Abstract
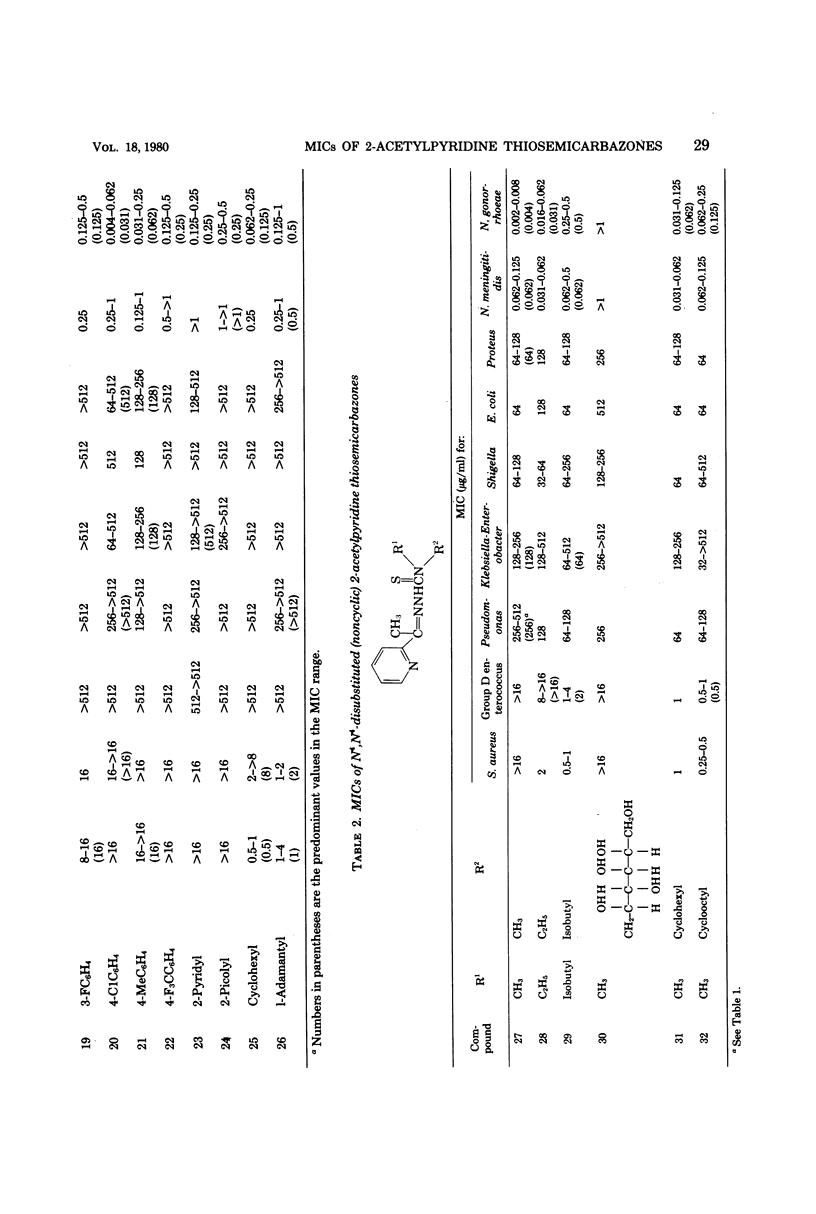
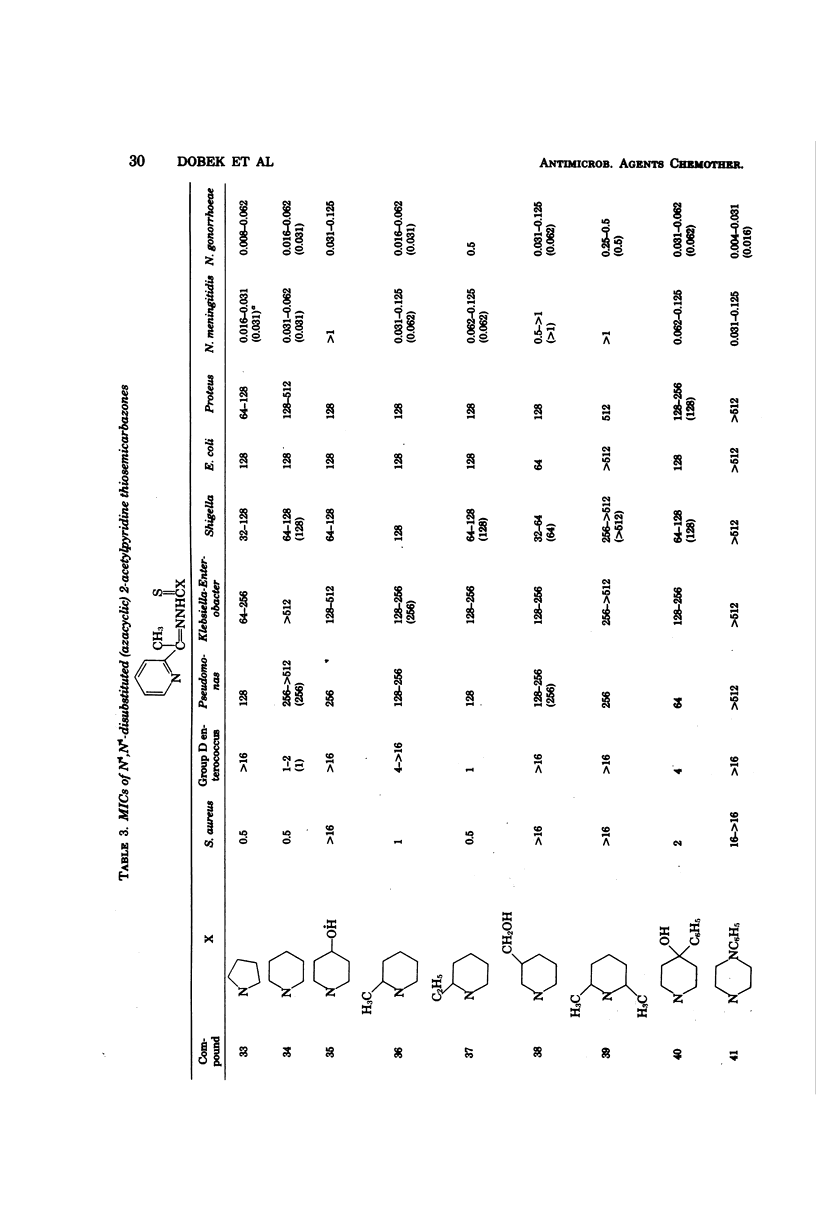
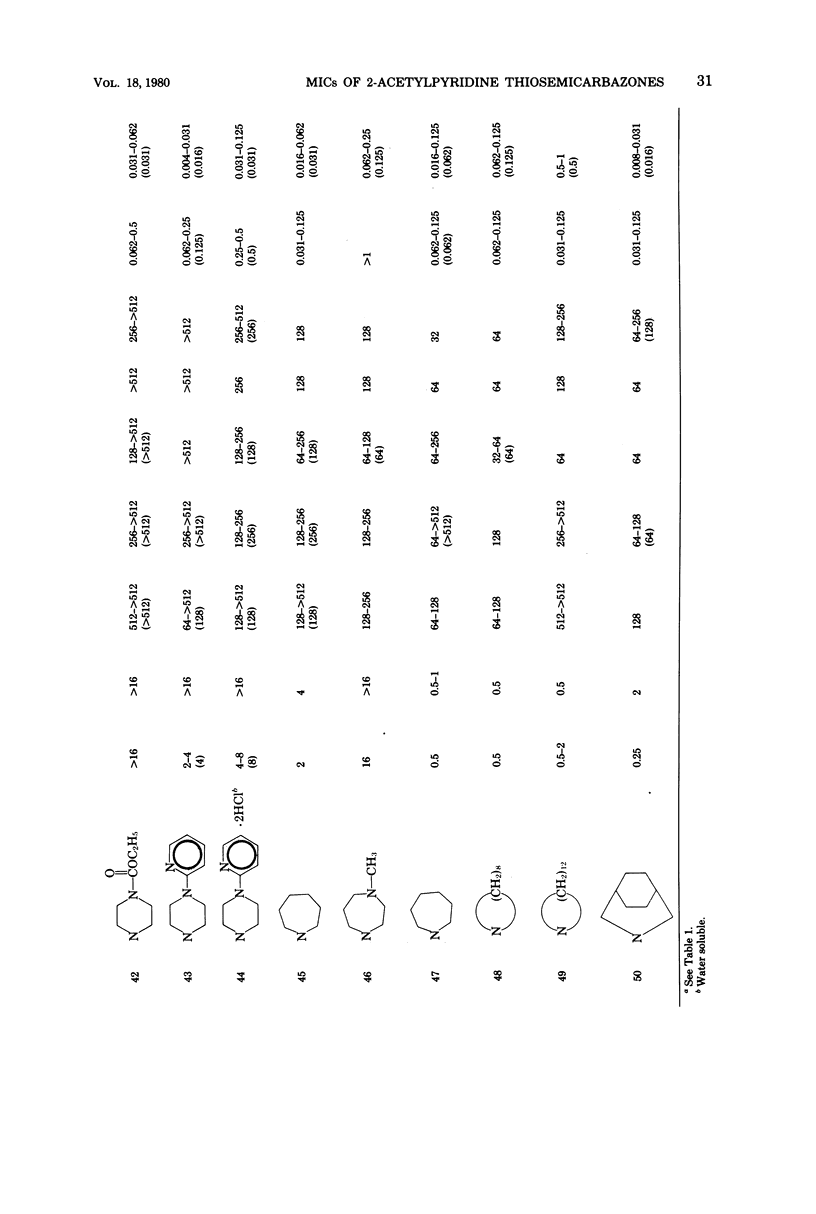
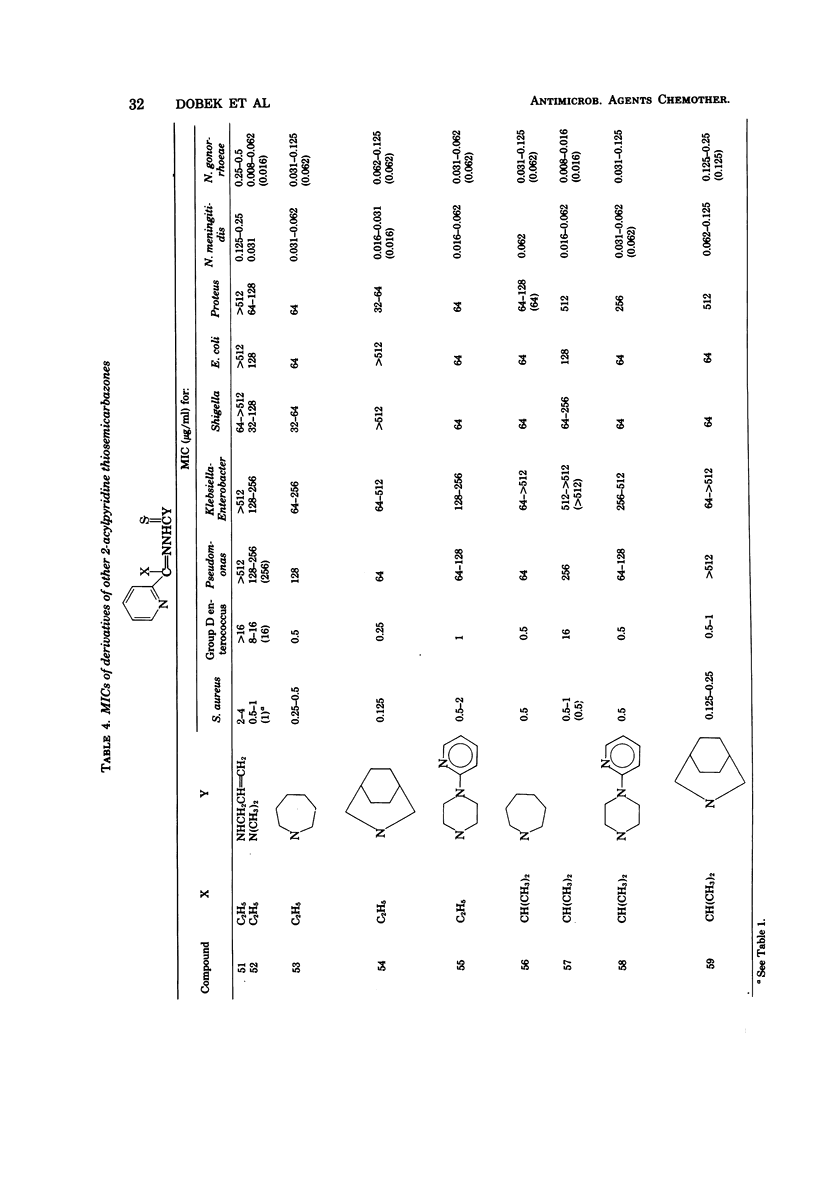
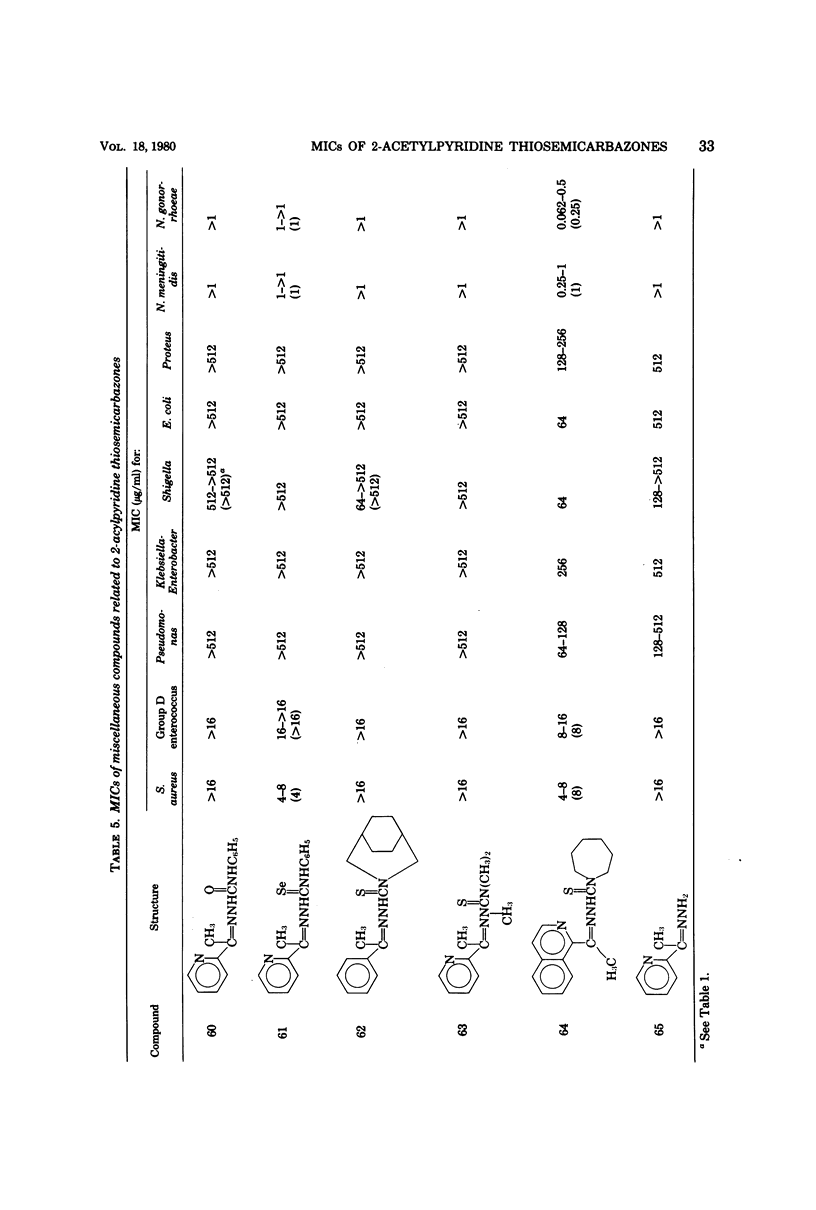
Antibacterial activity of 65 2-acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones and related compounds was determined by using clinical isolates of nine bacterial genera. Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 0.002 to 0.062 micrograms/ml were obtained with 23% of the compounds for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and 0.016 to 0.062 micrograms/ml with 17% of the compounds for N. meningitidis. Staphylococcus aureus was inhibited in the MIC range of 0.125 to 0.5 micrograms/ml by 18% of the thiosemicarbazones, whereas 26% inhibited group D enterococcus with an MIC of 0.25 to 2.0 micrograms/ml. Poor antibacterial activity was shown toward the gram-negative bacilli, i.e., Pseudomonas, Klebsiella-Enterobacter, Shigella, Escherichia coli, and Proteus.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FORMAL S. B., LABREC E. H., KENT T. H., FALKOW S. ABORTIVE INTESTINAL INFECTION WITH AN ESCHERICHIA COLI-SHIGELLA FLEXNERI HYBRID STRAIN. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1374–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1374-1382.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHARDT P., HEDEN C. G. Concentrated culture of gonococci in clear liquid medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Oct;105:49–51. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klayman D. L., Bartosevich J. F., Griffin T. S., Mason C. J., Scovill J. P. 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones. 1. A new class of potential antimalarial agents. J Med Chem. 1979 Jul;22(7):855–862. doi: 10.1021/jm00193a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaymann D. L., Scovill J. P., Bartosevich J. F., Mason C. J. 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones. 2. N4,N4-Disubstituted derivatives as potential antimalarial agents. J Med Chem. 1979 Nov;22(11):1367–1373. doi: 10.1021/jm00197a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDWELL O. M. Apparatus for phagetyping of Staphylococcus aureus. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1959 Mar;18:49–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protivinsky R. Chemotherapeutics with tuberculostatic action. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1971;17:101–121. doi: 10.1159/000392367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. J. Leprosy. A preliminary review of the experimental evaluation of drugs for the treatment of leprosy. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1967;61(4):581–595. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(67)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE L. A., KELLOGG D. S., Jr NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE IDENTIFICATION IN DIRECT SMEARS BY A FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY-COUNTERSTAIN METHOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:171–174. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.171-174.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner W. H., Winkelmann E. Untersuchungen über die tuberkulostatische Wirksamkeit neuartiger Benzaldehyd- und Thiophenaldehyd-Thiosemicarbazone in vitro and in vivo. Arzneimittelforschung. 1972 Oct;22(10):1713–1716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


