Abstract
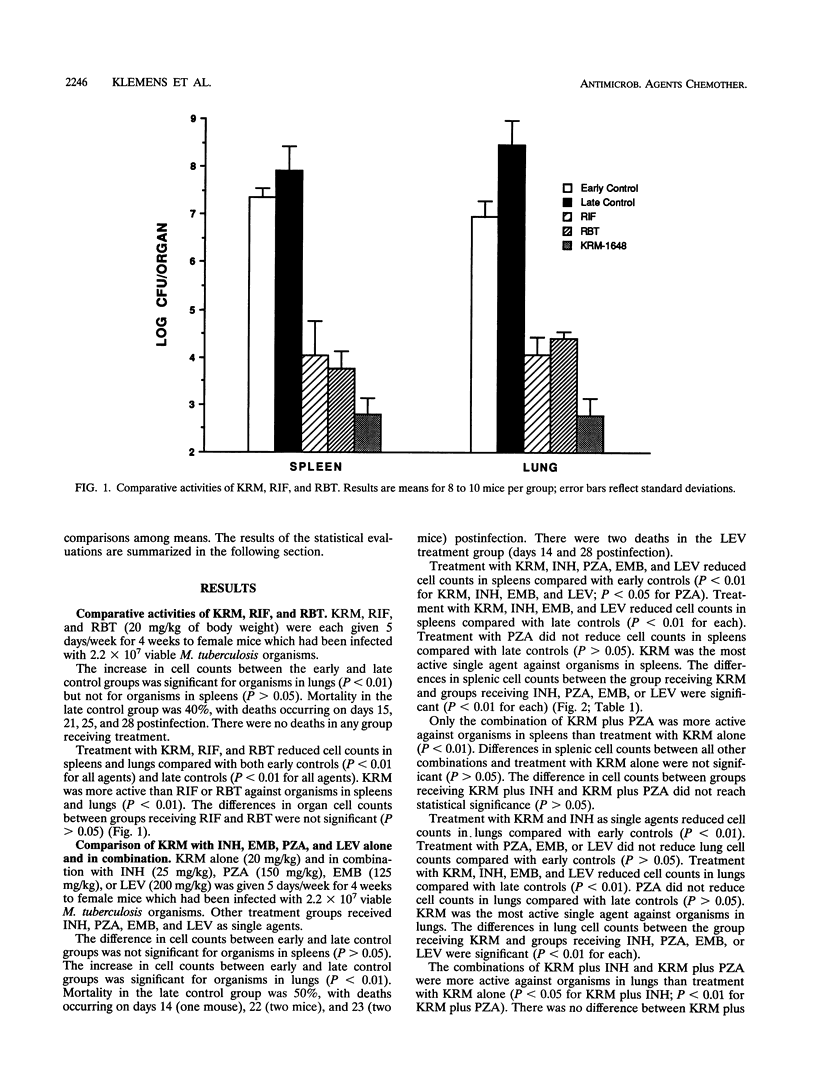
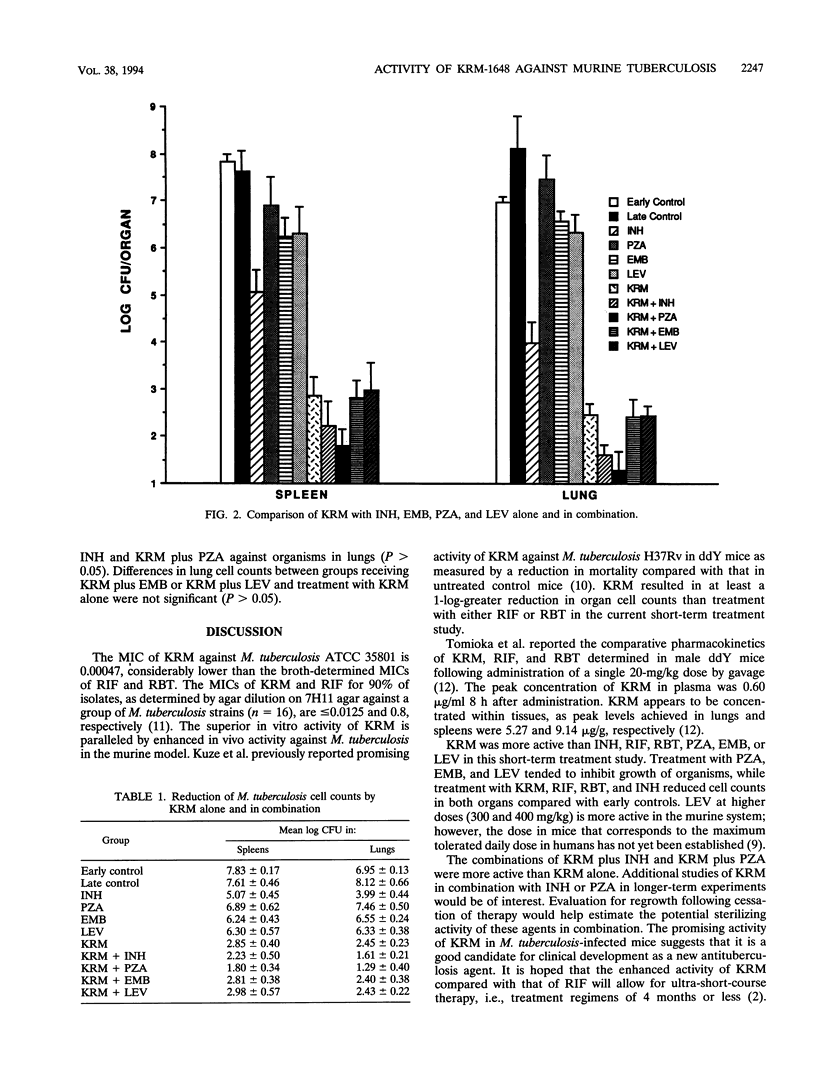
The activity of KRM-1648 was evaluated in a murine model of tuberculosis. Approximately 10(7) viable Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATCC 35801 organisms were given intravenously to 4-week-old female outbred mice. Treatment was started 1 week postinfection and given by gavage for 4 weeks. Viable-cell counts were determined from homogenates of spleen and lung tissues. The activity of KRM-1648 was compared with those of rifampin and rifabutin at 20 mg/kg of body weight. KRM-1648 was more active than either rifampin or rifabutin against organisms in spleens and lungs. KRM-1648 alone and in combination with either isoniazid, ethambutol, pyrazinamide, or levofloxacin was evaluated. Other treatment groups received isoniazid, ethambutol, pyrazinamide, or levofloxacin as single agents. KRM-1648 was the most active single agent evaluated. KRM-1648-pyrazinamide and KRM-1648-isoniazid were the most active combinations. These combinations were more active than KRM-1648 alone. The promising activity of KRM-1648 in M. tuberculosis-infected mice suggests that it is a good candidate for clinical development as a new antituberculosis agent.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cynamon M. H. Comparative in vitro activities of MDL 473, rifampin, and ansamycin against Mycobacterium intracellulare. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):440–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori M., Saito H., Sato K., Tomioka H., Setogawa T., Hidaka T. Therapeutic efficacy of the benzoxazinorifamycin KRM-1648 against experimental Mycobacterium avium infection induced in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):722–728. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoh M., Tsutsumi S., Yamane T., Yamashita K., Hosoe K., Hidaka T. Bactericidal action at low doses of a new rifamycin derivative, 3'-hydroxy-5'-(4-isobutyl-1-piperazinyl) benzoxazinorifamycin (KRM-1648) on Mycobacterium leprae inoculated into footpads of nude mice. Lepr Rev. 1992 Dec;63(4):319–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemens S. P., Grossi M. A., Cynamon M. H. Comparative in vivo activities of rifabutin and rifapentine against Mycobacterium avium complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Feb;38(2):234–237. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemens S. P., Sharpe C. A., Rogge M. C., Cynamon M. H. Activity of levofloxacin in a murine model of tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Jul;38(7):1476–1479. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.7.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuze F., Yamamoto T., Amitani R., Suzuki K. [In vivo activities of new rifamycin derivatives against mycobacteria]. Kekkaku. 1991 Jan;66(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tomioka H., Sato K., Emori M., Yamane T., Yamashita K., Hosoe K., Hidaka T. In vitro antimycobacterial activities of newly synthesized benzoxazinorifamycins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):542–547. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka H., Saito H., Sato K., Yamane T., Yamashita K., Hosoe K., Fujii K., Hidaka T. Chemotherapeutic efficacy of a newly synthesized benzoxazinorifamycin, KRM-1648, against Mycobacterium avium complex infection induced in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):387–393. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane T., Hashizume T., Yamashita K., Konishi E., Hosoe K., Hidaka T., Watanabe K., Kawaharada H., Yamamoto T., Kuze F. Synthesis and biological activity of 3'-hydroxy-5'-aminobenzoxazinorifamycin derivatives. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1993 Jan;41(1):148–155. doi: 10.1248/cpb.41.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


