Abstract
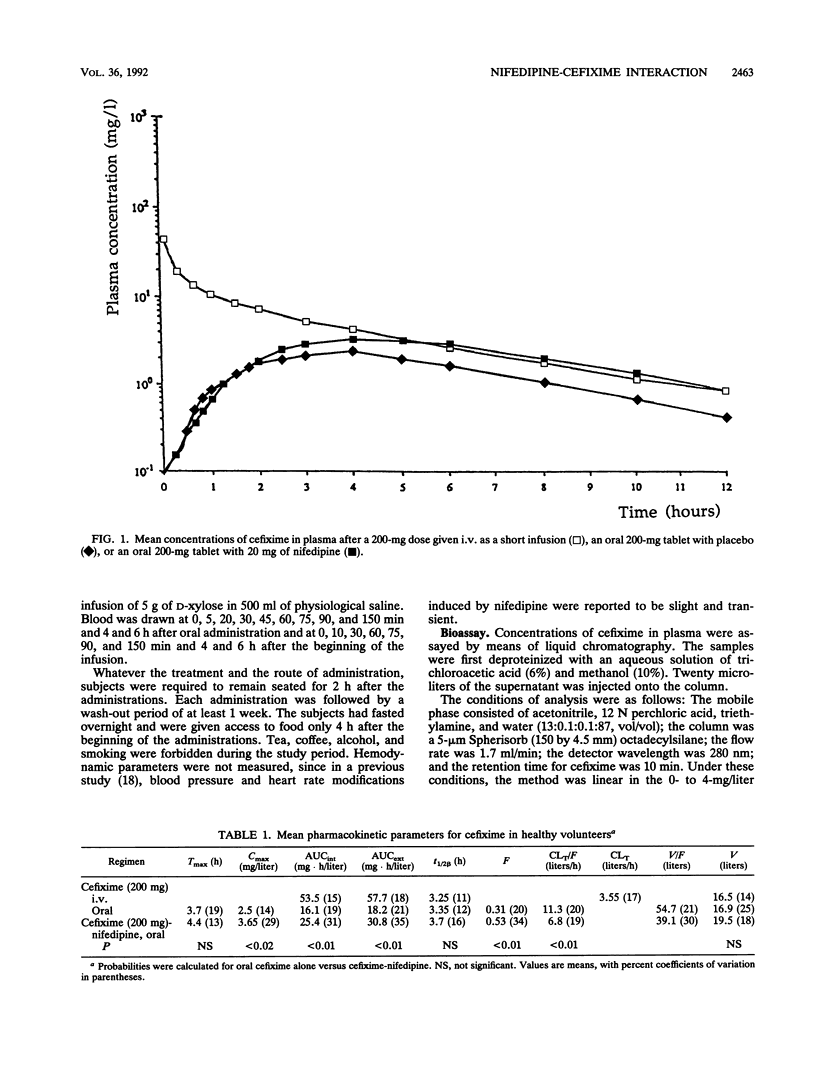
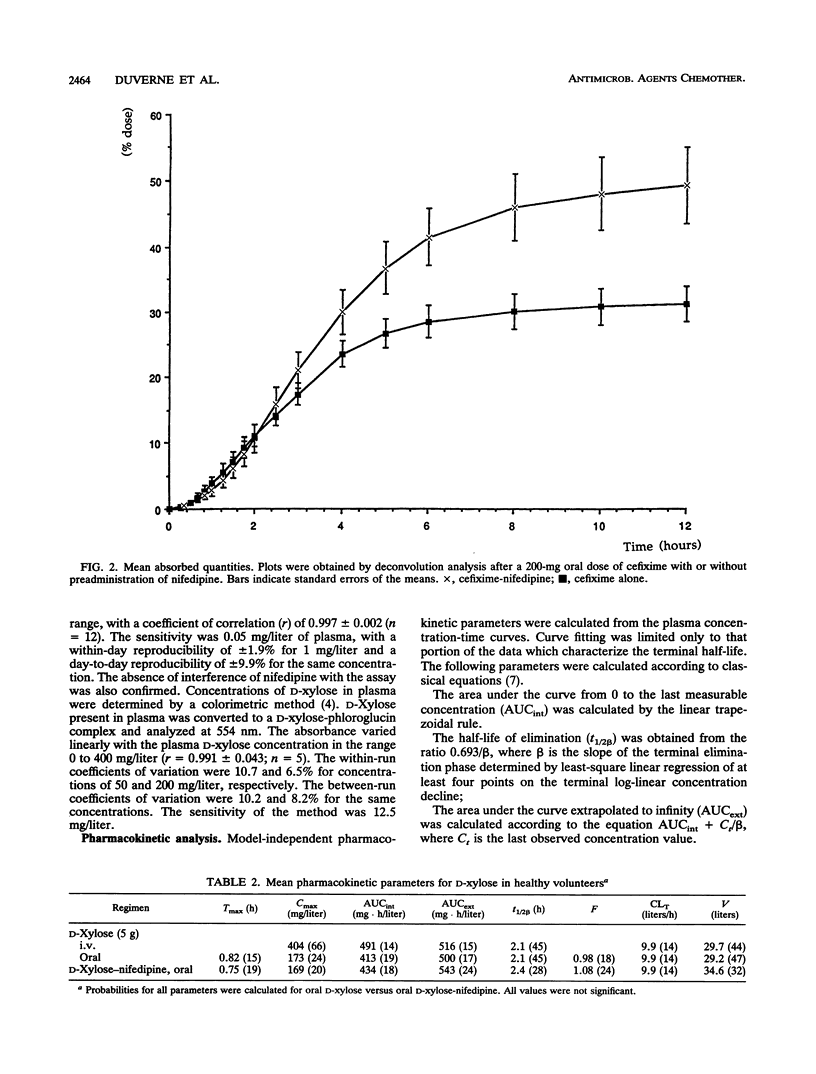
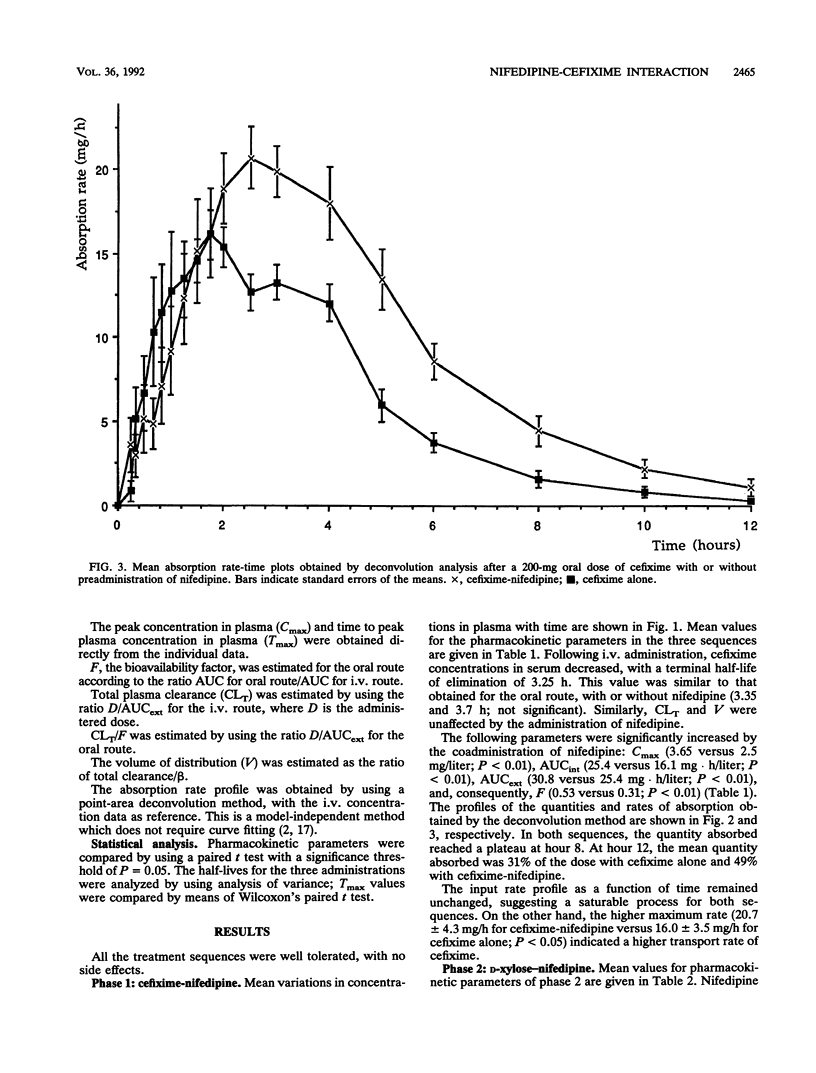
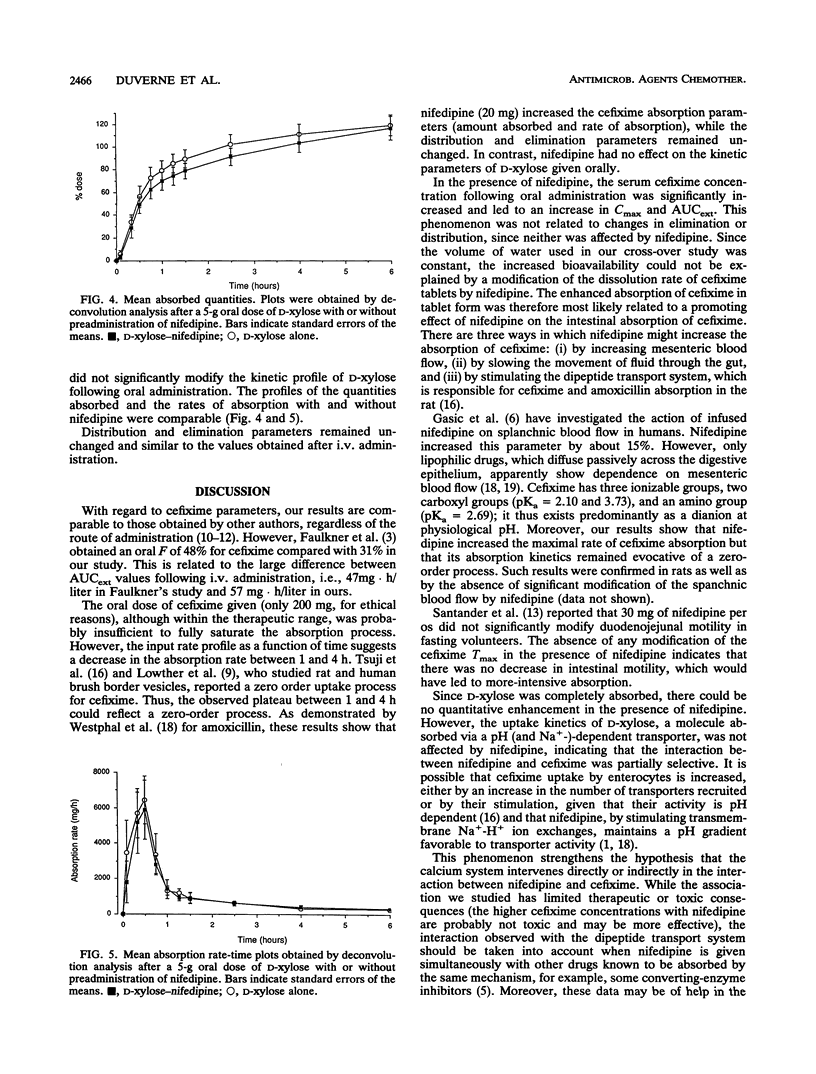
We studied the action of nifedipine on the bioavailability of cefixime, a molecule absorbed via the gut wall dipeptide carrier system in the rat, and on the bioavailability of D-xylose, which is absorbed via a pH (and Na(+)-)-dependent transporter. Each compound was administered alone or in combination with 20 mg of nifedipine to eight healthy male volunteers. Nifedipine significantly increased the absorption rate of cefixime (20.7 +/- 4.3 versus 16 +/- 3.5 mg/h in the absence of nifedipine). The absolute bioavailability of cefixime alone was 31% +/- 6% compared with 53% +/- 1% (P < 0.01) in the presence of nifedipine. The observed peak concentrations in serum were significantly different (2.5 +/- 0.3 mg/liter without nifedipine and 3.7 +/- 1.1 mg/liter with nifedipine; P < 0.02). In contrast, nifedipine induced no significant differences in the pharmacokinetic profile of xylose following oral administration. We conclude that (i) cefixime is absorbed in humans by an apparently active process which can be enhanced by a calcium channel blocker, in this case, nifedipine; and (ii) nifedipine does not modify the activity of the pentose transporter.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coruzzi G., Poli E. Changes in duodenal contractility induced by "calcium antagonists" with different modes of action. Gen Pharmacol. 1987;18(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(87)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deslandes A., Westphal J. F., Trouvin J. H., Farinotti R. Adaptive computer program for determination of absorption profiles by numerical deconvolution: application to amoxicillin absorption. J Pharm Sci. 1992 Aug;81(8):802–807. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600810816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner R. D., Fernandez P., Lawrence G., Sia L. L., Falkowski A. J., Weiss A. I., Yacobi A., Silber B. M. Absolute bioavailability of cefixime in man. J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;28(8):700–706. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb03203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Amidon G. L. Intestinal absorption mechanism of dipeptide angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors of the lysyl-proline type: lisinopril and SQ 29,852. J Pharm Sci. 1989 Dec;78(12):995–998. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600781205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic S., Eichler H. G., Korn A. Comparative effects of verapamil, tiapamil, diltiazem and nifedipine on systemic and splanchnic hemodynamics in man. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1987 Sep;25(9):498–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huguenin P., Cochet B., Balant L., Loizeau E. Test d'absorption du d-xylose. Etude pharmacocinétique et statistique. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1978 Feb 11;108(6):206–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowther J., Hammond S. M., Russell K., Fairclough P. D. Uptake of cephalosporins by human intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jan;25(1):183–184. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montay G., Le Liboux A., Thebault J. J., Roche G., Frydman A., Gaillot J. Pharmacocinétique du céfixime chez le volontaire sain après administration orale unique à la dose de 200 mg. Presse Med. 1989 Oct 11;18(32):1583–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santander R., Mena I., Gramisu M., Valenzuela J. E. Effect of nifedipine on gastric emptying and gastrointestinal motility in man. Dig Dis Sci. 1988 May;33(5):535–539. doi: 10.1007/BF01798353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Hirooka H., Tamai I., Terasaki T. Evidence for a carrier-mediated transport system in the small intestine available for FK089, a new cephalosporin antibiotic without an amino group. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1986 Nov;39(11):1592–1597. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.39.1592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Hirooka H., Terasaki T., Tamai I., Nakashima E. Saturable uptake of cefixime, a new oral cephalosporin without an alpha-amino group, by the rat intestine. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;39(4):272–277. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1987.tb06265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Terasaki T., Tamai I., Hirooka H. H+ gradient-dependent and carrier-mediated transport of cefixime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, across brush-border membrane vesicles from rat small intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):594–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan D. P., Dennis M. Mathematical basis of point-area deconvolution method for determining in vivo input functions. J Pharm Sci. 1978 May;67(5):663–665. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600670524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal J. F., Trouvin J. H., Deslandes A., Carbon C. Nifedipine enhances amoxicillin absorption kinetics and bioavailability in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):312–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


