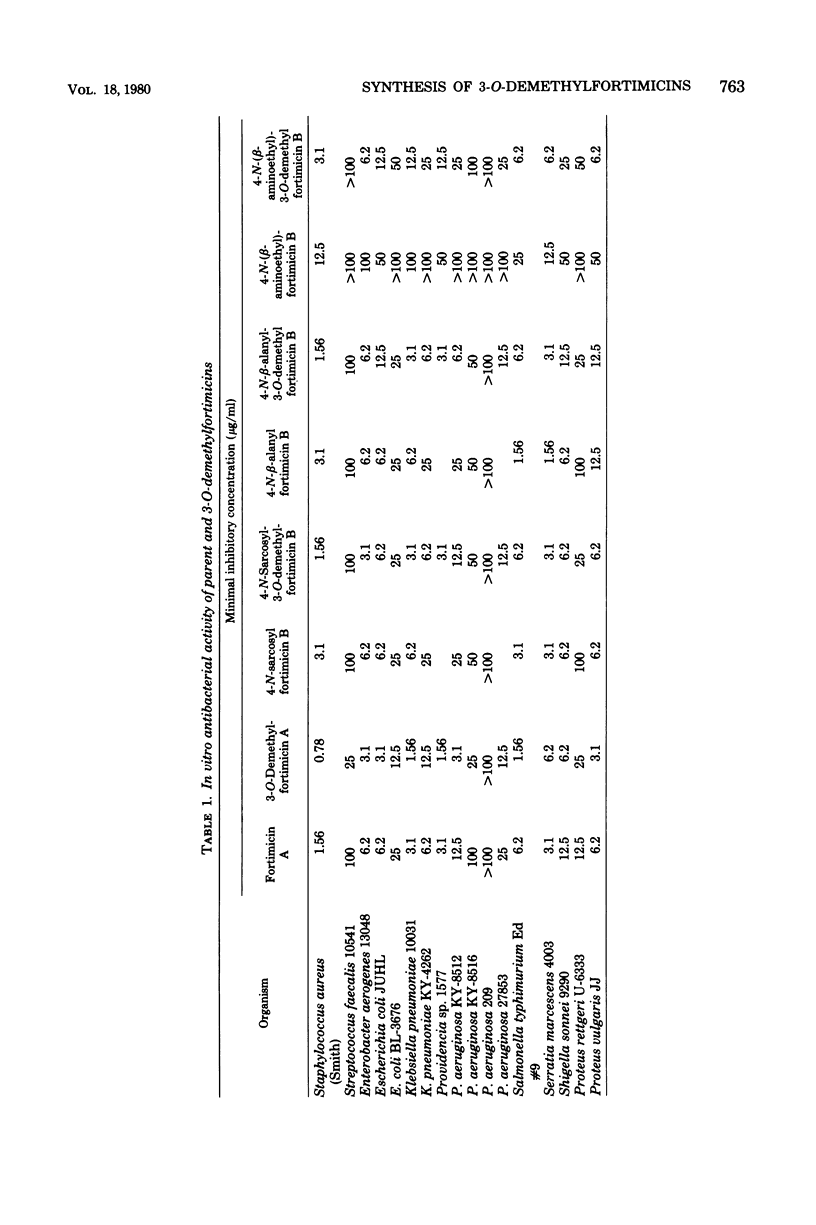
Abstract
Treatment of fortimicin B with lithium in ethylamine gave 3-O-demethylfortimicin B. The latter was converted by methodology developed with fortimicin B to 3-O-demethylfortimicin A, 4-N-sarcosyl-3-O-demethylfortimicin B, 4-N-beta-alanyl-3-O-demethylfortimicin B, and 4-N-(beta-aminoethyl)-3-O-demethylfortimicin B. 3-O-demethylfortimicin A and the 4-N-acyl-3-O-demethylfortimicins B had appreciably higher antibacterial activities than the corresponding parent fortimicins. Most significant was the increased activity of 3-O-demethylfortimicin A relative to fortimicin A against a variety of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Egan R. S., Stanaszek R. S., Cirovic M., Mueller S. L., Tadanier J., Martin J. R., Collum P., Goldstein A. W., De Vault R. L., Sinclair A. C. Fortimicins A and B, new aminoglycoside antibiotics. III. Structural identification. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Jul;30(7):552–563. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolami R. L., Stamm J. M. Comparative antimicrobial activity of O-demethylfortimicin A, a derivative of fortimicin A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):766–772. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolami R. L., Stamm J. M. Fortimicins A and B, new aminoglycoside antibiotics. IV. In vitro study of fortimicin A compared with other aminoglycosides. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Jul;30(7):564–570. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C., Gavan T. L., Sommers H. M., Gerlach E. H. Fortimicin A: collaborative in vitro susceptibility. Comparison with amikacin and gentamicin against 11,840 clinical bacterial isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):823–828. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Barry A. L., Packer R. R., Baker C. N., Badal R. E. Compound A49759, the 3-O-demethyl derivative of fortimicin A: in vitro comparison with six other aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):773–779. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara T., Yamamoto M., Kawamoto I., Takayama K., Okachi R., Takasawa S., Sato T., Sato S. Fortimicins A and B, new aminoglycoside antibiotics. I. Producing organism, fermentation and biological properties of fortimicins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Jul;30(7):533–540. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Mori Y. Chemical modification of fortimicins: preparation of 4-N-substituted fortimicin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1979 Apr;32(4):371–378. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.32.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadanier J., Martin J. R., Kurath P., Goldstein A. W., Johnson P. 4-N-acylfortimicins B and the preparation of fortimicin A from fortimicin B. Carbohydr Res. 1980 Feb;79(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


