Abstract
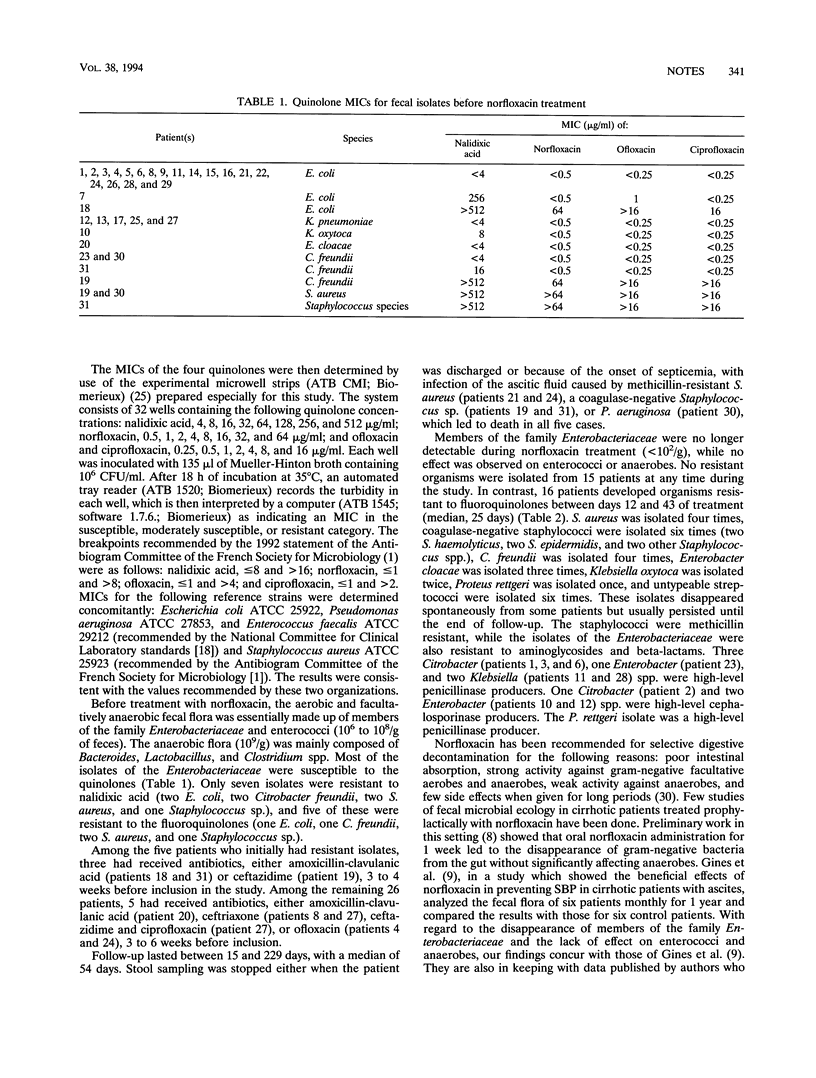
We carried out quantitative culturing of stools from 31 hospitalized alcoholic patients with cirrhosis and ascites, before treatment with 400 mg of norfloxacin per day, weekly for the first month, and then every 2 weeks thereafter for 15 to 229 days (median, 54 days). Members of the family Enterobacteriaceae virtually disappeared from the stools (< 10(2)/g), but treatment had little effect on enterococci. No selection of resistant organisms occurred in 15 patients, but the remaining 16 patients developed fecal organisms resistant to fluoroquinolones between days 14 and 43 of treatment (median, 25 days). Staphylococcus aureus was isolated four times, coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. were isolated six times, Citrobacter freundii was isolated four times, Enterobacter cloacae was isolated three times, Klebsiella oxytoca was isolated twice, Proteus rettgeri was isolated once, and untypeable streptococci were isolated six times. Some isolates persisted, while others were transient (one to seven consecutively positive cultures). The MICs of four quinolones (nalidixic acid, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and ciprofloxacin) were determined by use of experimental microwell strips (ATB CMI; Biomerieux S.A.). All the strains isolated before treatment were susceptible to the four quinolones, with low MICs, whereas those isolated during norfloxacin treatment were highly resistant. Long-term norfloxacin administration thus carries a risk of disturbing the bacterial ecology in these patients, suggesting that digestive decontamination should no longer be prescribed routinely to cirrhotic patients with ascites.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler-Mosca H., Lüthy-Hottenstein J., Martinetti Lucchini G., Burnens A., Altwegg M. Development of resistance to quinolones in five patients with campylobacteriosis treated with norfloxacin or ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Nov;10(11):953–957. doi: 10.1007/BF02005451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge K. E., Gelfand M. S., Schiro D. D., Barg N. L. The rapid emergence of fluoroquinolone-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in a community hospital. An in vitro look at alternative antimicrobial agents. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Sep-Oct;15(7):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(90)90037-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daschner F. Emergence of resistance during selective decontamination of the digestive tract. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;11(1):1–3. doi: 10.1007/BF01971262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vries-Hospers H. G., Welling G. W., Van der Waaij D. Norfloxacin for selective decontamination: a study in human volunteers. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;181:259–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund C., Bergan T., Josefsson K., Solberg R., Nord C. E. Effect of norfloxacin on human oropharyngeal and colonic microflora and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics. Scand J Infect Dis. 1987;19(1):113–121. doi: 10.3109/00365548709032386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn D. M., Weinstein R. A., Nathan C., Gaston M. A., Kabins S. A. Patients' endogenous flora as the source of "nosocomial" Enterobacter in cardiac surgery. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):363–368. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginés P., Rimola A., Planas R., Vargas V., Marco F., Almela M., Forné M., Miranda M. L., Llach J., Salmerón J. M. Norfloxacin prevents spontaneous bacterial peritonitis recurrence in cirrhosis: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Hepatology. 1990 Oct;12(4 Pt 1):716–724. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefs J. C., Canawati H. N., Sapico F. L., Hopkins R. R., Weiner J., Montgomerie J. Z. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Hepatology. 1982 Jul-Aug;2(4):399–407. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefs J. C. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: prevention and therapy. Hepatology. 1990 Oct;12(4 Pt 1):776–781. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer J., Dupeyron C., Vuillemin N., Leluan G., Fouet P. Apport des examens cytologiques et bactériologiques du liquide d'ascite cirrhotique au diagnostic de péritonite bactérienne. A propos de 610 prélevements chez 156 malades. Med Chir Dig. 1982;11(4):243–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer J., Taleb M., Dupeyron C., Vuillemin N., Leluan G., Fouet P. Péritonites bactériennes spontanées du cirrhotique. A propos de 26 épisodes. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1979 Oct;3(10):709–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernodle D. S., Barg N. L., Kaiser A. B. Low-level colonization of hospitalized patients with methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci and emergence of the organisms during surgical antimicrobial prophylaxis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):202–208. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline M. M., McCallum R. W., Guth P. H. The clinical value of ascitic fluid culture and leukocyte count studies in alcoholic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):408–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson B., Weinstein R. A., Nathan C., Chamberlin W., Kabins S. A. Epidemiology of endemic Pseudomonas aeruginosa: why infection control efforts have failed. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):808–816. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecquet S., Andremont A., Tancrède C. Effect of oral ofloxacin on fecal bacteria in human volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jan;31(1):124–125. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecquet S., Andremont A., Tancrède C. Selective antimicrobial modulation of the intestinal tract by norfloxacin in human volunteers and in gnotobiotic mice associated with a human fecal flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1047–1052. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piddock L. J., Griggs D. J., Hall M. C., Jin Y. F. Ciprofloxacin resistance in clinical isolates of Salmonella typhimurium obtained from two patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):662–666. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reina J., Borrell N., Serra A. Emergence of resistance to erythromycin and fluoroquinolones in thermotolerant Campylobacter strains isolated from feces 1987-1991. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;11(12):1163–1166. doi: 10.1007/BF01961137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohner P., Peyret M., Auckenthaler R. Determination of MICs for staphylococci using the API ATB quinolone and API ATB macrolide systems. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1993 Apr;41(4):323–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runyon B. A. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: an explosion of information. Hepatology. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):171–175. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano G., Guarner C., Teixidó M., Such J., Barrios J., Enríquez J., Vilardell F. Selective intestinal decontamination prevents spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Gastroenterology. 1991 Feb;100(2):477–481. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90219-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiström J., Gentry L. O., Palmgren A. C., Price M., Nord C. E., Ljungh A., Norrby S. R. Ecological effects of short-term ciprofloxacin treatment of travellers' diarrhoea. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Nov;30(5):693–706. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. Norfloxacin: a new targeted fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agent. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Feb;108(2):238–251. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-2-238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Strömberg A., Ostlund L., Sjögren E., Kaijser B. Rapid emergence of quinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni in patients treated with norfloxacin. Scand J Infect Dis. 1992;24(5):685–686. doi: 10.3109/00365549209054659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


