Abstract
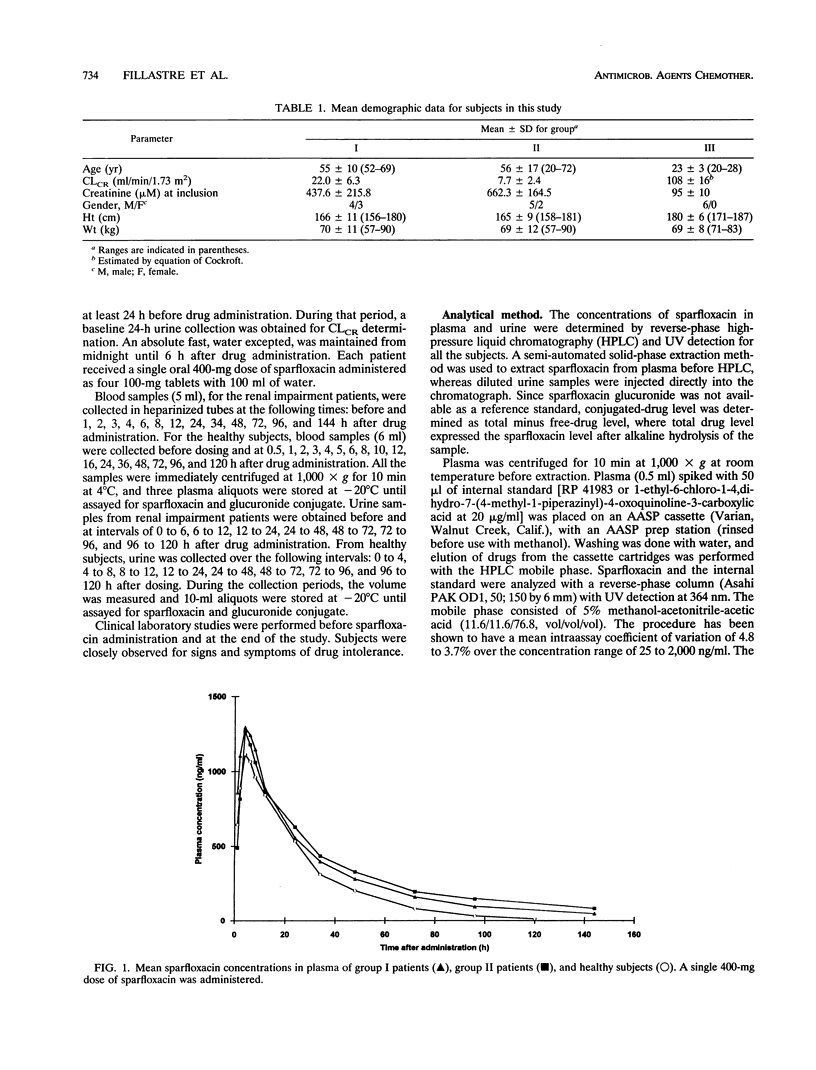
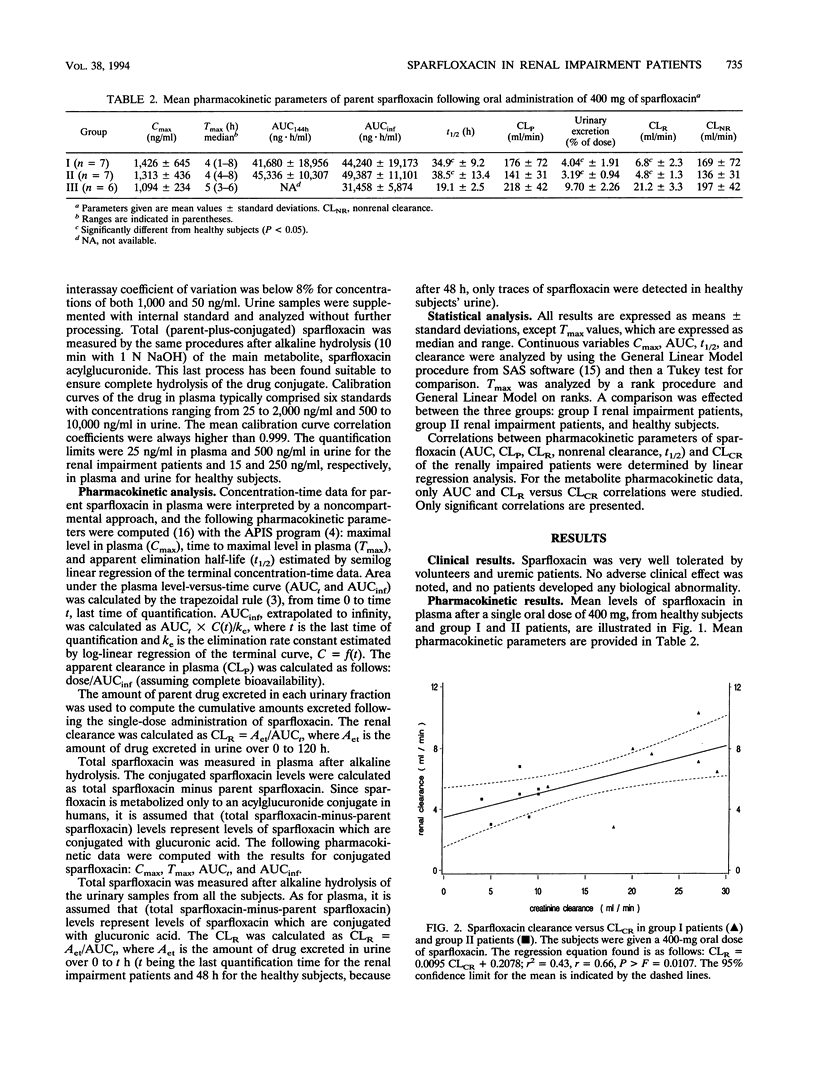
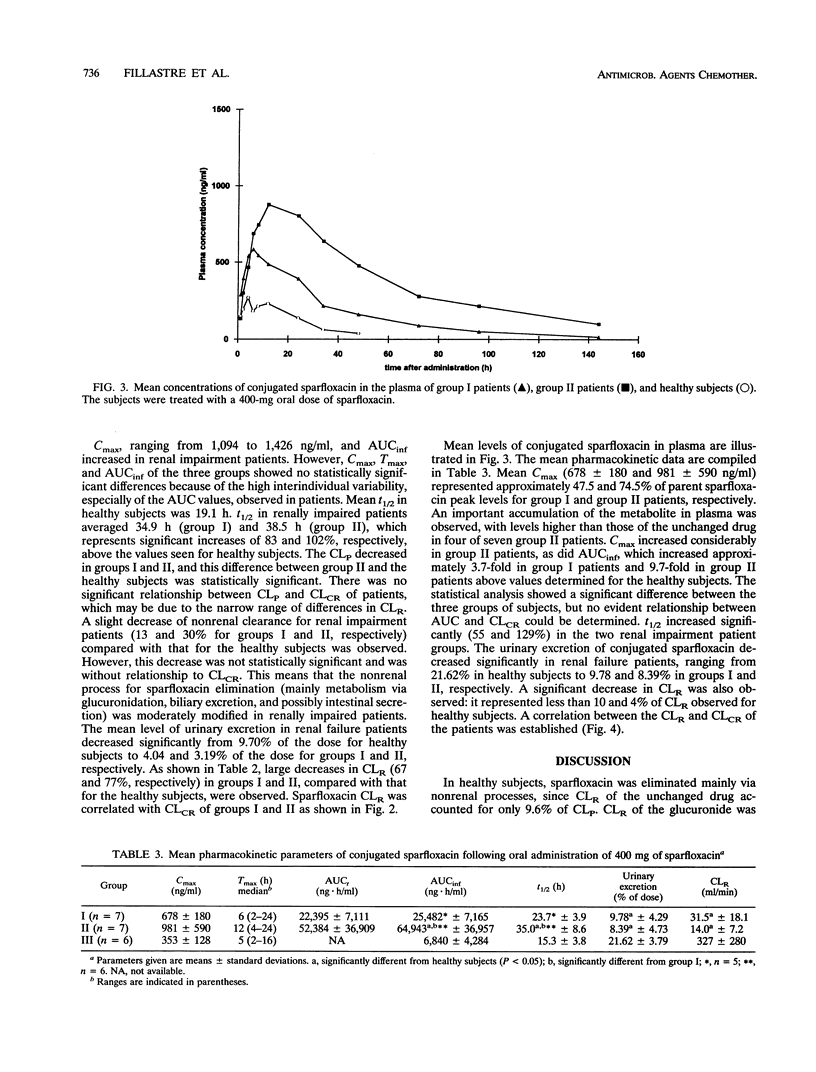
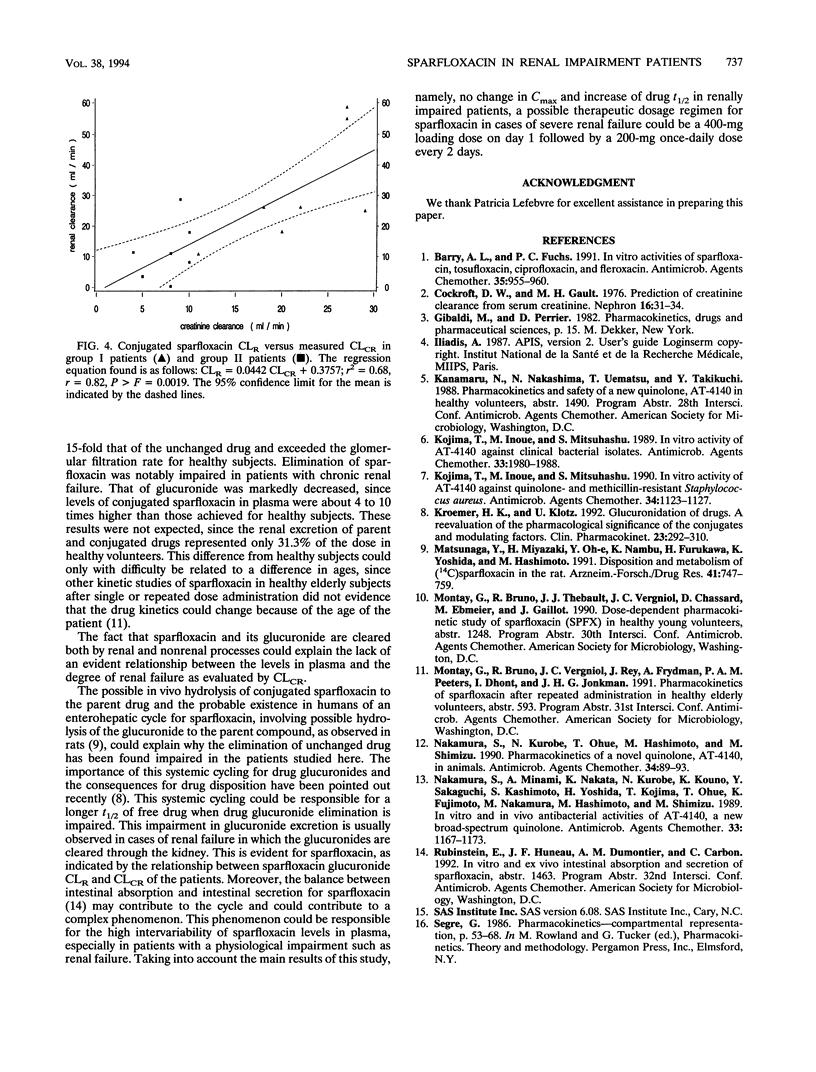
The pharmacokinetics of sparfloxacin were studied in 14 renal failure patients (group I, 7 with creatinine clearance of > 10 to 30 ml/min; and group II, 7 with creatinine clearance of < or = 10 ml/min) after a single oral dose of 400 mg. Plasma and urine samples were collected up to 144 h postdosing for determination of parent and total (parent-plus-glucuronide-conjugated) sparfloxacin levels, by high-pressure liquid chromatography assay and UV detection. The elimination of the drug in patients compared with that in healthy volunteers was markedly impaired. The mean elimination half-lives of sparfloxacin were 34.9 and 38.5 h in group I and group II, respectively, versus 19.1 h in healthy volunteers. Conjugated drug half-lives were 23.7, 35.0, and 15.3 h, respectively. The renal clearance of the drug was markedly reduced in the patients, with values of 6.8, 4.8, and 21.2 ml/min determined for group I, group II, and healthy subjects, respectively, for parent sparfloxacin and with values of 31.5, 14.0, and 327 ml/min for conjugated sparfloxacin. The nonrenal clearance of sparfloxacin was moderately, but not significantly, decreased in group II renal failure patients. No difference between the two groups of patients was detected in sparfloxacin levels in plasma. A significant relationship between pharmacokinetic parameters and creatinine clearance was observed only for renal clearance of parent or conjugated sparfloxacin.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C. In vitro activities of sparfloxacin, tosufloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and fleroxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):955–960. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Gault M. H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16(1):31–41. doi: 10.1159/000180580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima T., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro activity of AT-4140 against clinical bacterial isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1980–1988. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima T., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro activity of AT-4140 against quinolone- and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1123–1127. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroemer H. K., Klotz U. Glucuronidation of drugs. A re-evaluation of the pharmacological significance of the conjugates and modulating factors. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992 Oct;23(4):292–310. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199223040-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga Y., Miyazaki H., Oh-e Y., Nambu K., Furukawa H., Yoshida K., Hashimoto M. Disposition and metabolism of [14C]sparfloxacin in the rat. Arzneimittelforschung. 1991 Jul;41(7):747–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Kurobe N., Ohue T., Hashimoto M., Shimizu M. Pharmacokinetics of a novel quinolone, AT-4140, in animals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):89–93. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Minami A., Nakata K., Kurobe N., Kouno K., Sakaguchi Y., Kashimoto S., Yoshida H., Kojima T., Ohue T. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of AT-4140, a new broad-spectrum quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1167–1173. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


