Abstract
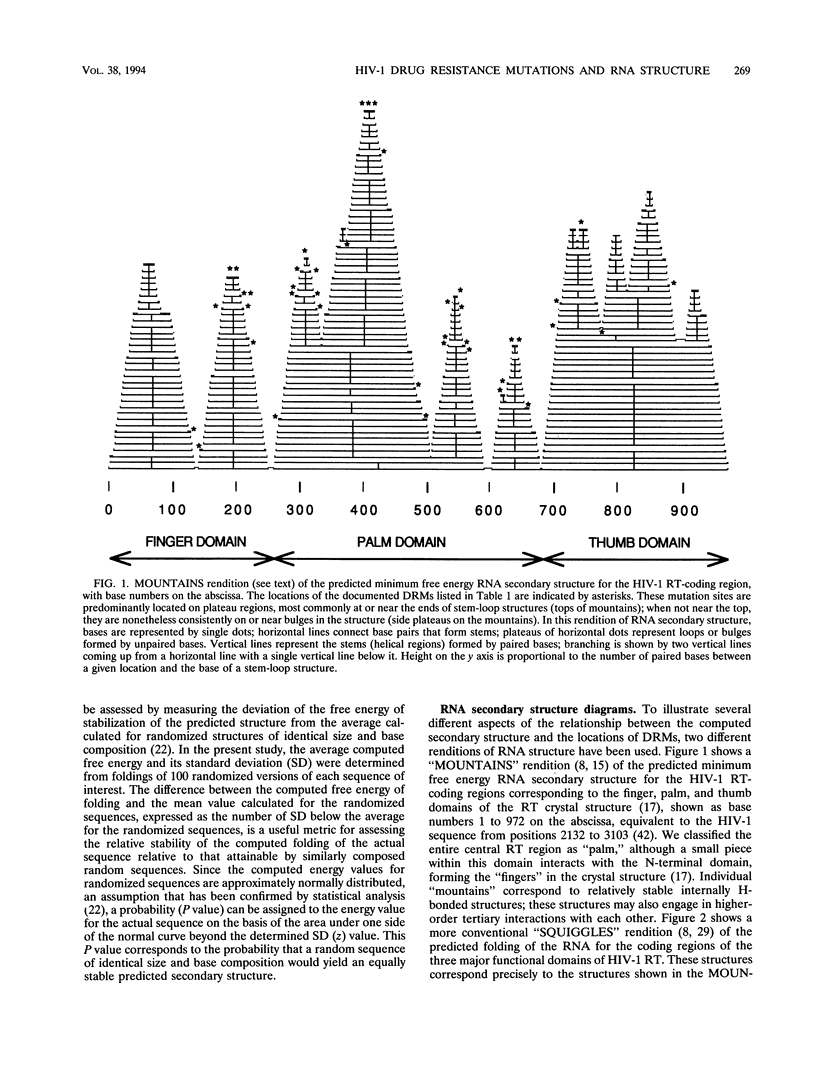
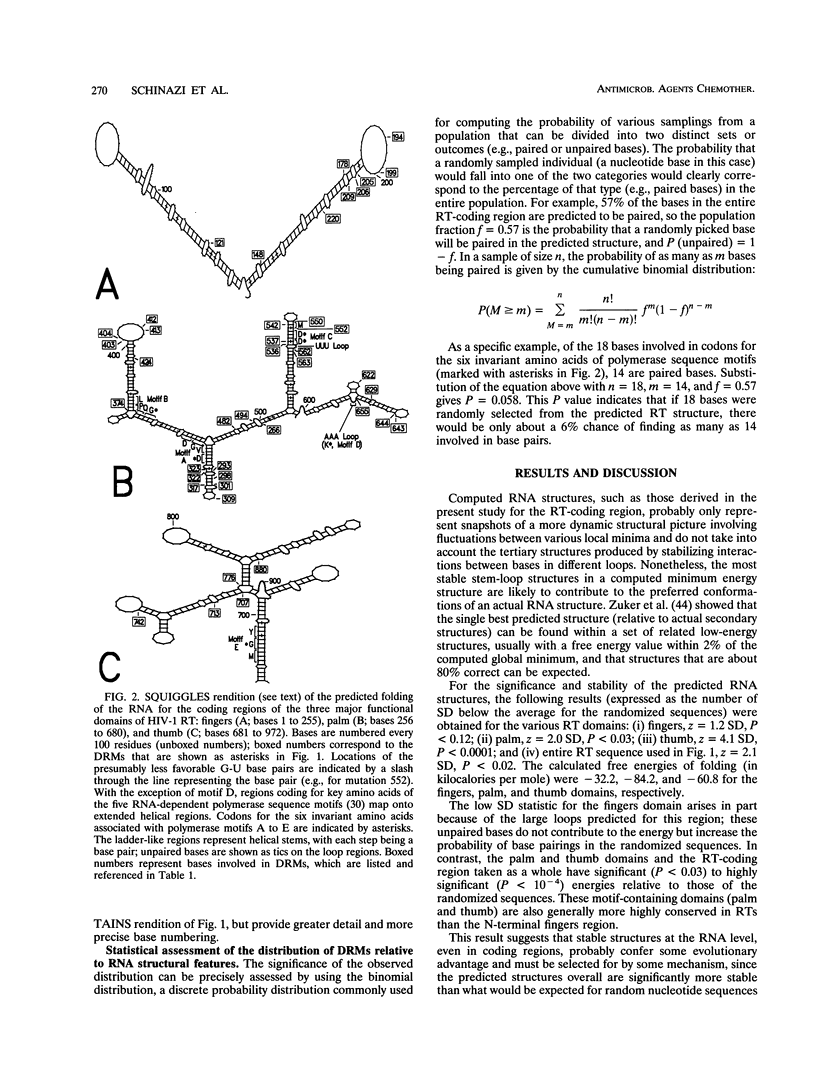
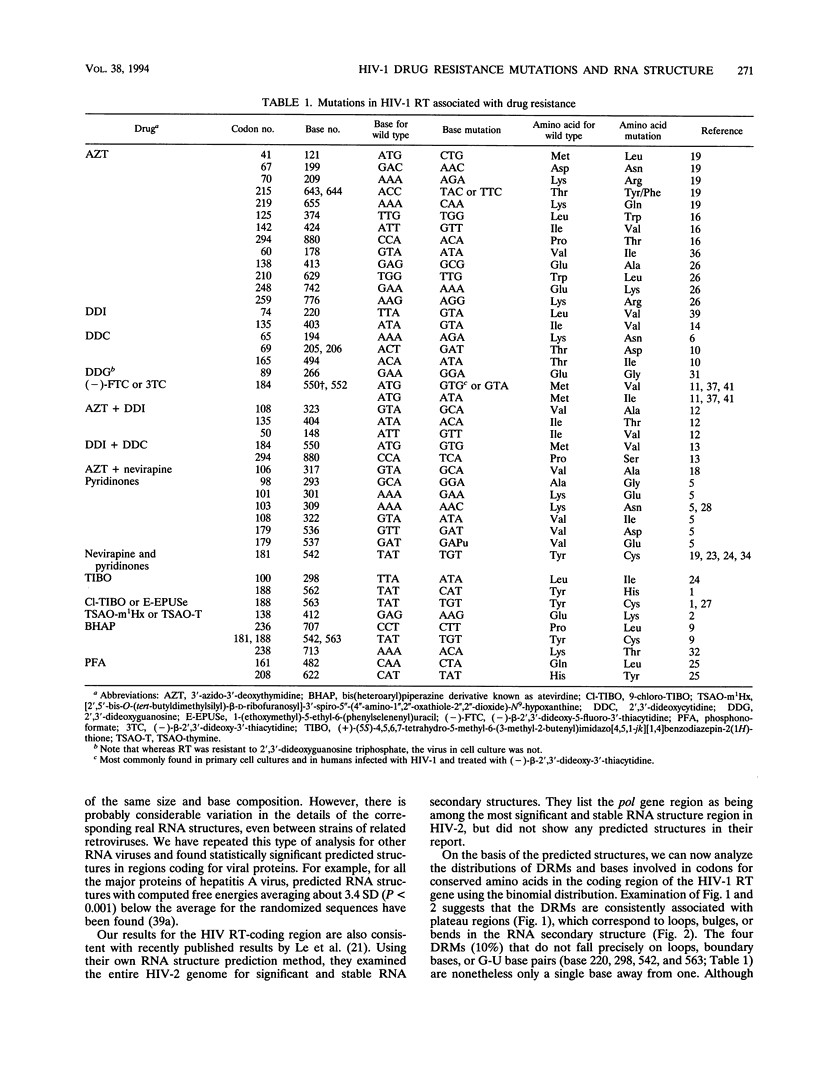
A statistically significant correlation exists between the locations of drug resistance mutations (DRMs) observed for various reverse transcriptase inhibitors and features of the secondary structure predicted for the RNA coding for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. The known DRMs map onto "unstable" bases, which are predominantly nonhelical regions (i.e., loops, bulges, and bends) of the predicted RNA secondary structure, whereas codons for the key conserved residues of polymerase sequence motifs map onto "stable" paired bases involved in helical regions. On the basis of these results, we hypothesize that the secondary structure of the RNA template (in this case, the reverse transcriptase gene itself) may be a previously unrecognized factor contributing to base misincorporation errors during reverse transcription and that, rather than being randomly distributed, mutations are more likely to occur in specific regions of the genome. The results suggest that these "mutation-prone" regions can be predicted by using a standard algorithm for RNA secondary structure.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balzarini J., Karlsson A., Pérez-Pérez M. J., Vrang L., Walbers J., Zhang H., Oberg B., Vandamme A. M., Camarasa M. J., De Clercq E. HIV-1-specific reverse transcriptase inhibitors show differential activity against HIV-1 mutant strains containing different amino acid substitutions in the reverse transcriptase. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):246–253. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Velazquez S., San-Felix A., Karlsson A., Perez-Perez M. J., Camarasa M. J., De Clercq E. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific [2',5'-bis-O-(tert- butyldimethylsilyl)-beta-D-ribofuranosyl]-3'-spiro-5"-(4"-amino-1",2"- oxathiole-2",2"-dioxide)-purine analogues show a resistance spectrum that is different from that of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific non-nucleoside analogues. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;43(1):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Schoneveld I. Secondary structure of the HIV-2 leader RNA comprising the tRNA-primer binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1171–1178. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borzakian S., Pelletier I., Calvez V., Colbere-Garapin F. Precise missense and silent point mutations are fixed in the genomes of poliovirus mutants from persistently infected cells. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2914–2917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2914-2917.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes V. W., Sardana V. V., Schleif W. A., Condra J. H., Waterbury J. A., Wolfgang J. A., Long W. J., Schneider C. L., Schlabach A. J., Wolanski B. S. Comprehensive mutant enzyme and viral variant assessment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase resistance to nonnucleoside inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Aug;37(8):1576–1579. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.8.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeStefano J. J., Buiser R. G., Mallaber L. M., Fay P. J., Bambara R. A. Parameters that influence processive synthesis and site-specific termination by human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase on RNA and DNA templates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 15;1131(3):270–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90025-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dueweke T. J., Pushkarskaya T., Poppe S. M., Swaney S. M., Zhao J. Q., Chen I. S., Stevenson M., Tarpley W. G. A mutation in reverse transcriptase of bis(heteroaryl)piperazine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 that confers increased sensitivity to other nonnucleoside inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4713–4717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgibbon J. E., Howell R. M., Haberzettl C. A., Sperber S. J., Gocke D. J., Dubin D. T. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 pol gene mutations which cause decreased susceptibility to 2',3'-dideoxycytidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jan;36(1):153–157. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Q., Gu Z. X., Parniak M. A., Li X. G., Wainberg M. A. In vitro selection of variants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistant to 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine and 2',3'-dideoxyinosine. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):12–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.12-19.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Q., Gu Z., Parniak M. A., Cameron J., Cammack N., Boucher C., Wainberg M. A. The same mutation that encodes low-level human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistance to 2',3'-dideoxyinosine and 2',3'-dideoxycytidine confers high-level resistance to the (-) enantiomer of 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jun;37(6):1390–1392. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.6.1390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z., Gao Q., Li X., Parniak M. A., Wainberg M. A. Novel mutation in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase gene that encodes cross-resistance to 2',3'-dideoxyinosine and 2',3'-dideoxycytidine. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7128–7135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7128-7135.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogeweg P., Hesper B. Energy directed folding of RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Japour A. J., Chatis P. A., Eigenrauch H. A., Crumpacker C. S. Detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clinical isolates with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine and dideoxyinosine by RNA.RNA hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Wang J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1377403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A. 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine resistance suppressed by a mutation conferring human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistance to nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2664–2669. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D. Multiple mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase confer high-level resistance to zidovudine (AZT). Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1155–1158. doi: 10.1126/science.2479983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le S. Y., Chen J. H., Chatterjee D., Maizel J. V. Sequence divergence and open regions of RNA secondary structures in the envelope regions of the 17 human immunodeficiency virus isolates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3275–3288. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le S. Y., Chen J. H., Maizel J. V. Detection of unusual RNA folding regions in HIV and SIV sequences. Comput Appl Biosci. 1991 Jan;7(1):51–55. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/7.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Jr A method for assessing the statistical significance of RNA folding. J Theor Biol. 1989 Jun 22;138(4):495–510. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(89)80047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors J. W., Dutschman G. E., Im G. J., Tramontano E., Winkler S. R., Cheng Y. C. In vitro selection and molecular characterization of human immunodeficiency virus-1 resistant to non-nucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):446–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors J. W., Im G. J., Tramontano E., Winkler S. R., Medina D. J., Dutschman G. E., Bazmi H. Z., Piras G., Gonzalez C. J., Cheng Y. C. A single conservative amino acid substitution in the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus-1 confers resistance to (+)-(5S)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-5-methyl-6-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)imidazo[4,5, 1- jk][1,4]benzodiazepin-2(1H)-thione (TIBO R82150). Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;43(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muckenthaler M., Gunkel N., Levantis P., Broadhurst K., Goh B., Colvin B., Forster G., Jackson G. G., Oxford J. S. Sequence analysis of an HIV-1 isolate which displays unusually high-level AZT resistance in vitro. J Med Virol. 1992 Feb;36(2):79–83. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890360204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Schleif W. A., Boots E. J., O'Brien J. A., Quintero J. C., Hoffman J. M., Emini E. A., Goldman M. E. Viral resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific pyridinone reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4887–4892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4887-4892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterburg G., Sommer R. Computer support of DNA sequence analysis. Comput Programs Biomed. 1981 Mar-Jun;13(1-2):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(81)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Sauvaget I., Delarue M., Tordo N. Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad V. R., Lowy I., de los Santos T., Chiang L., Goff S. P. Isolation and characterization of a dideoxyguanosine triphosphate-resistant mutant of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11363–11367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricchetti M., Buc H. Reverse transcriptases and genomic variability: the accuracy of DNA replication is enzyme specific and sequence dependent. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1583–1593. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D. Resistance of clinical isolates of human immunodeficiency virus to antiretroviral agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jun;37(6):1207–1213. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.6.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D., Shih C. K., Lowy I., Rose J., Prodanovich P., Goff S., Griffin J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutants resistant to nonnucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase arise in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11241–11245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen-Waigmann H., Schröder B., Biesert L., Bauermeister C. D., von Briesen H., Suhartono H., Zimmermann F., Brede H. D., Regeniter A., Gerte S. Markers for HIV-disease progression in untreated patients and patients receiving AZT: evaluation of viral activity, AZT resistance, serum cholesterol, beta 2-microglobulin, CD4+ cell counts, and HIV antigen. Infection. 1991;19 (Suppl 2):S77–S82. doi: 10.1007/BF01644472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Lloyd R. M., Jr, Nguyen M. H., Cannon D. L., McMillan A., Ilksoy N., Chu C. K., Liotta D. C., Bazmi H. Z., Mellors J. W. Characterization of human immunodeficiency viruses resistant to oxathiolane-cytosine nucleosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):875–881. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Mead J. R., Feorino P. M. Insights into HIV chemotherapy. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Jun;8(6):963–990. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Martin J. L., Tudor-Williams G., Bach M. C., Vavro C. L., King D. M., Kellam P., Kemp S. D., Larder B. A. Resistance to ddI and sensitivity to AZT induced by a mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1716788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teare J., Wollenzien P. The structure of a pre-mRNA molecule in solution determined with a site directed cross-linking reagent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):855–864. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M., Kemp S. D., Parry N. R., Larder B. A. Rapid in vitro selection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistant to 3'-thiacytidine inhibitors due to a mutation in the YMDD region of reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5653–5656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Sonigo P., Danos O., Cole S., Alizon M. Nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, LAV. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistow G. Protein structure and introns. Nature. 1993 Jul 8;364(6433):107–108. doi: 10.1038/364107b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H. A comparison of optimal and suboptimal RNA secondary structures predicted by free energy minimization with structures determined by phylogenetic comparison. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2707–2714. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


