Abstract
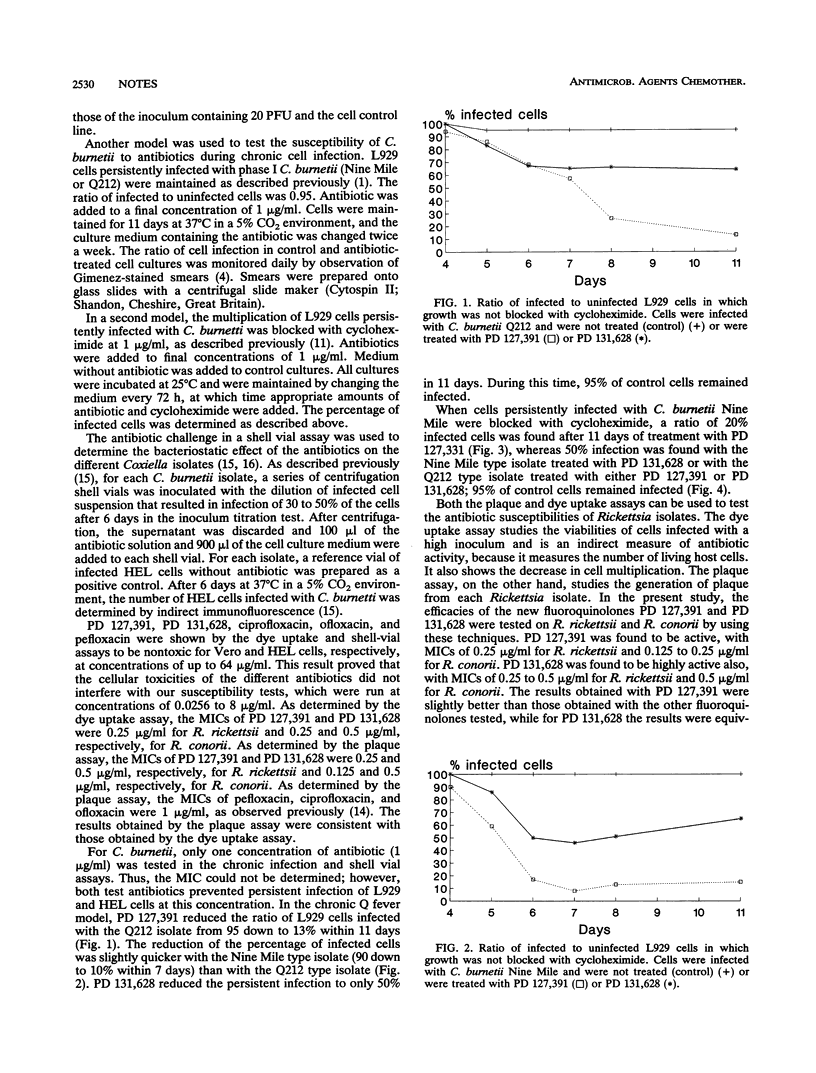
Plaque formation and dye uptake assays were used to measure the MICs of PD 127,391 and PD 131,628 against Rickettsia species. The MICs of PD 127,391 were 0.25 microgram/ml for Rickettsia rickettsii and 0.125 to 0.25 microgram/ml for Rickettsia conorii. The MICs of PD 131,628 were 0.25 to 0.5 microgram/ml for R. rickettsii and 0.5 microgram/ml for R. conorii. As determined by the shell vial technique, 15 strains of Coxiella burnetii were susceptible to PD 127,391 and PD 131,628 (MIC, < or = 1 microgram/ml), while one strain of C. burnetii (MP10) was of intermediate susceptibility.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baca O. G., Scott T. O., Akporiaye E. T., DeBlassie R., Crissman H. A. Cell cycle distribution patterns and generation times of L929 fibroblast cells persistently infected with Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):366–369. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.366-369.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand A., Janbon F., Jonquet O., Reynes J. Infections par les rickettsiales et fluoroquinolones. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1988 May;36(5):493–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein D. B., Frontini M. G., Giles R., Vernon L. L. Fatal cases of Rocky Mountain spotted fever in the United States, 1981-1988. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:246–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T. The role of lipopolysaccharides in the virulence of Coxiella burnetii. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:27–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL O. W., KENNEDY K. P., McIVER M., SILVERSTONE H. Tetracycline in the treatment of "Q" fever. Australas Ann Med. 1962 Aug;11:184–188. doi: 10.1111/imj.1962.11.3.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey P. G., Press O. W. Successful treatment of Rocky Mountain 'spotless' fever. West J Med. 1984 Jan;140(1):94–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Bres P., Drancourt M., Vestris G. In vitro susceptibilities of Coxiella burnetii, Rickettsia rickettsii, and Rickettsia conorii to the fluoroquinolone sparfloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):88–91. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Drancourt M. Antimicrobial therapy of rickettsial diseases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2457–2462. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Drancourt M., Vestris G. Bactericidal effect of doxycycline associated with lysosomotropic agents on Coxiella burnetii in P388D1 cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1512–1514. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Gallais H., De Micco P., Casanova P. Ciprofloxacin therapy for Mediterranean spotted fever. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):606–607. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D. Host factors in the severity of Q fever. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Roussellier P., Galicher V., Perez R., Tamalet J. In vitro susceptibility of Rickettsia conorii to ciprofloxacin as determined by suppressing lethality in chicken embryos and by plaque assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):424–425. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Torres H., Drancourt M. Shell-vial assay: evaluation of a new technique for determining antibiotic susceptibility, tested in 13 isolates of Coxiella burnetii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Oct;35(10):2070–2077. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.10.2070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Vestris G., Enea M. Isolation of 16 strains of Coxiella burnetii from patients by using a sensitive centrifugation cell culture system and establishment of the strains in HEL cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2482–2484. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2482-2484.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Zuchelli P., Weiller P. J., Charrel C., San Marco J. L., Gallais H., Casanova P. Incidence, clinical observations and risk factors in the severe form of Mediterranean spotted fever among patients admitted to hospital in Marseilles 1983-1984. J Infect. 1986 Mar;12(2):111–116. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(86)93508-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelman D. W. Q fever: a study of 111 consecutive cases. Med J Aust. 1982 Jun 26;1(13):547-8, 551, 553. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1982.tb124169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turck W. P., Howitt G., Turnberg L. A., Fox H., Longson M., Matthews M. B., Das Gupta R. Chronic Q fever. Q J Med. 1976 Apr;45(178):193–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman M. R., Mitscher L. A., Baca O. G. In vitro susceptibility of Coxiella burnetii to antibiotics, including several quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1079–1084. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman M. R., Roman M. J., Baca O. G. Antibiotic susceptibilities of two Coxiella burnetii isolates implicated in distinct clinical syndromes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1052–1057. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


