88–97. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.88-97.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson R. H., Bacchetti S., Smiley J. R. Cells that constitutively express the herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein ICP4 allow efficient activation of viral delayed-early genes in trans. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):414–421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.414-421.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman A. A., Teschner M., Sethi K. K., Brandis H. Appearance of IgG (Fc) receptor(s) on cultured human fibroblasts infected with human cytomegalovirus. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Buckmaster A., Bell S., Hodgman C., Minson A. C. Identification of a new glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1 and genetic mapping of the gene that codes for it. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):647–655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.647-655.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Norrild B., Chan C., Pereira L. Identification and preliminary mapping with monoclonal antibodies of a herpes simplex virus 2 glycoprotein lacking a known type 1 counterpart. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Wickus G. G., Burge B. W. Enzymatic iodination of Sindbis virus proteins. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):730–735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.730-735.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F., Campadelli-Fiume G. Studies on benzhydrazone, a specific inhibitor of herpesvirus glycoprotein synthesis. Size distribution of glycopeptides and endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase-H treatment. Arch Virol. 1981;70(4):331–343. doi: 10.1007/BF01320248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognon M., Furlong D., Conley A. J., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. V. Characterization of a mutant defective in ability to form plaques at low temperatures and in a viral fraction which prevents accumulation of coreless capsids at nuclear pores late in infection. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):870–880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.870-880.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATKINS J. F. ADSORPTION OF SENSITIZED SHEEP ERYTHROCYTES TO HELA CELLS INFECTED WITH HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. Nature. 1964 Jun 27;202:1364–1365. doi: 10.1038/2021364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Weis J. H., Salstrom J. S., Enquist L. W. Herpes simplex virus type-1 glycoprotein D gene: nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):381–384. doi: 10.1126/science.6289440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenske E. A., Bratton M. W., Courtney R. J. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H sensitivity of precursors to herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins gB and gC. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):241–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.241-248.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westmoreland D., St Jeor S., Rapp F. The development by cytomegalovirus-infected cells of binding affinity for normal human immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1976 Jun;116(6):1566–1570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westmoreland D., Watkins J. F. The IgG receptor induced by herpes simplex virus: studies using radioiodinated IgG. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):167–178. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda J., Milgrom F. Hemadsorption by herpes simplex-infected cell cultures. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;33(2):151–170. doi: 10.1159/000229985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zezulak K. M., Spear P. G. Limited proteolysis of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins that occurs during their extraction from vero cells. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):258–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.258-262.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]