Abstract
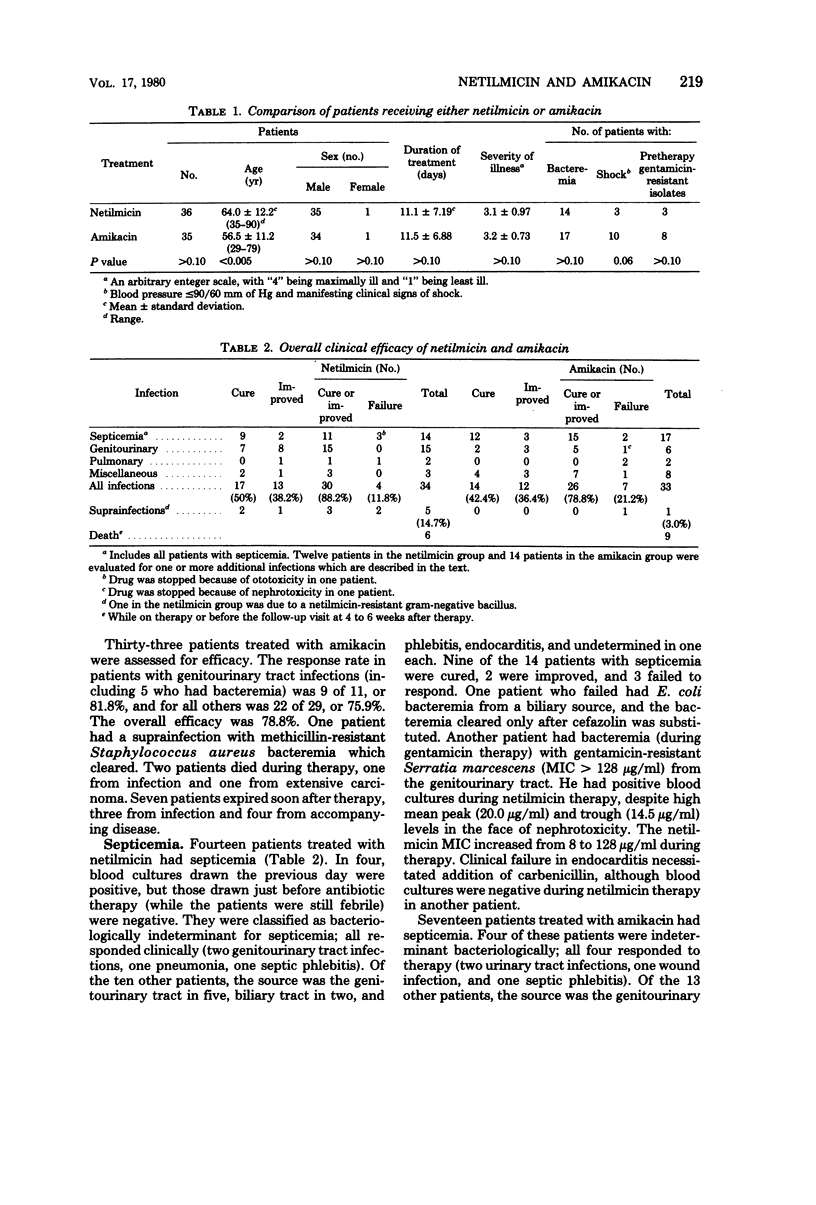
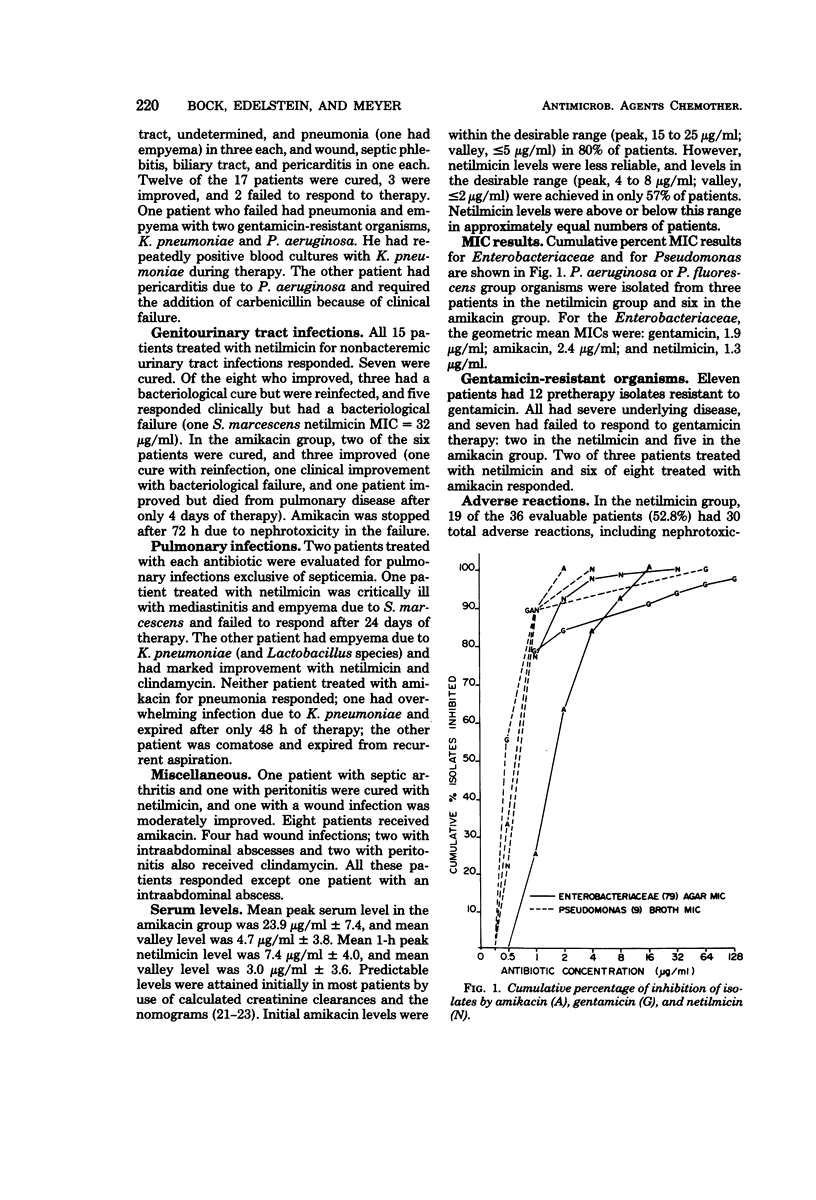
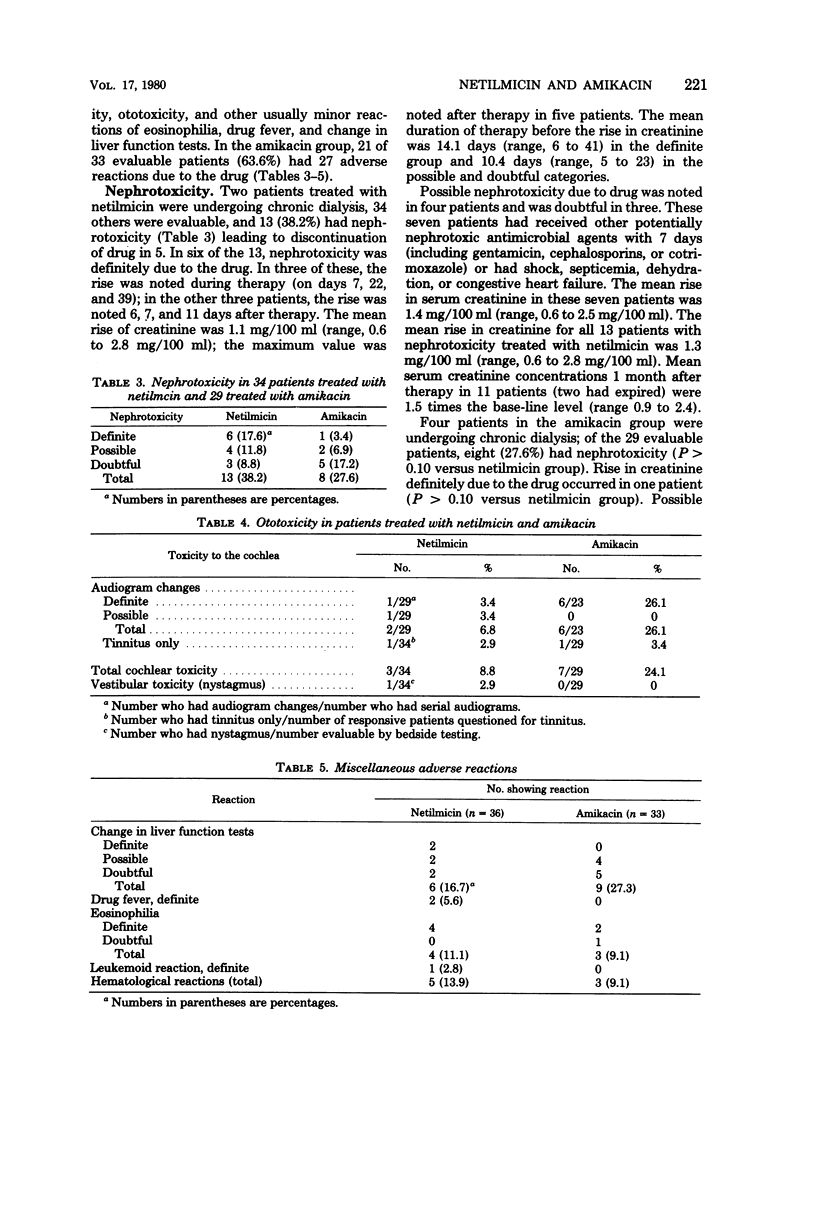
Eighty patients were treated with either amikacin or netilmicin in a prospective randomized study of serious gram-negative bacillary infections, including 11 due to gentamicin-resistant pathogens. Thirty-six treated with netilmicin and 35 treated with amikacin were evaluable for efficacy or toxicity, or both. The overall groups differed significantly only in age. There were no significant differences in efficacy of the two drugs. There were no statistically significant differences at the 95% level between the netilmicin group and the amikacin group with respect to nephrotoxic reactions (38 versus 28%, respectively) or ototoxic reactions (9 versus 25%, respectively). Further comparative trials of netilmicin and other aminoglycosides appear warranted before it is widely used.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckwold F. J., Ronald A. R., Lank B., Thompson L., Fox L., Harding G. K. Clinical efficacy and toxicity of netilmicin in the treatment of gram-negative infections. Can Med Assoc J. 1979 Jan 20;120(2):161–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Gault M. H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16(1):31–41. doi: 10.1159/000180580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan V., Marso E., Martin W. J., Young L. S. In vitro studies with netilmicin compared with amikacin, gentamicin, and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):64–73. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Meyer R. D. Netilmicin therapy of serious Gram-negative bacillary infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Nov;4(6):495–502. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.6.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagstrom G. L., Luft F. C., Yum M. N., Sloan R. S., Maxwell D. R. Nephrotoxicity of netilmicin in combination with non-aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):490–493. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull J. H., Sarubbi F. A., Jr Gentamicin serum concentrations: pharmacokinetic predictions. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Aug;85(2):183–189. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-2-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert G., Leroy A., Fillastre J. P., Oksenhendler G. Pharmacokinetics of netilmicin in the presence of normal or impaired renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jul;14(1):40–44. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi M., Levy J. K., Jerger J. Comparative toxicity of netilmicin and gentamicin in squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus). J Infect Dis. 1978 Apr;137(4):476–480. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.4.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahre J. A., Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Clinical evaluation of netilmicin therapy in serious infections. Am J Med. 1979 Jan;66(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90484-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Meunier-Carpentier F., Coppens-Kahan L., Daneau D., Prevost J. M. Clinical and bacteriological evaluation of netilmicin in gram-negative infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Oct;12(4):503–509. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.4.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Bloch R., Sloan R. S., Yum M. N., Costello R., Maxwell D. R. Comparative nephrotoxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics in rats. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):541–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Brannon D. R., Stropes L. L., Costello R. J., Sloan R. S., Maxwell D. R. Pharmacokinetics of netilmicin in patients with renal impairment and in patients on dialysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):403–407. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Yum M. N., Kleit S. A. Comparative nephrotoxicities of netilmicin and gentamicin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):845–849. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maigaard S., Frimodt-Möller N., Madsen P. O. Comparison of netilmicin and amikacin in treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):544–548. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Draus L. L., Pasieczinik K. A. In vitro susceptibility of gentamicin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to netilmicin and selected aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):677–681. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Lewis R. P., Carmalt E. D., Finegold S. M. Amikacin therapy for serious gram-negative bacillary infections. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Dec;83(6):790–800. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-6-790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Lewis R. P., Finegold S. M. Amikacin therapy for gram-negative septicemia. Am J Med. 1977 Jun;62(6):930–935. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Lewis R. P., Halter J., White M. Gentamicin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens in a general hospital. Lancet. 1976 Mar 13;1(7959):580–583. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. H., Arcieri G., Weinstein M. J., Waitz J. A. Biological activity of netilmicin, a broad-spectrum semisynthetic aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):827–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panwalker A. P., Malow J. B., Zimelis V. M., Jackson G. G. Netilmicin: clinical efficacy, tolerance, and toxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogwizd S. M., Lerner S. A. In vitro activity of gentamicin, amikacin and netilmicin alone and in combination with carbenicillin against Serratia marcescens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):878–884. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr, Simberkoff M. S., Kagan K., Moldover N. H. Bactericidal efficacy of Sch 20569 and amikacin against gentamicin-sensitive and -resistant organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):595–599. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L. J., Moreschi G. Netilmicin and gentamicin: comparative pharmacology in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):609–614. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. R., Baughman K. L., Edwards C. Q., Rogers J. F., Lietman P. S. Controlled comparison of amikacin and gentamicin. N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 17;296(7):349–353. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197702172960701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. R., Maxwell R. R., Edwards C. Q., Rogers J. F., Lietman P. S. Nephrotoxicity induced by gentamicin and amikacin. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1978 Mar;142(3):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trestman I., Parsons J., Santoro J., Goodhart G., Kaye D. Pharmacology and efficacy of netilmicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):832–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


