Abstract
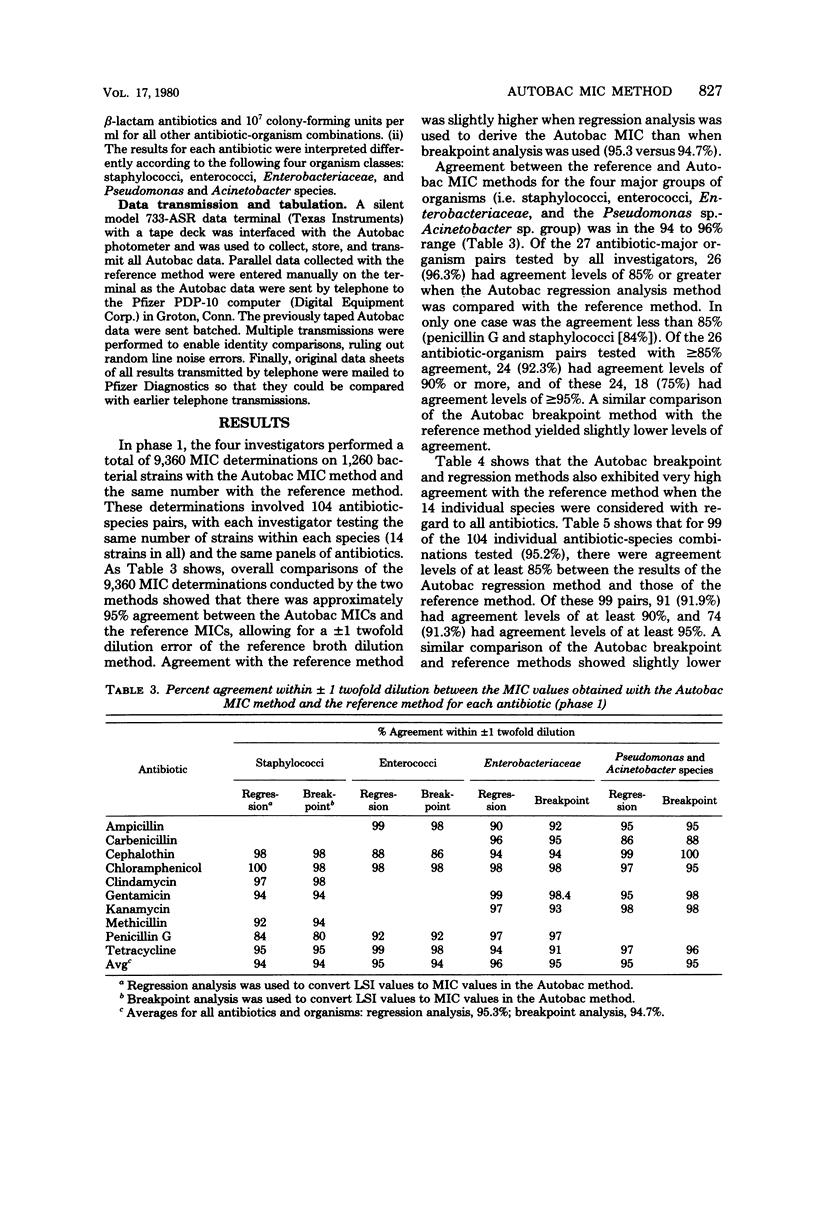
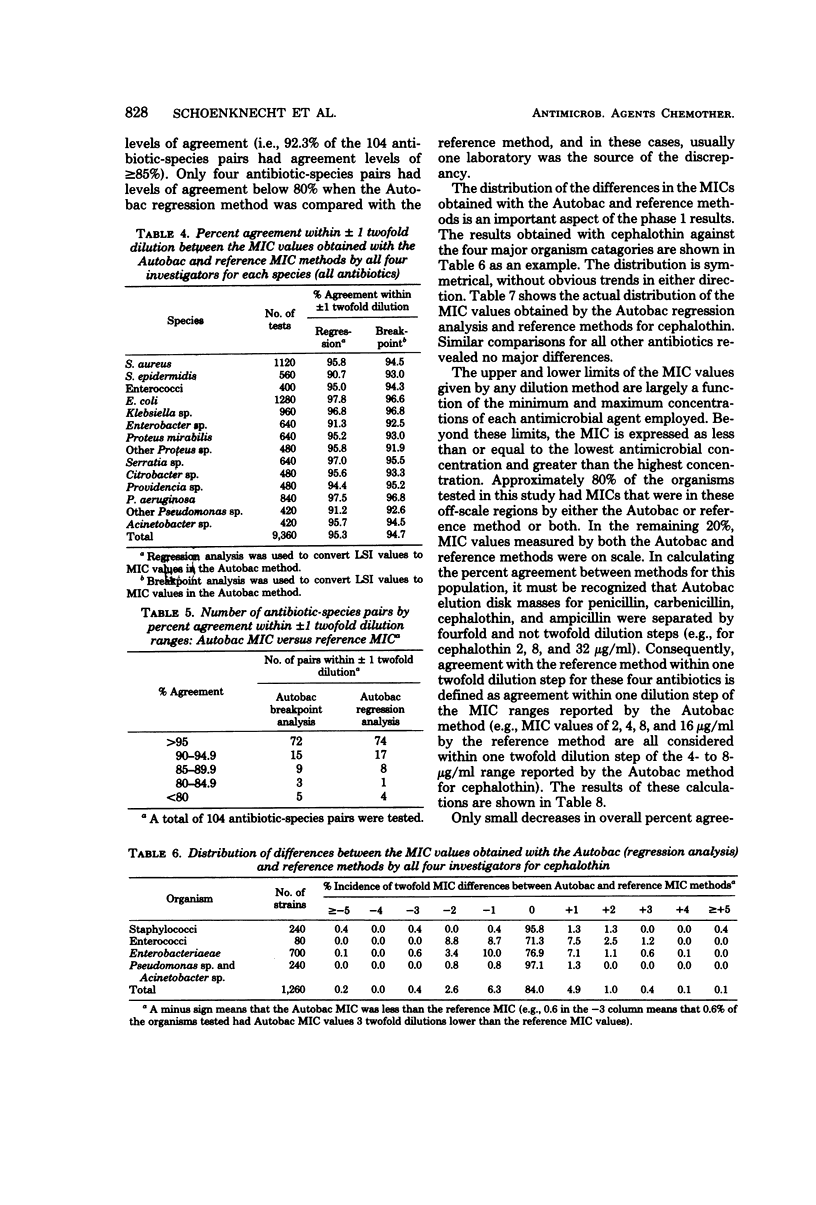
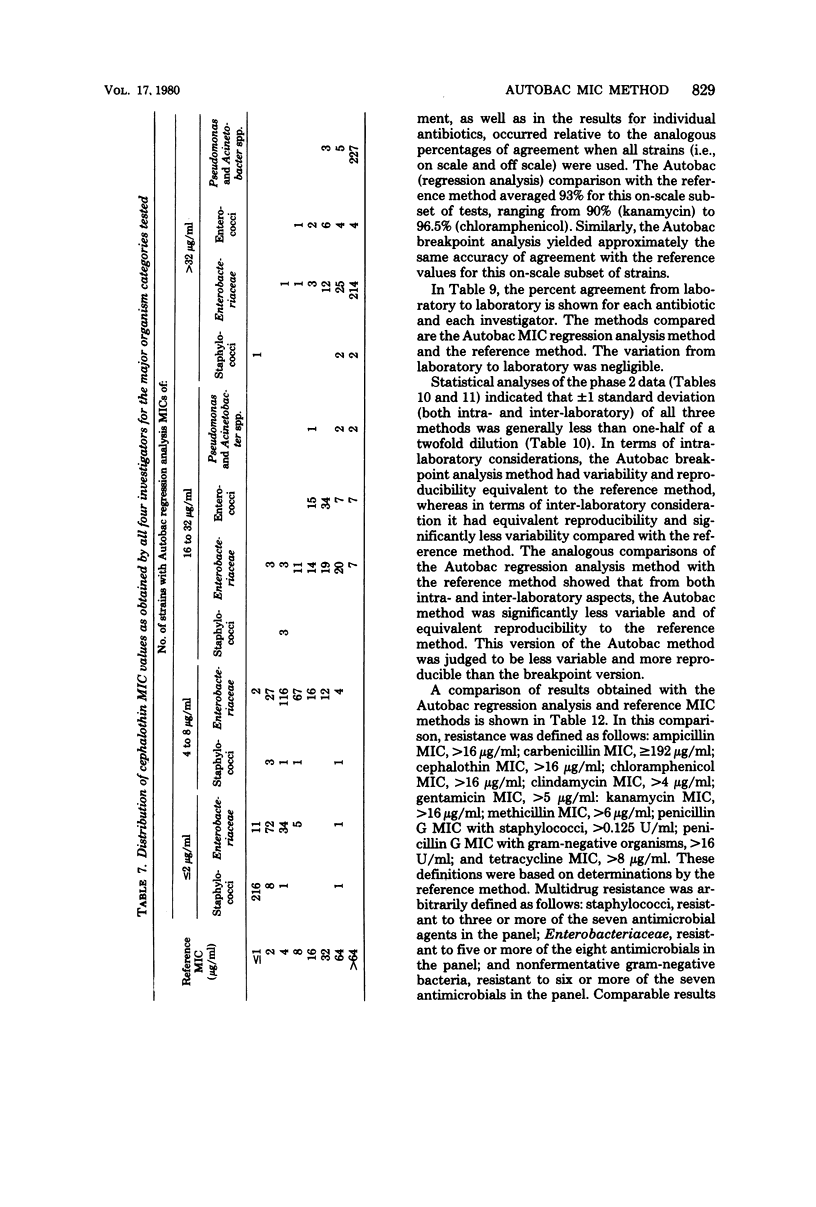
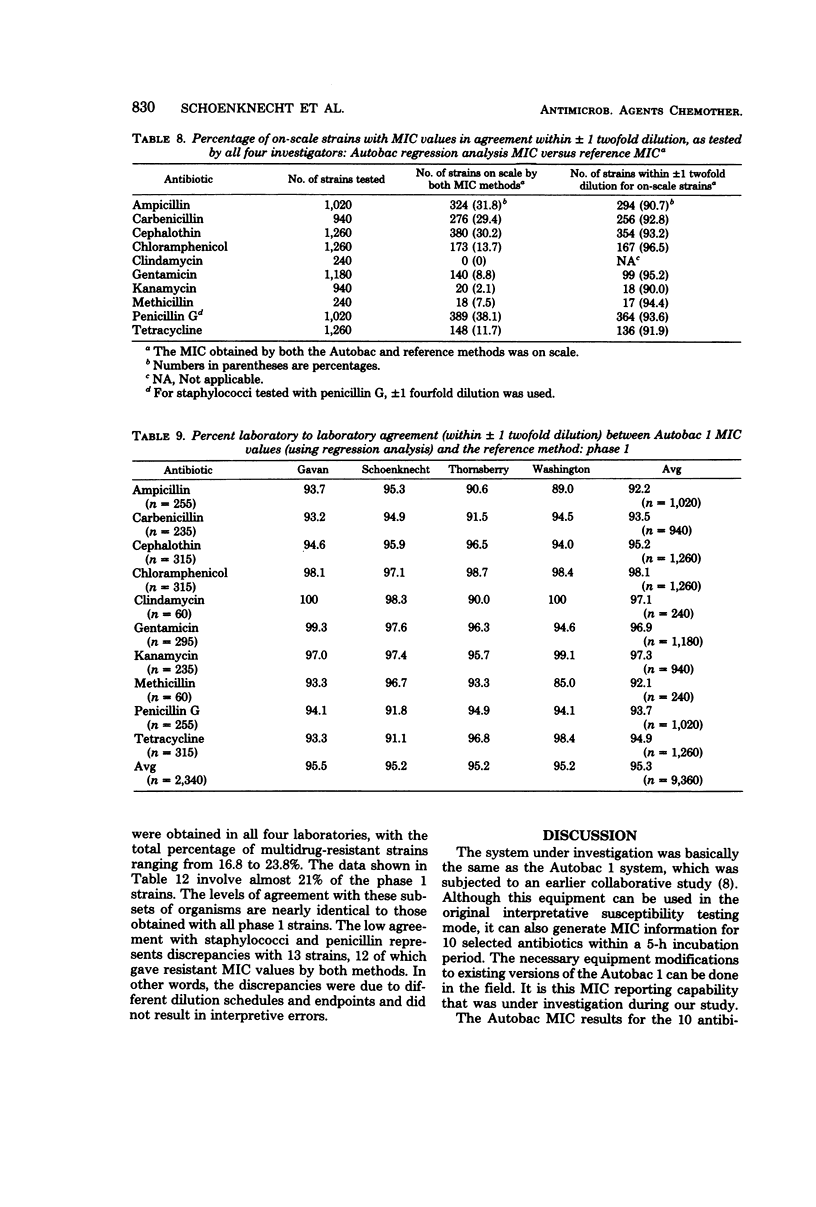
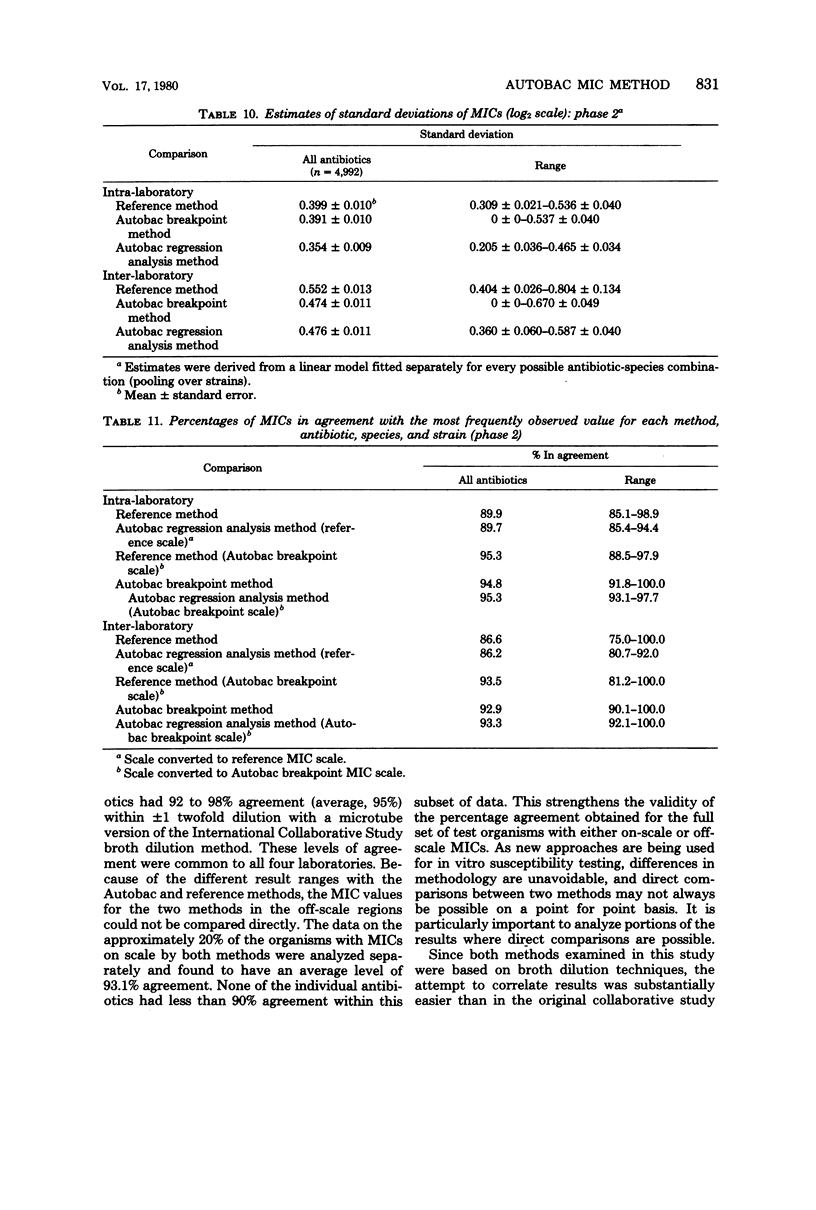
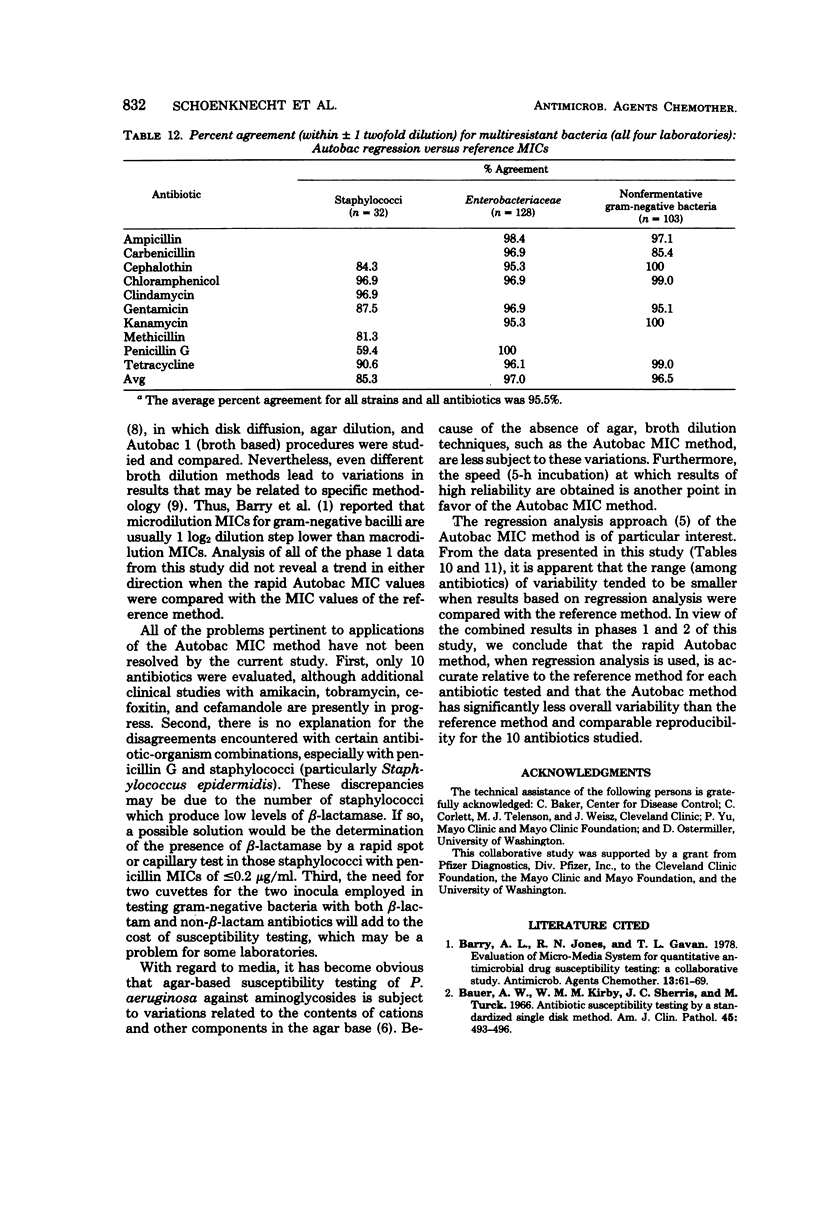
Four laboratories collaborated in an evaluation of the Autobac minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) test system. The MICs of ranges of MICs determined in this system were compared with the MICs obtained with a microtube modification of the International Collaborative Study broth dilution technique. A total of 1,260 strains, mostly recent clinical isolates and including multiresistant strains, were tested by the four laboratories against 10 antibiotics; 9,360 separate MIC determinations were made. There was an overall agreement of approximately 95% between the two methods. Levels of agreement below 80% were obtained with only 4 of the 104 antibiotic-species pairs. In only one of the four major organism groups (staphylococci and penicillin G) was agreement less than 85%. There was a symmetrical distribution of MIC differences between the two methods. Tests with 56 selected strains were performed in each of four laboratories in an inter- and intra-laboratory reproducibility study. Both methods showed a standard deviation (both inter- and intra-laboratory) of one-half of a twofold dilution step. The Autobac method was actually less variable than the reference method and had equivalent reproducibility. This was particularly true when the Autobac system was operated so that the results generated permitted calculations of MICs via regression analysis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Gavan T. L. Evaluation of the micro-media system for quantitative antimicrobial drug susceptibility testing: a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):61–69. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKie J. E., Seo J., Arvesen J. N. Rapid determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations of antimicrobial agents by regression analysis of light scattering data. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):813–823. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock H. M., Minshew B. H., Kenny M. A., Schoenknecht F. D. Effect of different lots of Mueller-Hinton agar on the interpretation of the gentamicin susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):360–367. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Gavan T. L., Sherris J. C., Balows A., Matsen J. M., Sabath L. D., Schoenknecht F., Thrupp L. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Laboratory evaluation of a rapid, automatic susceptibility testing system: report of a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):466–480. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


