Abstract
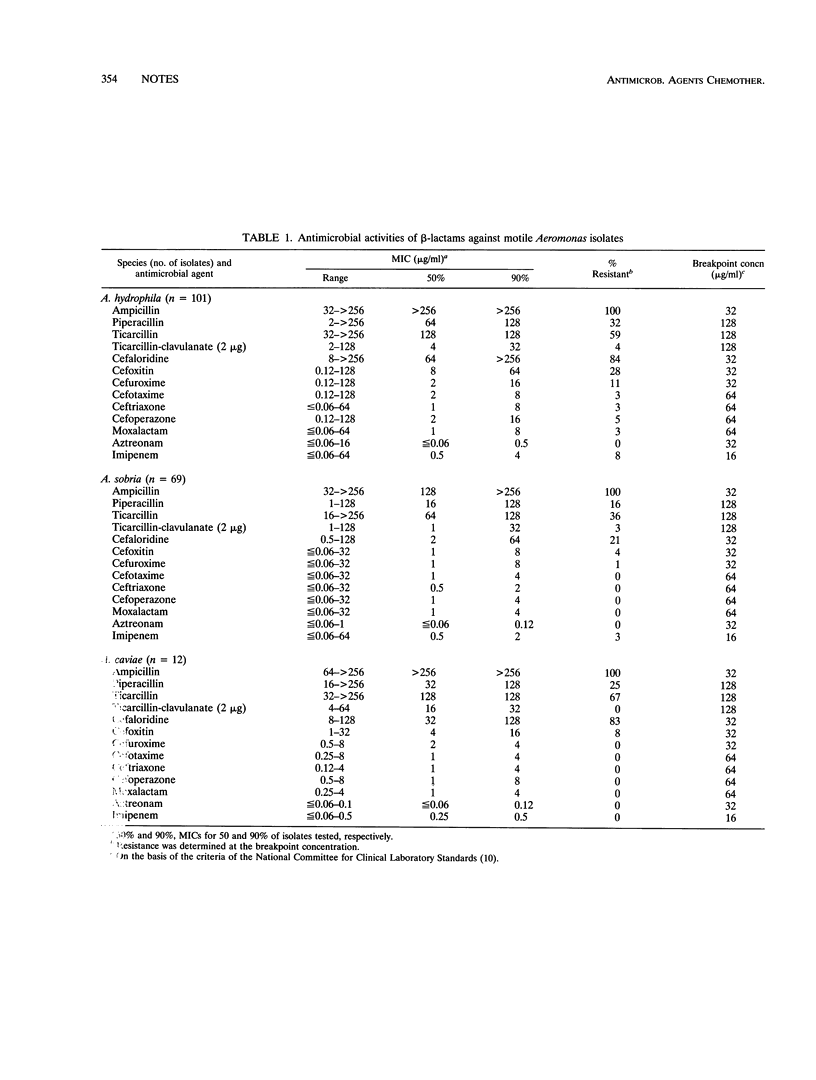
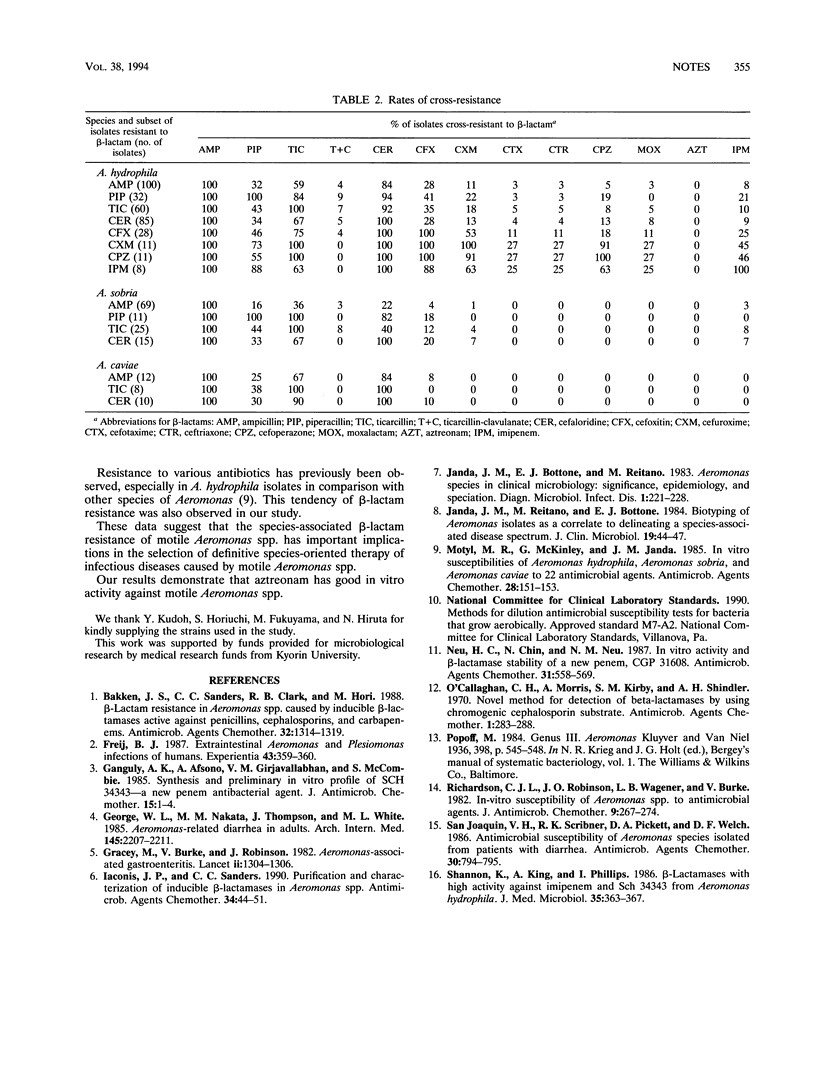
The MICs of various beta-lactams for 182 isolates of Aeromonas species, i.e., A. hydrophila (n = 101), A. sobria (n = 69), and A. caviae (n = 12), from clinical and environmental sources were determined by an agar dilution technique. All strains were resistant to ampicillin and susceptible to aztreonam. A. sobria and A. caviae demonstrated lower resistance rates than A. hydrophila. Penicillin-hydrolyzing beta-lactamases were detected in all strains.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakken J. S., Sanders C. C., Clark R. B., Hori M. Beta-lactam resistance in Aeromonas spp. caused by inducible beta-lactamases active against penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1314–1319. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly A. K., Afonso A., Girijavallabhan V. M., McCombie S. Synthesis and preliminary in-vitro profile of Sch 34343--a new penem antibacterial agent. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jun;15 (Suppl 100):1–4. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_c.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Nakata M. M., Thompson J., White M. L. Aeromonas-related diarrhea in adults. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Dec;145(12):2207–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Robinson J. Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1982 Dec 11;2(8311):1304–1306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91510-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iaconis J. P., Sanders C. C. Purification and characterization of inducible beta-lactamases in Aeromonas spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):44–51. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Bottone E. J., Reitano M. Aeromonas species in clinical microbiology: significance, epidemiology, and speciation. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;1(3):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(83)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Reitano M., Bottone E. J. Biotyping of Aeromonas isolates as a correlate to delineating a species-associated disease spectrum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):44–47. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.44-47.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motyl M. R., McKinley G., Janda J. M. In vitro susceptibilities of Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas sobria, and Aeromonas caviae to 22 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):151–153. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Chin N. X., Neu N. M. In vitro activity and beta-lactamase stability of a new penem, CGP 31608. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):558–569. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. J., Robinson J. O., Wagener L. B., Burke V. In-vitro susceptibility of Aeromonas app. to antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Apr;9(4):267–274. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.4.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Joaquin V. H., Scribner R. K., Pickett D. A., Welch D. F. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Aeromonas species isolated from patients with diarrhea. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):794–795. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


