Abstract
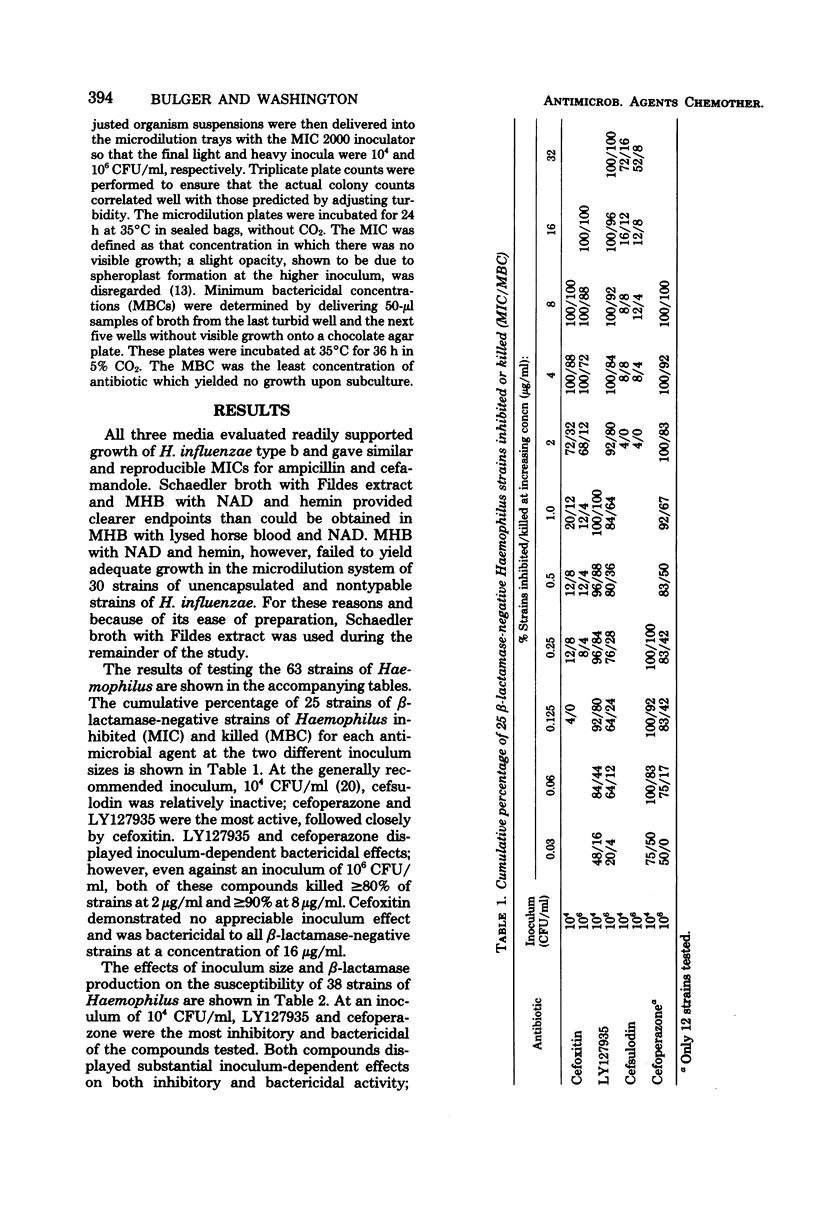
Sixty-three strains of Haemophilus species, 38 of which were beta-lactamase producers (37 H. influenzae type b, 1 H. parainfluenzae) and 25 of which were beta-lactamase negative (20 H. influenzae, 5 H. parainfluenzae), were tested for susceptibility to cefoxitin, moxalactam (LY127935) (Lilly), cefsulodin (CGP 7174 E, Ciba), and cefoperazone (T 1551, Pfizer). Cefsulodin was relatively inactive at both low and high inocula. LY127935 and cefoperazone displayed inoculum-dependent bactericidal activity. Cefoxitin displayed little inoculum effect against beta-lactamase-producing strains: 8 and 16 microgram/ml killed at least 90% of those tested at 10(4) and 10(6) colony-forming units per ml, respectively.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker J. The in vitro sensitivity of Haemophilus influenzae to clindamycin. Med Lab Technol. 1974 Apr;31(2):167–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bill N. J., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of in vitro activity of cephalexin, cephradine, and cefaclor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):470–474. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkley A. W., Huber T. W. Method for evaluating broth culture media: application to Haemophilus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Nov;8(5):520–524. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.5.520-524.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickhoff T. C., Ehret J. M. In vitro comparison of cefoxitin, cefamandole, cephalexin, and cephalothin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):994–999. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. B., Smith A. L., Harding A. L., Smith D. H. Hemophilus influenzae type B susceptibility to 17 antibiotics. J Pediatr. 1975 Apr;86(4):617–620. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman W. E. Concentrations of bacteria in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr. 1976 Apr;88(4 Pt 1):549–552. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M., Hubbell C. A., Dillon H. C., Jr Manner and meaning of susceptibility testing of ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):1021–1026. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Jones P. M. Simplified medium for ampicillin susceptibility testing of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):186–190. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer R. B., Preston D. A., Turner J. R., Hawley L. C. Rapid detection of ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae and their susceptibility to sixteen antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirven L. A., Thornsberry C. Minimum bactericidal concentration of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim for Haemophilus influenzae: correlation with prophylaxis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Nov;14(5):731–736. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.5.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. D., Luginbuhl G. H. Ampicillin-induced morphological alterations of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):559–562. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Aswapokee N., Fu K. P., Aswapokee P. Antibacterial activity of a new 1-oxa cephalosporin compared with that of other beta-lactam compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):141–149. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P., Aswapokee N., Aswapokee P., Kung K. Comparative activity and beta-lactamase stability of cefoperazone, a piperazine cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):150–157. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. E., Neumann A. M. A rapid slide test for penicillinase. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Mar;69(3):351–354. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.1.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Ryan D. M. Comparative acitivity of ampicillin and cefuroxime against three types of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):599–604. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syriopoulou V. P., Scheifele D. W., Sack C. M., Smith A. L. Effect of inoculum size on the susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae b to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):510–513. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Baker C. N., Kirven L. A., Swenson J. M. Susceptibility of ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae to seven penicillins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):70–73. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):620–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd, Snyder R. J., Kohner P. C. Spurious ampicillin resistance by testing Haemophilus influenzae with agar containing supplement C. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):199–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C., Glotzbecker C. Comparative susceptibility of Haemophilus species to cefaclor, cefamandole, and five other cephalosporins and ampicillin, chloramphenicol, and tetracycline. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):836–838. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yourassowsky E., Van Der Linden M. P., Lismont M. J. Growth curves, microscopic morphology, and subcultures of beta-lactamase-positive and -negative Haemophilus influenzae under the influence of ampicillin and cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):325–331. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


