Abstract
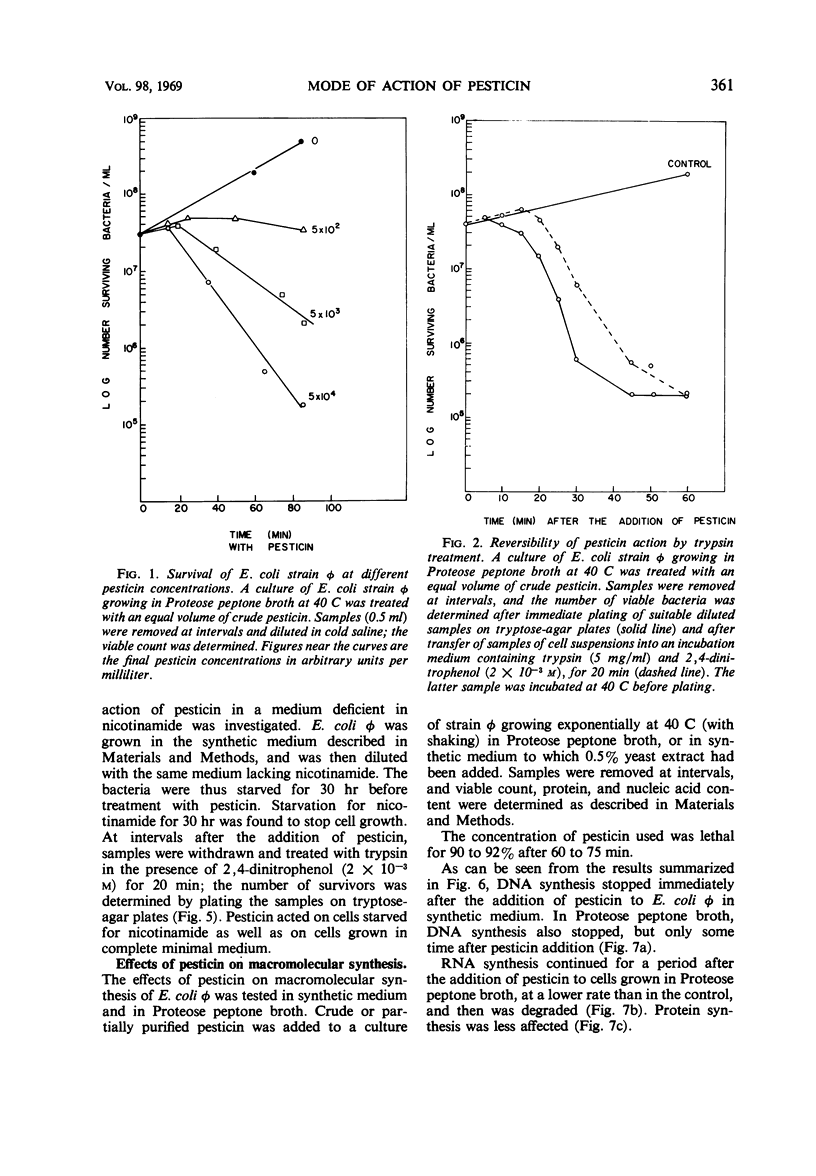
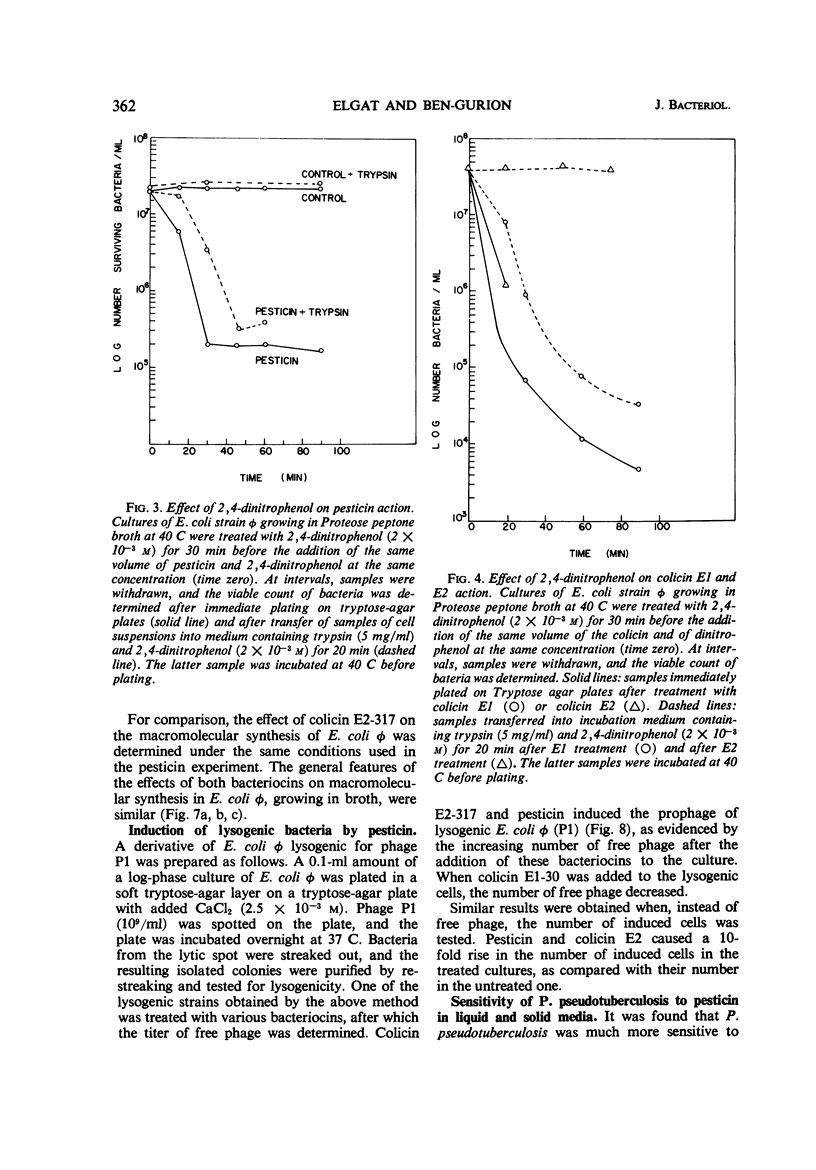
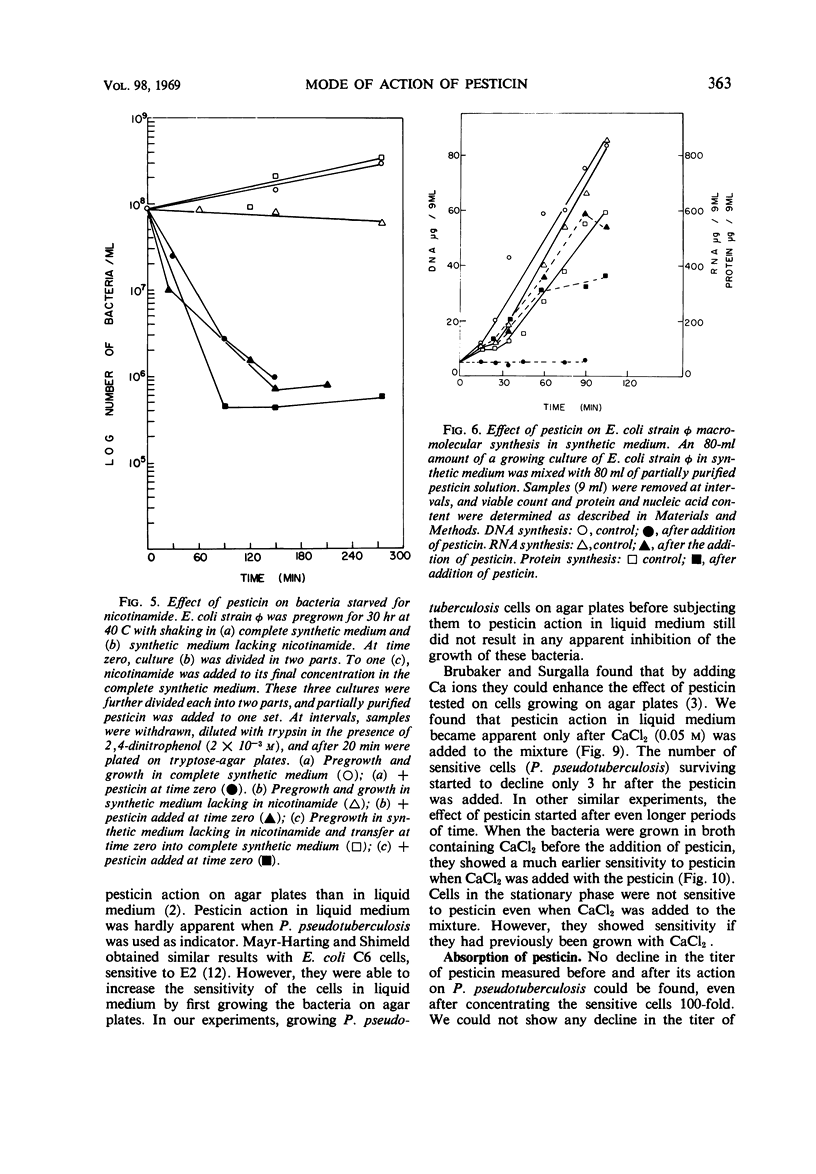
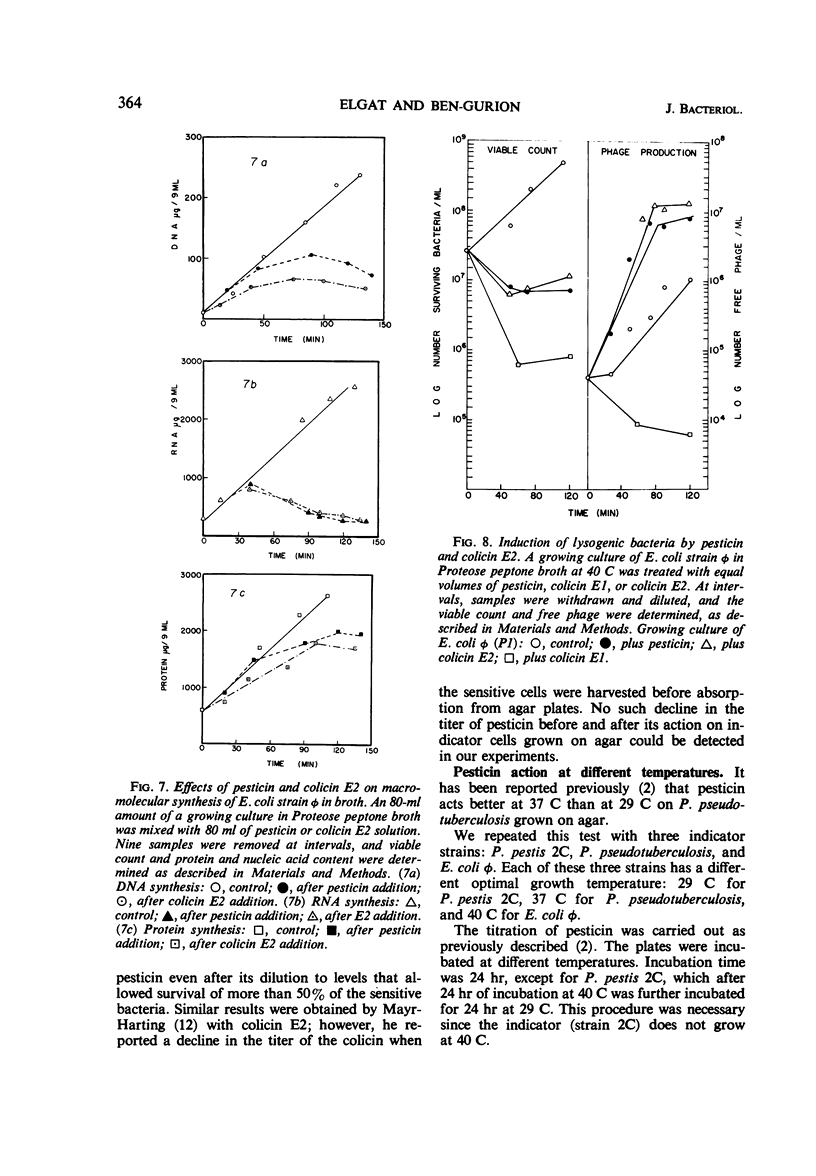
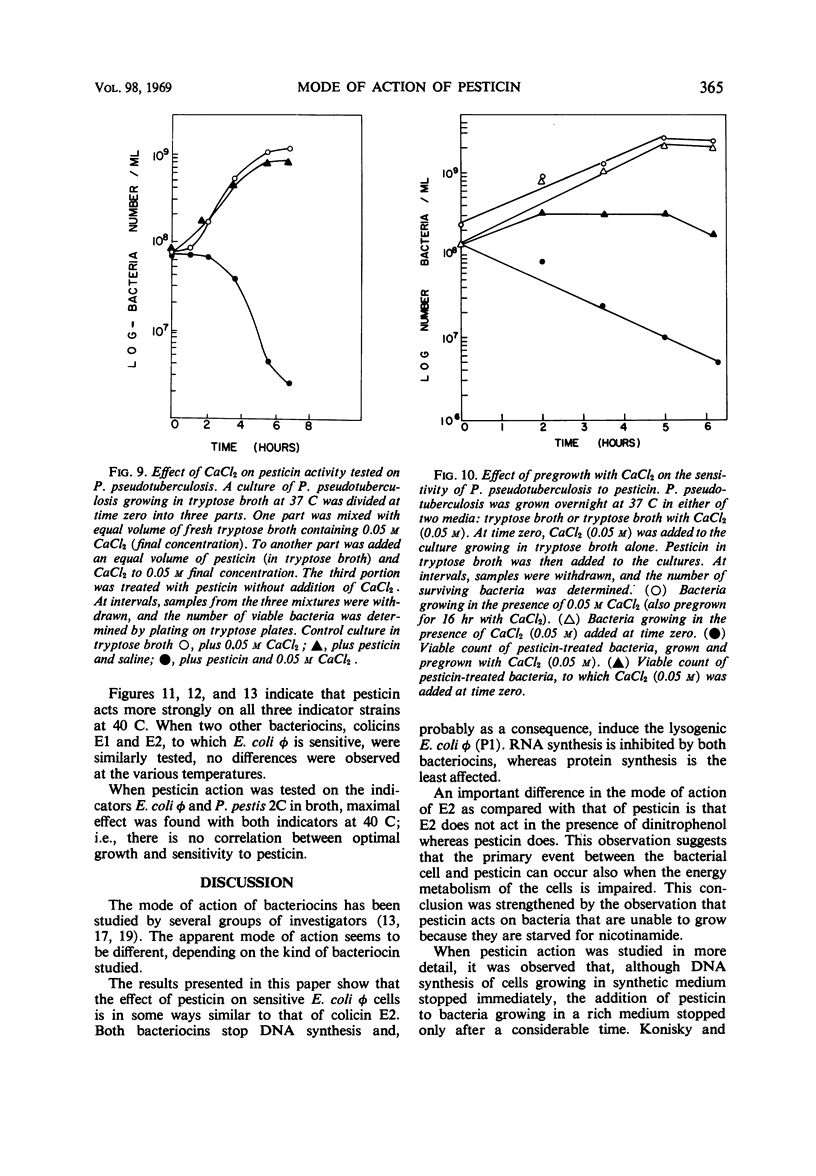
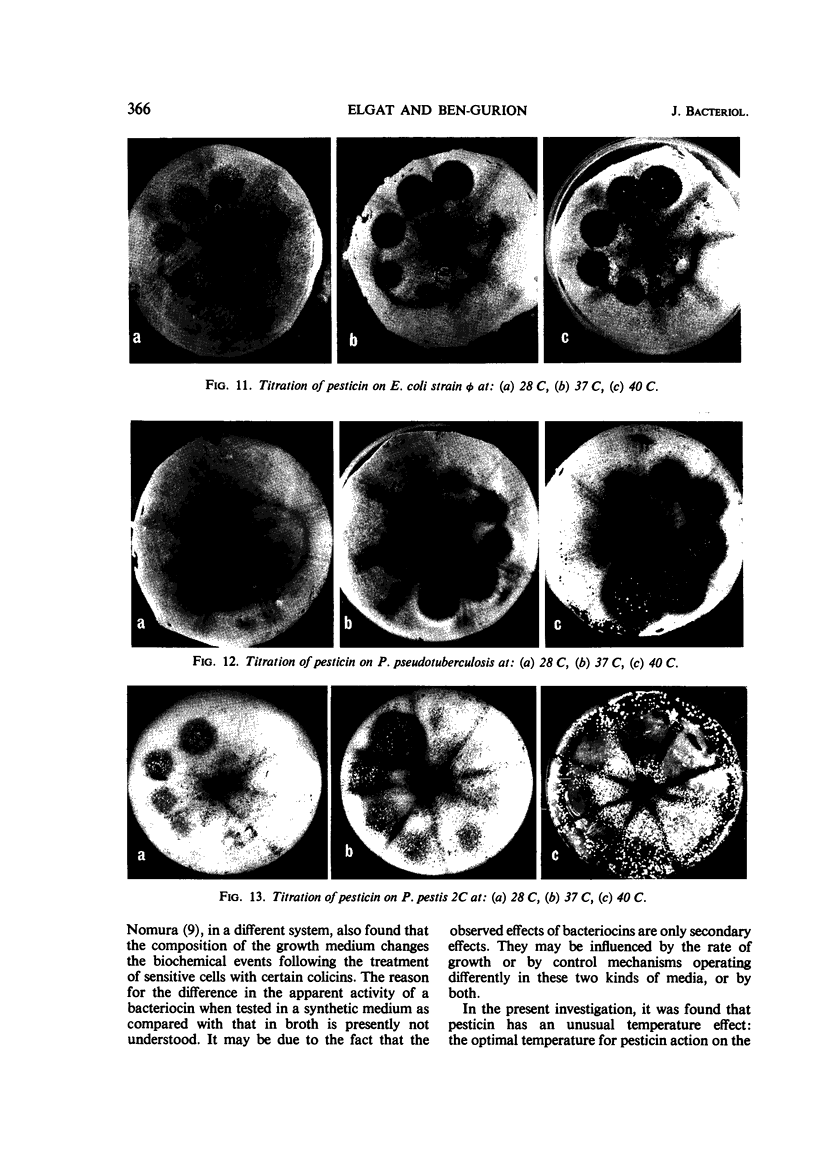
The mode of action of pesticin, a bacteriocin produced by many strains of Pasturella pestis, was studied. Pesticin action on macromolecular synthesis of a sensitive strain of Escherichia coli, strain φ, was found to have features similar to those of colicin E2-317 acting on the same strain. After exposure to pesticin, deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis was arrested and ribonucleic acid was degraded, but little effect was observed on protein synthesis. Pesticin, like colicin E2-317, induced lysogenic E. coli φ (P1), but, unlike the colicin, was active in the presence of dinitrophenol. Trypsin was found to reverse pesticin action up to 15 min after its addition at 40 C to E. coli φ. Pesticin action was studied on three sensitive bacterial strains, P. pestis 2C, P. pseudotuberculosis, and E. coli strain φ, which vary widely in their optimal growth temperature. P. pestis grows best at 29 C, P. pseudotuberculosis at 37 C, and E. coli φ at 40 C. It was found that pesticin action on all three strains was optimal at 40 C. Whereas the titer of pesticin was the same on all three strains when determined on agar, E. coli φ was the most sensitive to pesticin action in broth. No action of pesticin in broth on P. pseudotuberculosis was observed unless Ca ions were added. The effect was not immediate; that is, the cells had to be grown in a medium containing Ca++ before they displayed sensitivity to pesticin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEN-GURION R., HERTMAN I. Bacteriocin-like material produced by Pasteurella pestis. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):289–297. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUBAKER R. R., SURGALLA M. J. Pesticins. I. Pesticinbacterium interrelationships, and environmental factors influencing activity. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:940–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.940-949.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUBAKER R. R., SURGALLA M. J. Pesticins. II. Production of pesticin I and II. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84:539–545. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.539-545.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins and colicinogenic factors. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1958;12:104–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. [Study of the method of fixation of colicins and pyocins on sensitive bacteria]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1960 Oct 24;251:1840–1842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTMAN I., BEN-GURION R. A study on pesticin biosynthesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:135–143. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. II. Specific alteration of Escherichia coli ribosomes induced by colicin E3 in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):181–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M., NAKAMURA M. Reversibility of inhibition of nucleic acids and protein synthesis by colicin K. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 4;7:306–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVES P. THE BACTERIOCINS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:24–45. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.24-45.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS B. L., REEVES P. R. Some observations on the mode of action of colicin F. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Apr 23;11:140–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]