Abstract
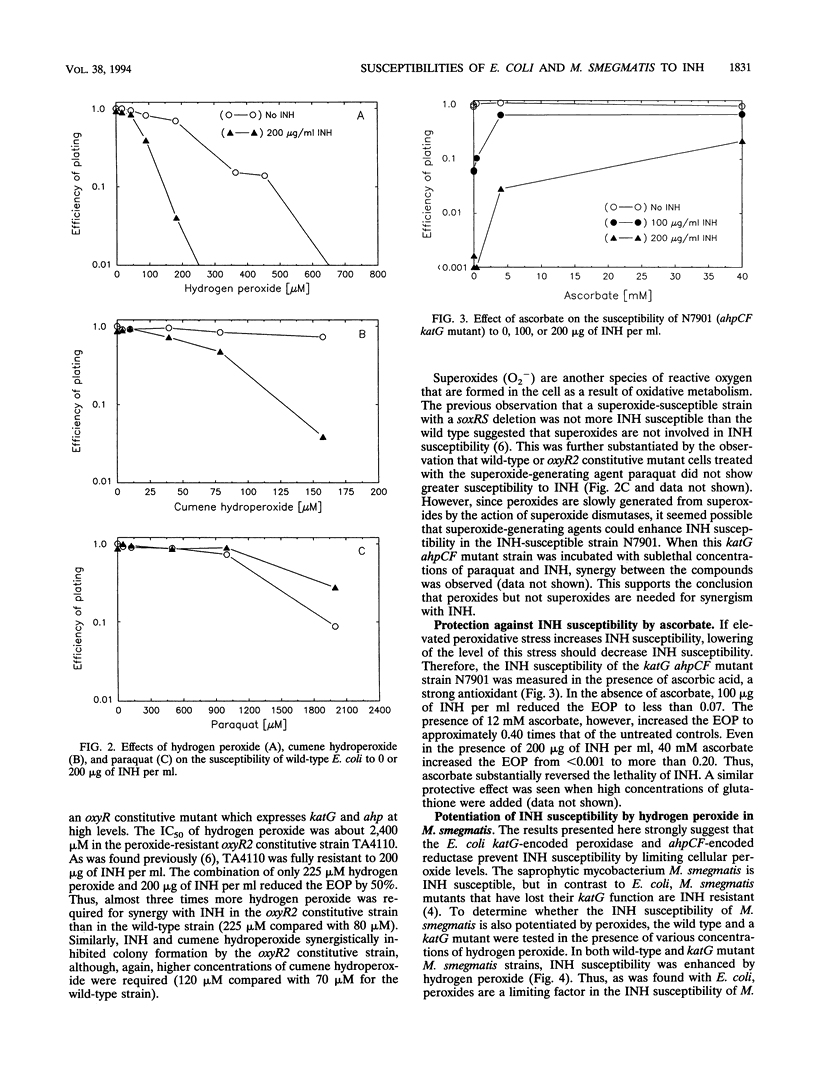
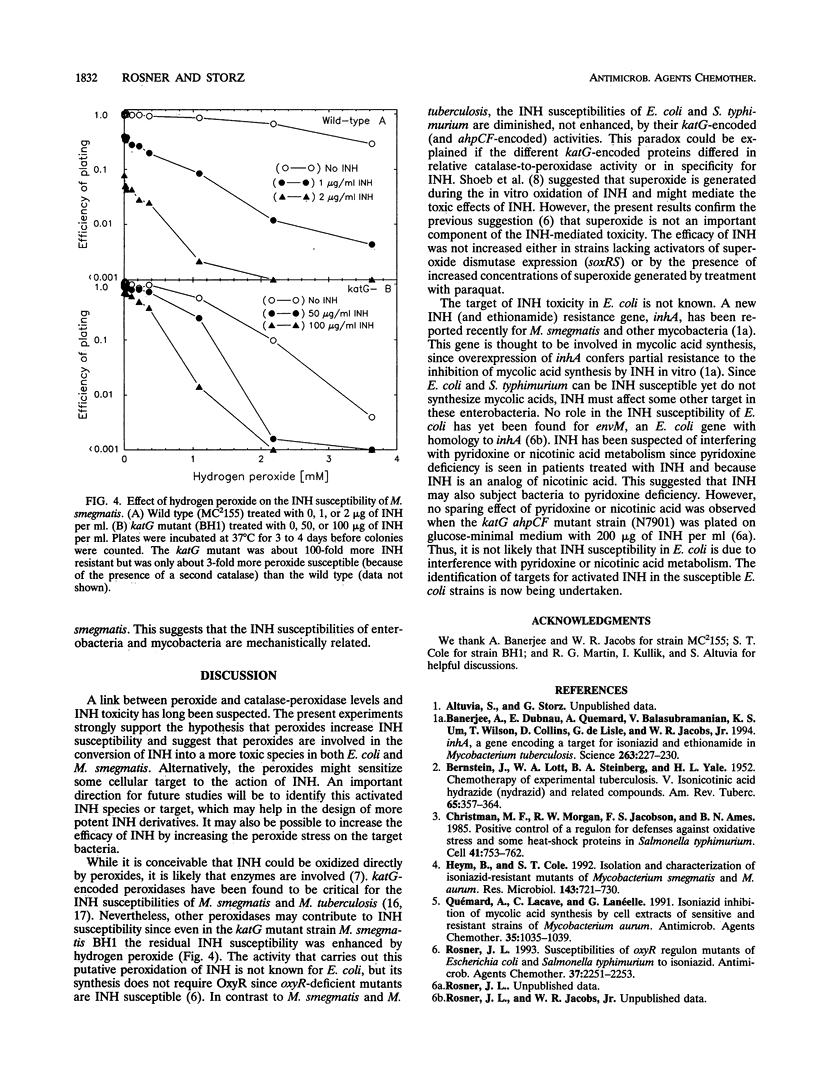
Escherichia coli strains were previously found to be susceptible to the antituberculosis drug isonicotinic acid hydrazide (isoniazid [INH]) when they carried certain mutations that also sensitize them to peroxides: a deletion in oxyR, a redox-sensitive regulator of hydrogen peroxide-inducible genes, or mutations in both katG and ahpCF, OxyR-regulated genes encoding hydroperoxidase I, and an alkyl hydroperoxide reductase. To test whether INH, like peroxides, activates OxyR, the effect of INH on OxyR regulation was examined. Primer extension assays showed that transcription of the OxyR-regulated oxyS gene was not significantly induced by INH in wild-type cells, indicating that INH does not activate OxyR. However, the INH-susceptible katG ahpCF mutant strain was found to have constitutively high levels of oxyS transcription. This suggested that the lack of peroxidase expression in these strains allows endogenous oxidants to accumulate, and this leads not only to constitutive OxyR activation but also to INH susceptibility. Consistent with this concept, hydrogen peroxide or cumene hydroperoxide potentiated the INH susceptibilities of wild-type cells, while the antioxidant ascorbic acid protected the susceptible katG ahpCF mutant strain from INH. Superoxide radicals, generated by paraquat, did not enhance the INH susceptibilities of wild-type cells. Hydrogen peroxide also potentiated the INH susceptibilities of susceptible and resistant (katG mutant) Mycobacterium smegmatis strains. Our results suggest that INH is converted to a more active drug by reaction with peroxides and that the INH susceptibilities of enterobacteria and mycobacteria are mechanistically related.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNSTEIN J., LOTT W. A., STEINBERG B. A., YALE H. L. Chemotherapy of experimental tuberculosis. V. Isonicotinic acid hydrazide (nydrazid) and related compounds. Am Rev Tuberc. 1952 Apr;65(4):357–364. doi: 10.1164/art.1952.65.4.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A., Dubnau E., Quemard A., Balasubramanian V., Um K. S., Wilson T., Collins D., de Lisle G., Jacobs W. R., Jr inhA, a gene encoding a target for isoniazid and ethionamide in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 1994 Jan 14;263(5144):227–230. doi: 10.1126/science.8284673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Morgan R. W., Jacobson F. S., Ames B. N. Positive control of a regulon for defenses against oxidative stress and some heat-shock proteins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heym B., Cole S. T. Isolation and characterization of isoniazid-resistant mutants of Mycobacterium smegmatis and M. aurum. Res Microbiol. 1992 Sep;143(7):721–730. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quémard A., Lacave C., Lanéelle G. Isoniazid inhibition of mycolic acid synthesis by cell extracts of sensitive and resistant strains of Mycobacterium aurum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jun;35(6):1035–1039. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.6.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Susceptibilities of oxyR regulon mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium to isoniazid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Oct;37(10):2251–2253. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoeb H. A., Bowman B. U., Jr, Ottolenghi A. C., Merola A. J. Enzymatic and nonenzymatic superoxide-generating reactions of isoniazid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):408–412. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoeb H. A., Bowman B. U., Jr, Ottolenghi A. C., Merola A. J. Peroxidase-mediated oxidation of isoniazid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):399–403. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper S. B., Melton R. E., Mustafa S., Kieser T., Jacobs W. R., Jr Isolation and characterization of efficient plasmid transformation mutants of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1911–1919. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider D. E., Jr, Roper W. L. The new tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 5;326(10):703–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203053261011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Altuvia S. OxyR regulon. Methods Enzymol. 1994;234:217–223. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)34088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Jacobson F. S., Tartaglia L. A., Morgan R. W., Silveira L. A., Ames B. N. An alkyl hydroperoxide reductase induced by oxidative stress in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: genetic characterization and cloning of ahp. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2049–2055. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2049-2055.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Tartaglia L. A., Ames B. N. Transcriptional regulator of oxidative stress-inducible genes: direct activation by oxidation. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):189–194. doi: 10.1126/science.2183352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winder F. G., Collins P. B. Inhibition by isoniazid of synthesis of mycolic acids in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Sep;63(1):41–48. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Garbe T., Young D. Transformation with katG restores isoniazid-sensitivity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates resistant to a range of drug concentrations. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(3):521–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Heym B., Allen B., Young D., Cole S. The catalase-peroxidase gene and isoniazid resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):591–593. doi: 10.1038/358591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



