Abstract
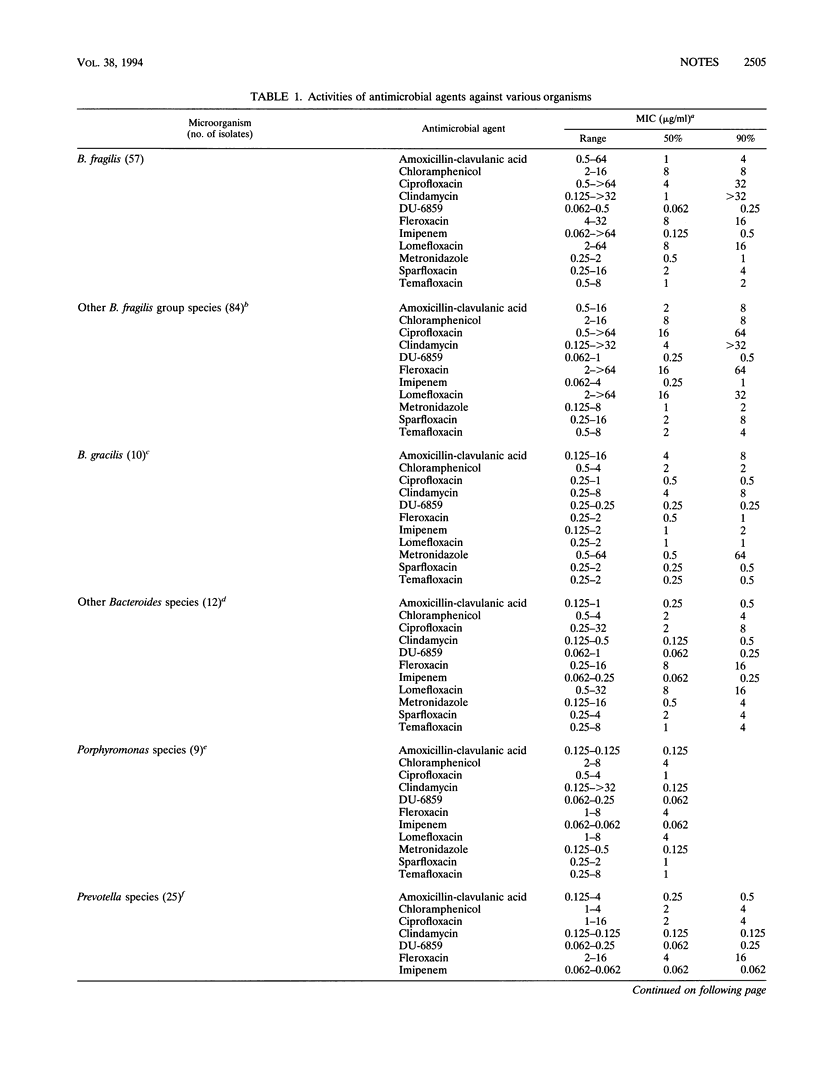
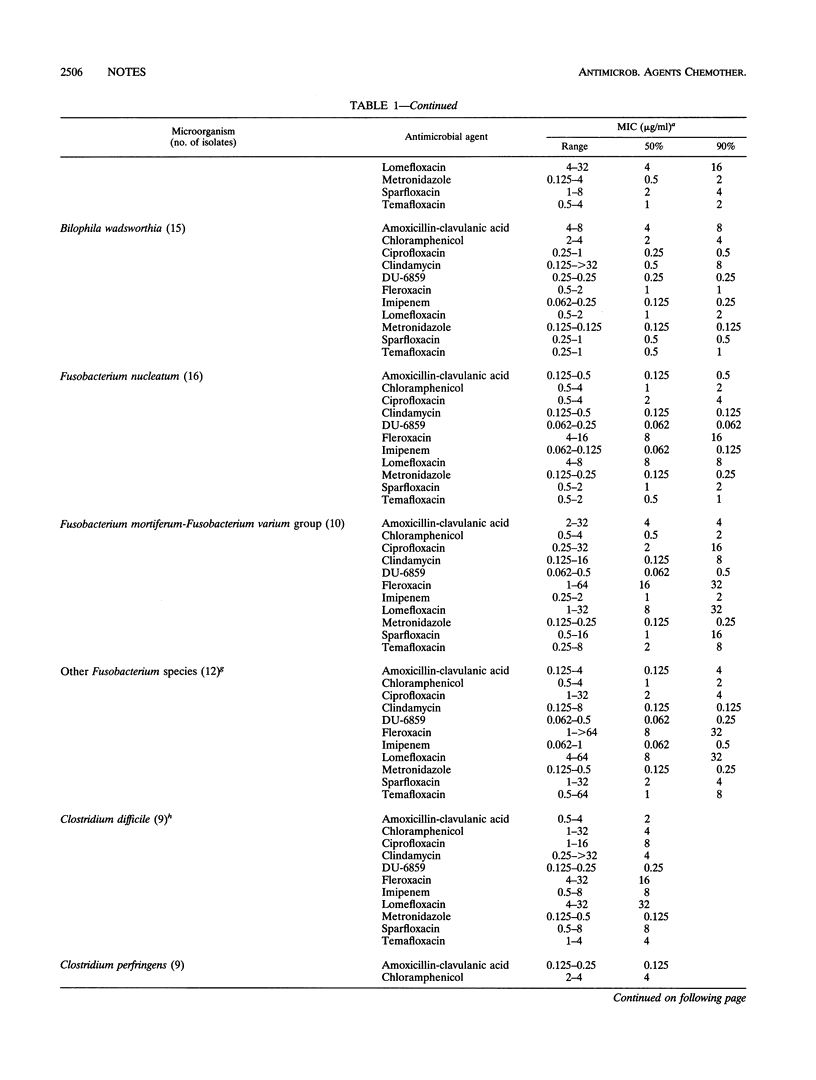
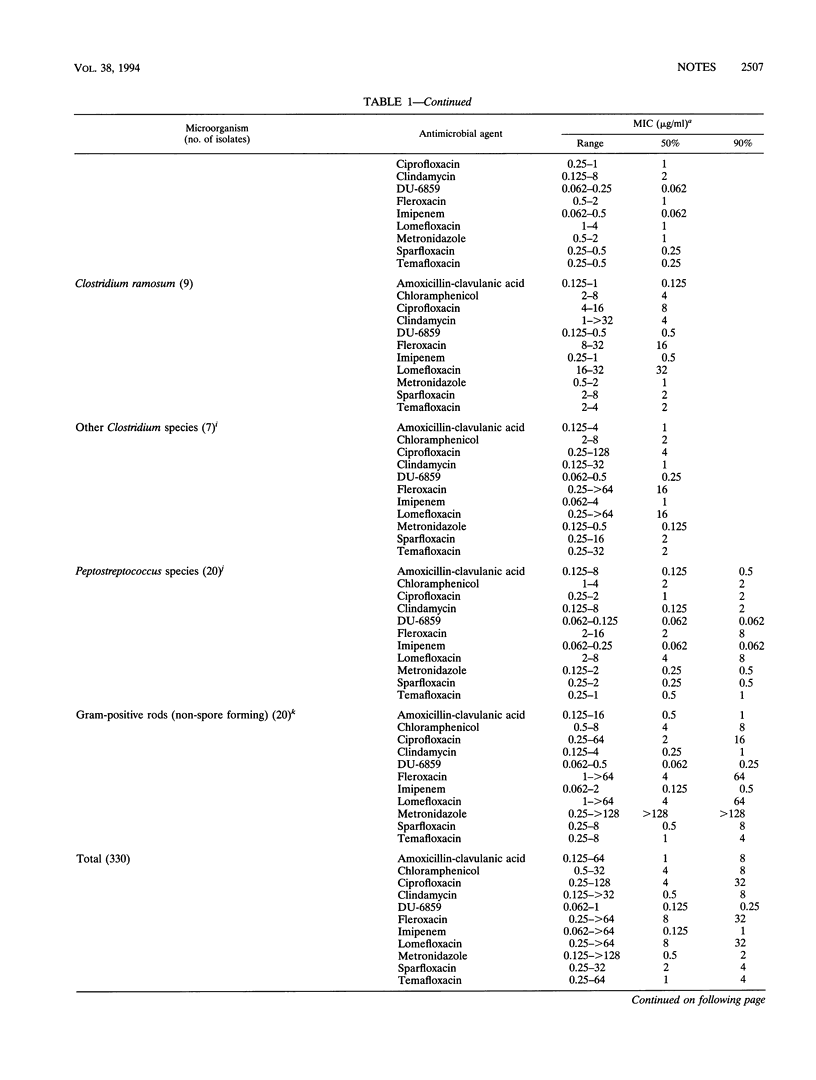
The activity of a new quinolone agent, DU-6859a, against 330 strains of anaerobic bacteria was determined by using the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards-approved Wadsworth brucella laked blood agar method; the activity of DU-6859a was compared with those of amoxicillin-clavulanate (2:1), chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, clindamycin, fleroxacin, imipenem, lomefloxacin, metronidazole, sparfloxacin, and temafloxacin. DU-6859a and chloramphenicol inhibited all of the isolates at concentrations of 1 and 16 micrograms/ml, respectively; amoxicillin-clavulanate, imipenem, and metronidazole inhibited > or = 94% of the isolates at their respective breakpoints (8, 8, and 16 micrograms/ml). MICs of DU-6859a at which 90% of the strains were susceptible were 1 to 5 twofold dilutions lower than those of the other quinolones for every group of organisms. MICs of DU-6859a at which 90% of the strains were susceptible (total numbers of strains tested are in parentheses) were < or = 0.25 micrograms/ml for Bacteroides fragilis (57), other B. fragilis group species (84), Bilophila wadsworthia (15), Clostridium species (27) (including C. difficile, C. perfringens, and C. ramosum), Fusobacterium nucleatum (16), Fusobacterium mortiferum-F. varium group species (10), Peptostreptococcus species (20), non-spore-forming gram-positive rods (20), and Prevotella species (25).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Marshall S. A., Jones R. N. In vitro activity of DU-6859a, a new fluorocyclopropyl quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Dec;37(12):2747–2753. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.12.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S. A., Jones R. N., Murray P. R., Washington J. A., Allen S. D., Gerlach E. H., Erwin M. E. In-vitro comparison of DU-6859a, a novel fluoroquinolone, with other quinolones and oral cephalosporins tested against 5086 recent clinical isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 Dec;32(6):877–884. doi: 10.1093/jac/32.6.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Hoshino K., Tanaka M., Hayakawa I., Osada Y. Antimicrobial activity of DU-6859, a new potent fluoroquinolone, against clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jul;36(7):1491–1498. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.7.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler H. M., Molitoris E., Finegold S. M. In vitro activities of three of the newer quinolones against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jan;36(1):239–243. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.1.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler H. M., Molitoris E., Finegold S. M. In vitro activity of Bay Y3118 against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2509–2513. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.11.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


