Abstract
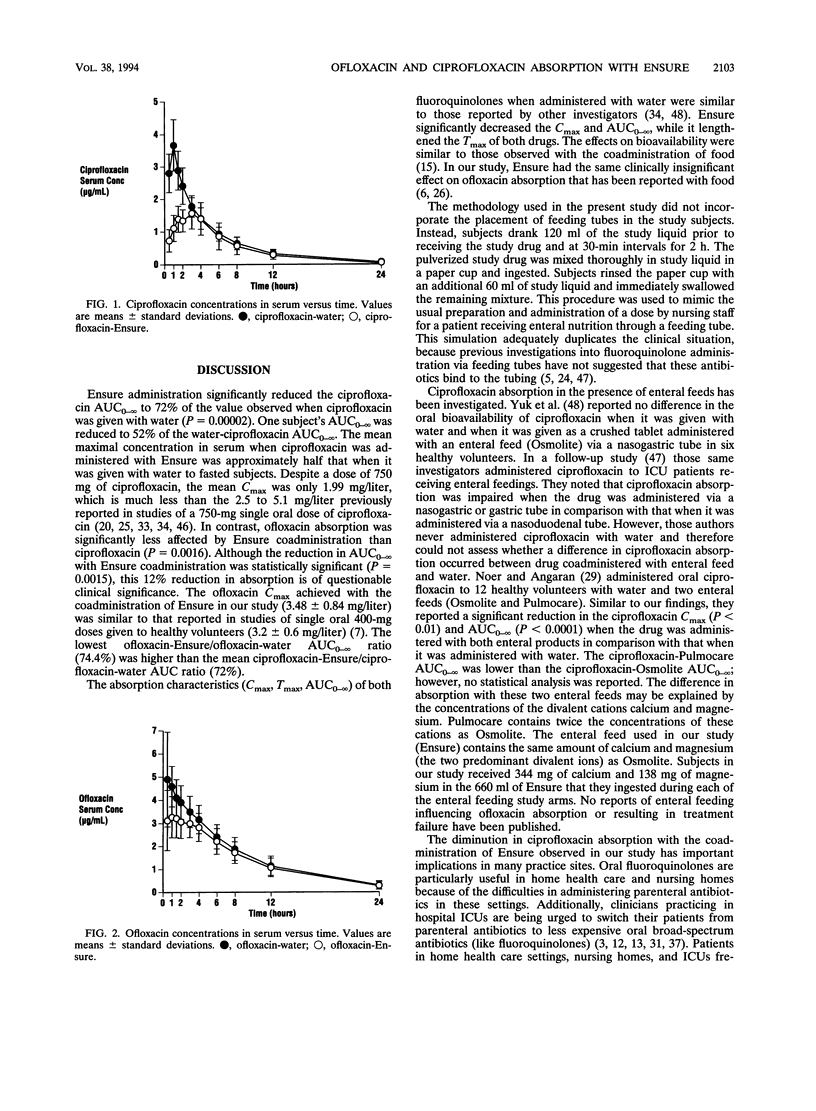
The relative oral bioavailabilities of ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin when they were coadministered with water or an enteral feeding product (Ensure) were assessed in 13 healthy volunteers. The area under the concentration time curve from time zero to infinity and the maximum concentration of drug in serum for both drugs were reduced by Ensure in comparison with those by water (P < 0.01). However, Ensure reduced the percent relative bioavailability of ciprofloxacin (72% +/- 14%; range, 52 to 96%) significantly more than ofloxacin (90% +/- 8.3%; range, 74 to 105%) (P < 0.005). Coadministration of Ensure significantly diminished ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin absorption, but ciprofloxacin absorption was reduced significantly more than ofloxacin absorption.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerele J. O., Okhamafe A. O. Influence of oral co-administered metallic drugs on ofloxacin pharmacokinetics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Jul;28(1):87–94. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balfour J. A., Faulds D. Oral ciprofloxacin: a pharmacoeconomic evaluation of its use in the treatment of serious infections. Pharmacoeconomics. 1993 May;3(5):398–421. doi: 10.2165/00019053-199303050-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druckenbrod R. W., Healy D. P. In vitro delivery of crushed ciprofloxacin through a feeding tube. Ann Pharmacother. 1992 Apr;26(4):494–495. doi: 10.1177/106002809202600409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M. N., Marchbanks C. R., Flor S. C., Beals B. The effect of food or milk on the absorption kinetics of ofloxacin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1991;41(6):569–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00314986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flor S., Guay D. R., Opsahl J. A., Tack K., Matzke G. R. Effects of magnesium-aluminum hydroxide and calcium carbonate antacids on bioavailability of ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2436–2438. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flor S. Pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin. An overview. Am J Med. 1989 Dec 29;87(6C):24S–30S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost R. W., Carlson J. D., Dietz A. J., Jr, Heyd A., Lettieri J. T. Ciprofloxacin pharmacokinetics after a standard or high-fat/high-calcium breakfast. J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;29(10):953–955. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1989.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman G. R., Varga L. L. High-performance liquid chromatographic procedures for the determination of temafloxacin in biological matrices. J Chromatogr. 1991 Jul 17;568(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(91)80353-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasela T. H., Jr, Paladino J. A., Schentag J. J., Huepenbecker D., Rybacki J., Purcell J. B., Fiedler J. B. Clinical and economic impact of oral ciprofloxacin as follow-up to parenteral antibiotics. DICP. 1991 Jul-Aug;25(7-8):857–862. doi: 10.1177/106002809102500724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay D. R. Sequential antimicrobial therapy: a realistic approach to cost containment? Pharmacoeconomics. 1993 May;3(5):341–344. doi: 10.2165/00019053-199303050-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper W. D., Dickinson R. G., Eadie M. J. Effect of food on absorption of lomefloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1797–1799. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffken G., Borner K., Glatzel P. D., Koeppe P., Lode H. Reduced enteral absorption of ciprofloxacin in the presence of antacids. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):345–345. doi: 10.1007/BF02013667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara M., Hasinoff B. B., McKay D. W., Campbell N. R. Clinical and chemical interactions between iron preparations and ciprofloxacin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;31(3):257–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb05526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivistö K. T., Ojala-Karlsson P., Neuvonen P. J. Inhibition of norfloxacin absorption by dairy products. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):489–491. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy A., Borsa F., Humbert G., Bernadet P., Fillastre J. P. The pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin in healthy adult male volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;31(5):629–630. doi: 10.1007/BF00606645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lettieri J. T., Rogge M. C., Kaiser L., Echols R. M., Heller A. H. Pharmacokinetic profiles of ciprofloxacin after single intravenous and oral doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):993–996. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomaestro B. M., Bailie G. R. Effect of staggered dose of calcium on the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):1004–1007. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomaestro B. M., Bailie G. R. Quinolone-cation interactions: a review. DICP. 1991 Nov;25(11):1249–1258. doi: 10.1177/106002809102501115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomaestro B. M., Lesar T. S. Concurrent administration of ciprofloxacin and potentially interacting drugs. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1989 Sep;46(9):1770–1770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubowski T. J., Nightingale C. H., Sweeney K., Quintiliani R. The relative bioavailability of temafloxacin administered through a nasogastric tube with and without enteral feeding. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992;22 (Suppl 1):43–47. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199200221-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Cabarga M., Sánchez Navarro A., Colino Gandarillas C. I., Domínguez-Gil A. Effects of two cations on gastrointestinal absorption of ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Oct;35(10):2102–2105. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.10.2102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J., Kivistö K. T., Lehto P. Interference of dairy products with the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Nov;50(5 Pt 1):498–502. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1991.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J., Kivistö K. T. Milk and yoghurt do not impair the absorption of ofloxacin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;33(3):346–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb04050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix D. E., Watson W. A., Lener M. E., Frost R. W., Krol G., Goldstein H., Lettieri J., Schentag J. J. Effects of aluminum and magnesium antacids and ranitidine on the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Dec;46(6):700–705. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes M., Polk R. E. Norfloxacin and absorption of magnesium-aluminum. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 15;109(2):168–169. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-2-168_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paladino J. A., Sperry H. E., Backes J. M., Gelber J. A., Serrianne D. J., Cumbo T. J., Schentag J. J. Clinical and economic evaluation of oral ciprofloxacin after an abbreviated course of intravenous antibiotics. Am J Med. 1991 Nov;91(5):462–470. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90181-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parpia S. H., Nix D. E., Hejmanowski L. G., Goldstein H. R., Wilton J. H., Schentag J. J. Sucralfate reduces the gastrointestinal absorption of norfloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):99–102. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaisance K. I., Drusano G. L., Forrest A., Bustamante C. I., Standiford H. C. Effect of dose size on bioavailability of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):956–958. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk R. E. Drug-drug interactions with ciprofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones. Am J Med. 1989 Nov 30;87(5A):76S–81S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk R. E., Healy D. P., Sahai J., Drwal L., Racht E. Effect of ferrous sulfate and multivitamins with zinc on absorption of ciprofloxacin in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1841–1844. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers T., Bingham D. H. Clinical and economic effect of ciprofloxacin as an alternative to injectable antimicrobial therapy. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1990 Aug;47(8):1781–1784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preheim L. C., Cuevas T. A., Roccaforte J. S., Mellencamp M. A., Bittner M. J. Ciprofloxacin and antacids. Lancet. 1986 Jul 5;2(8497):48–48. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92596-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahai J., Gallicano K., Oliveras L., Khaliq S., Hawley-Foss N., Garber G. Cations in the didanosine tablet reduce ciprofloxacin bioavailability. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Mar;53(3):292–297. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1993.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahai J., Healy D. P., Stotka J., Polk R. E. The influence of chronic administration of calcium carbonate on the bioavailability of oral ciprofloxacin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;35(3):302–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada J., Shiba K., Oguma T., Miwa H., Yoshimura Y., Nishikawa T., Okabayashi Y., Kitagawa T., Yamamoto S. Effect of antacid on absorption of the quinolone lomefloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1219–1224. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi A. A., Bochner F., Keal J. A., Rolan P. E., Smith M. Effect of food on enoxacin absorption. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):638–639. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Slooten A. D., Nix D. E., Wilton J. H., Love J. H., Spivey J. M., Goldstein H. R. Combined use of ciprofloxacin and sucralfate. DICP. 1991 Jun;25(6):578–582. doi: 10.1177/106002809102500601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verho M., Malerczyk V., Dagrosa E., Korn A. The effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin. Curr Med Res Opin. 1986;10(3):166–171. doi: 10.1185/03007998609110436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. P., Deeter R. G., Swanson K. A., Gross J. S. Crossover assessment of serum bactericidal activity and pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin alone and in combination in healthy elderly volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2352–2358. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuk J. H., Nightingale C. H., Sweeney K. R., Quintiliani R., Lettieri J. T., Frost R. W. Relative bioavailability in healthy volunteers of ciprofloxacin administered through a nasogastric tube with and without enteral feeding. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1118–1120. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuk J. H., Williams T. W., Jr Drug interaction with quinolone antibiotics in intensive care unit patients. Arch Intern Med. 1991 Mar;151(3):619–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


