Abstract
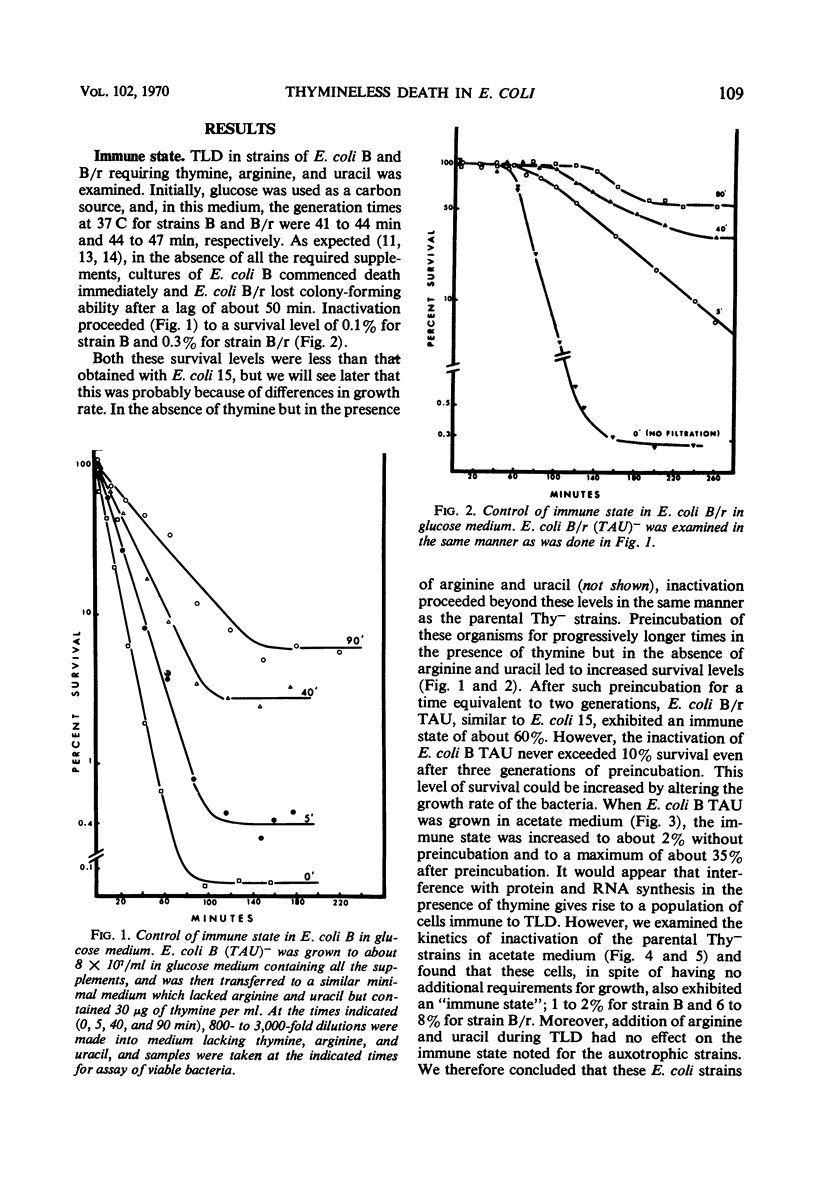
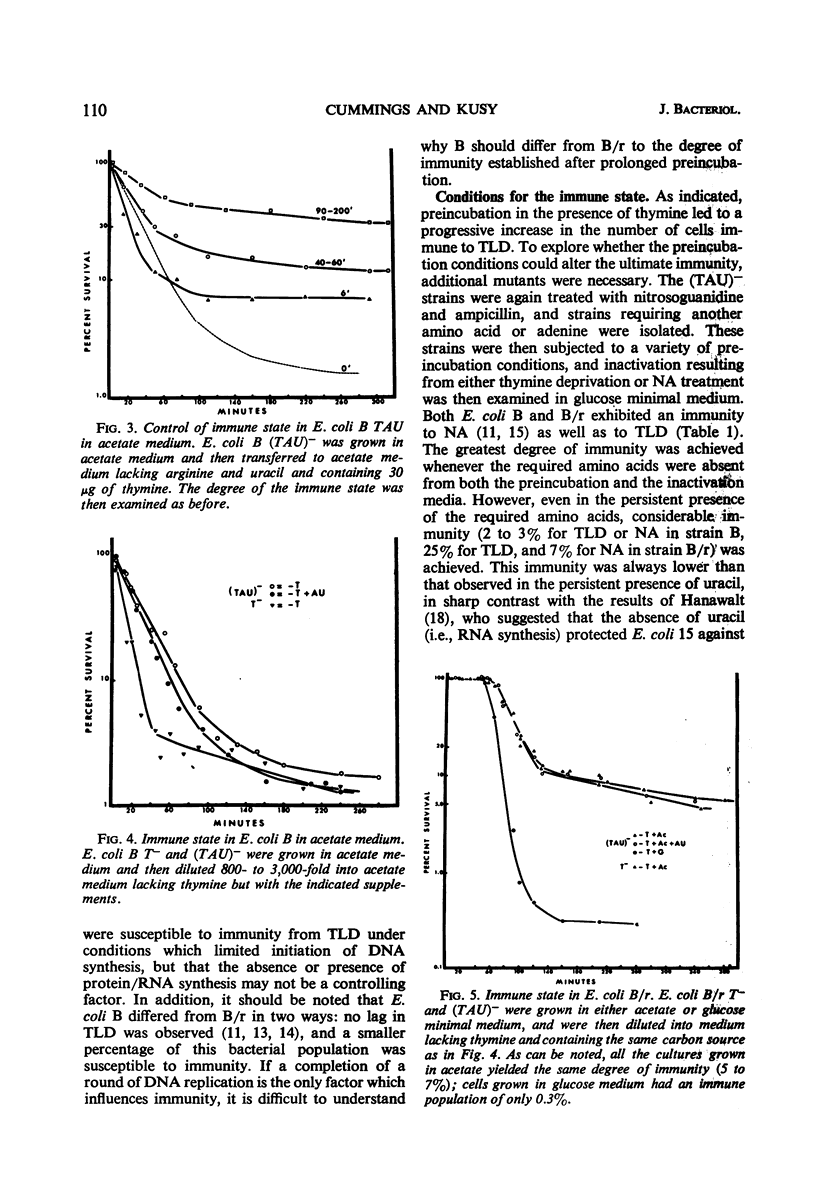
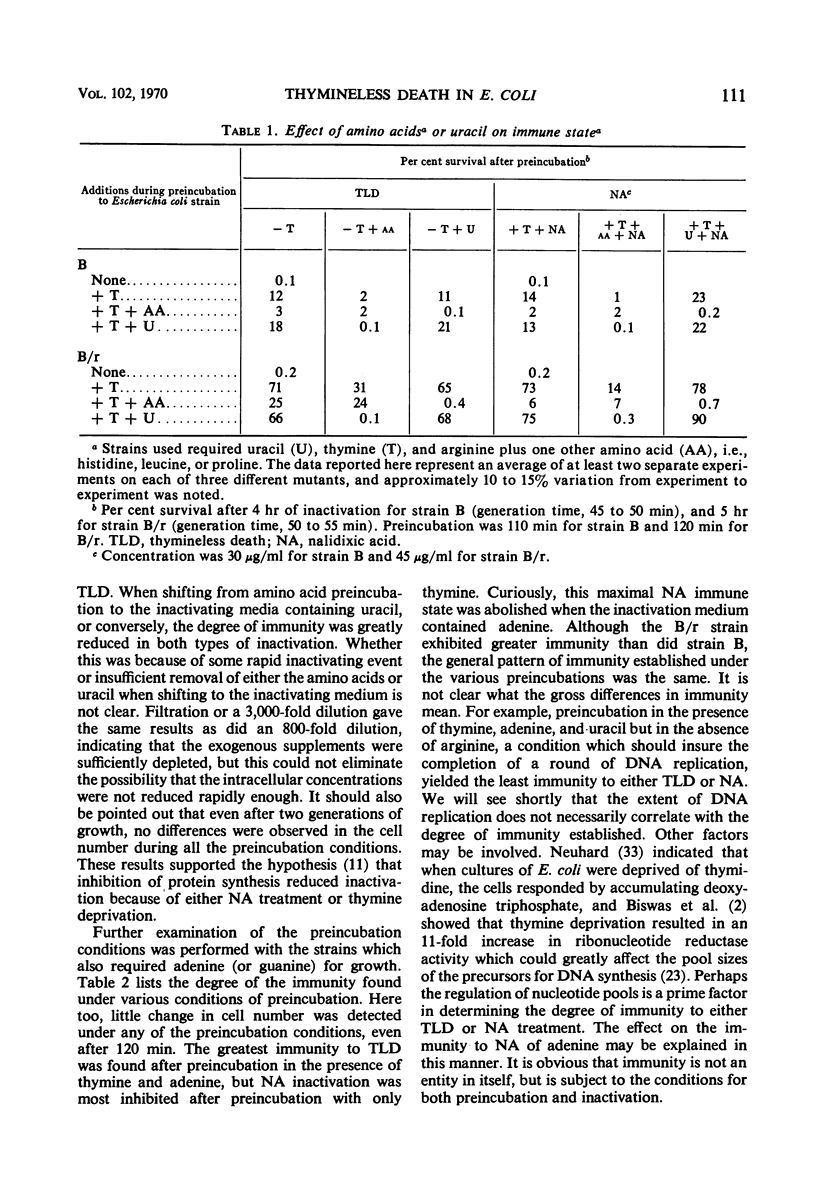
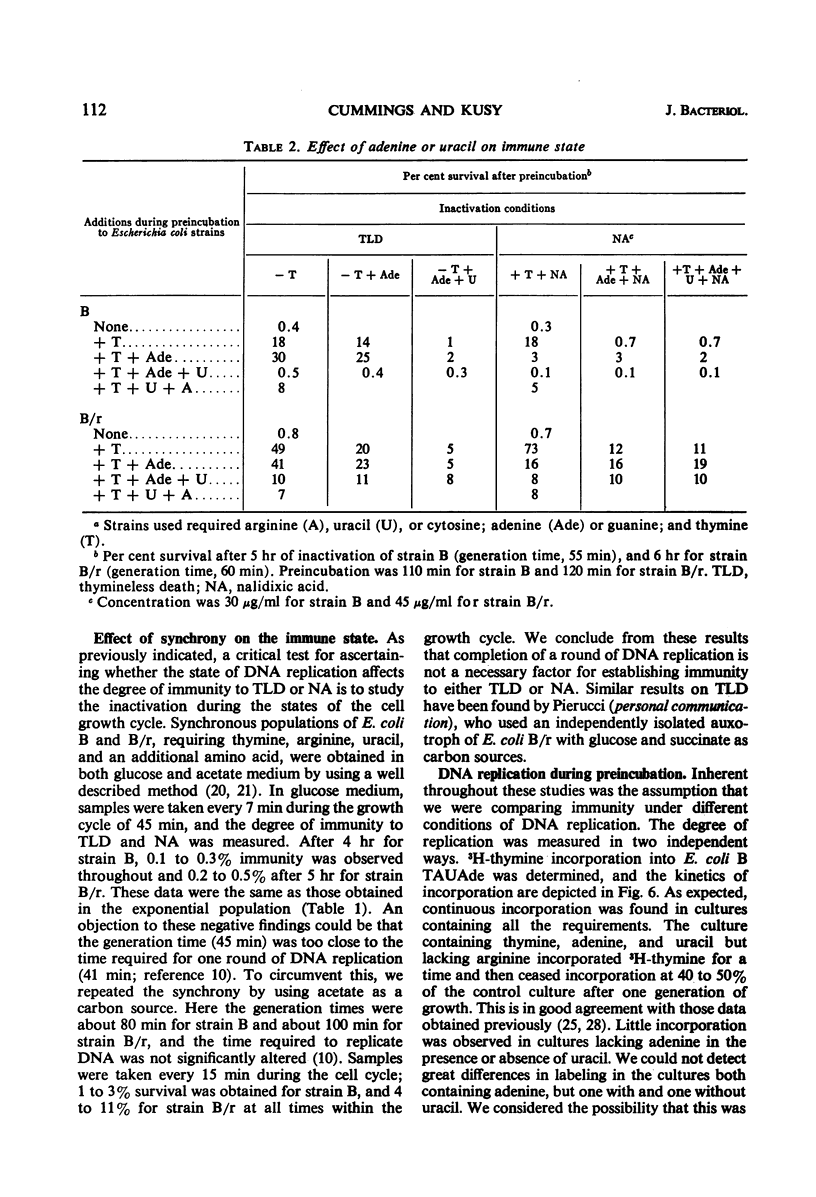
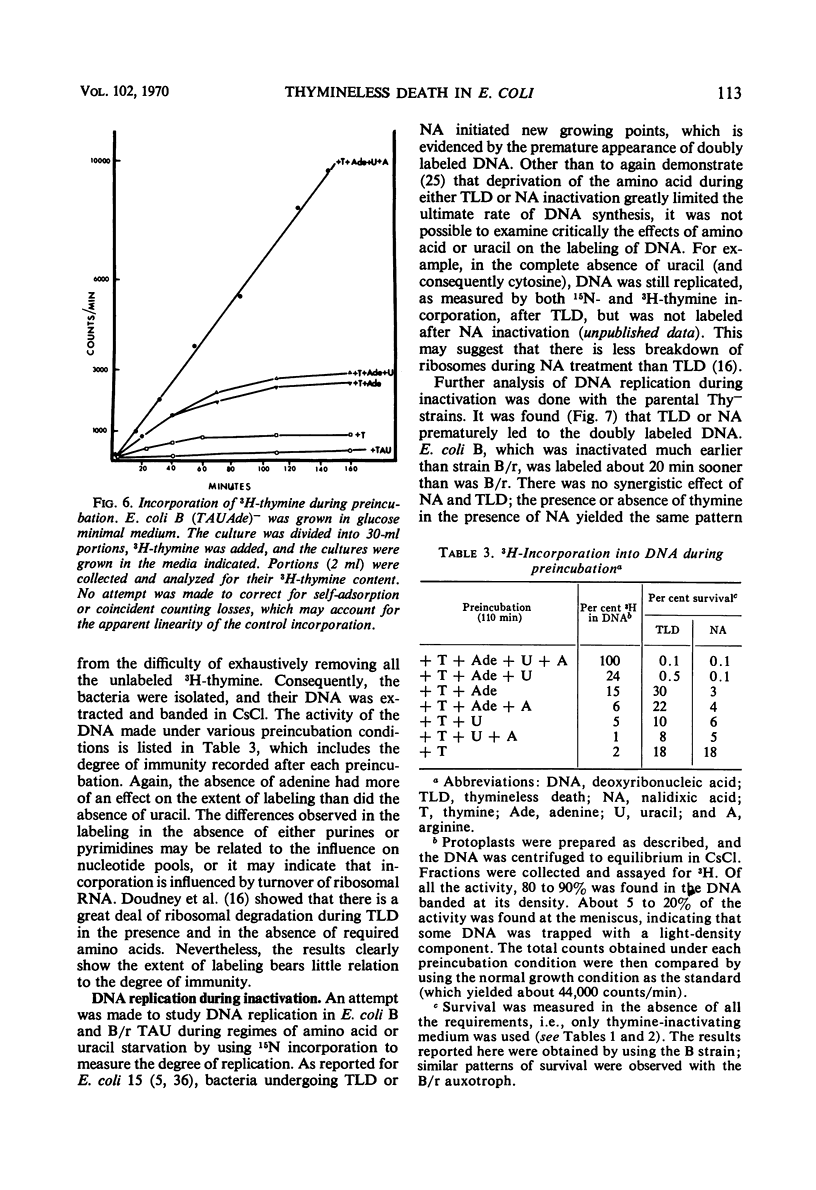
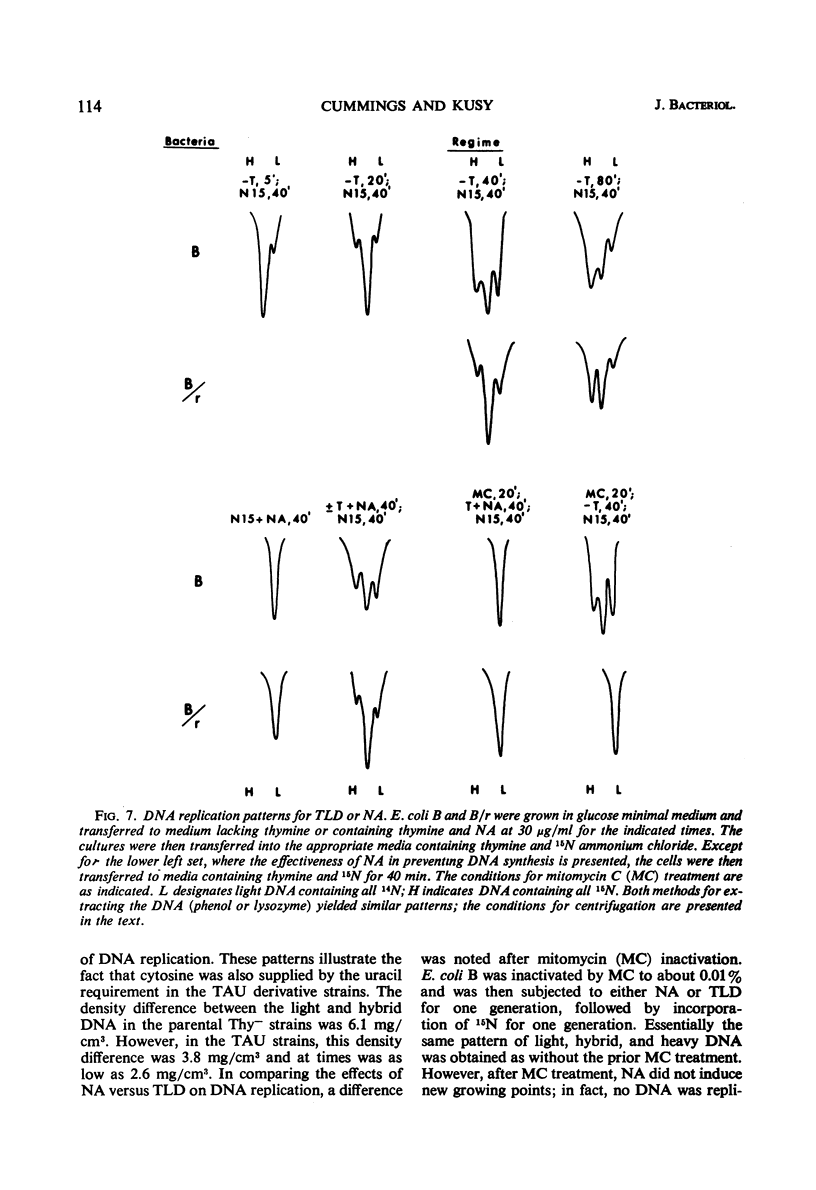
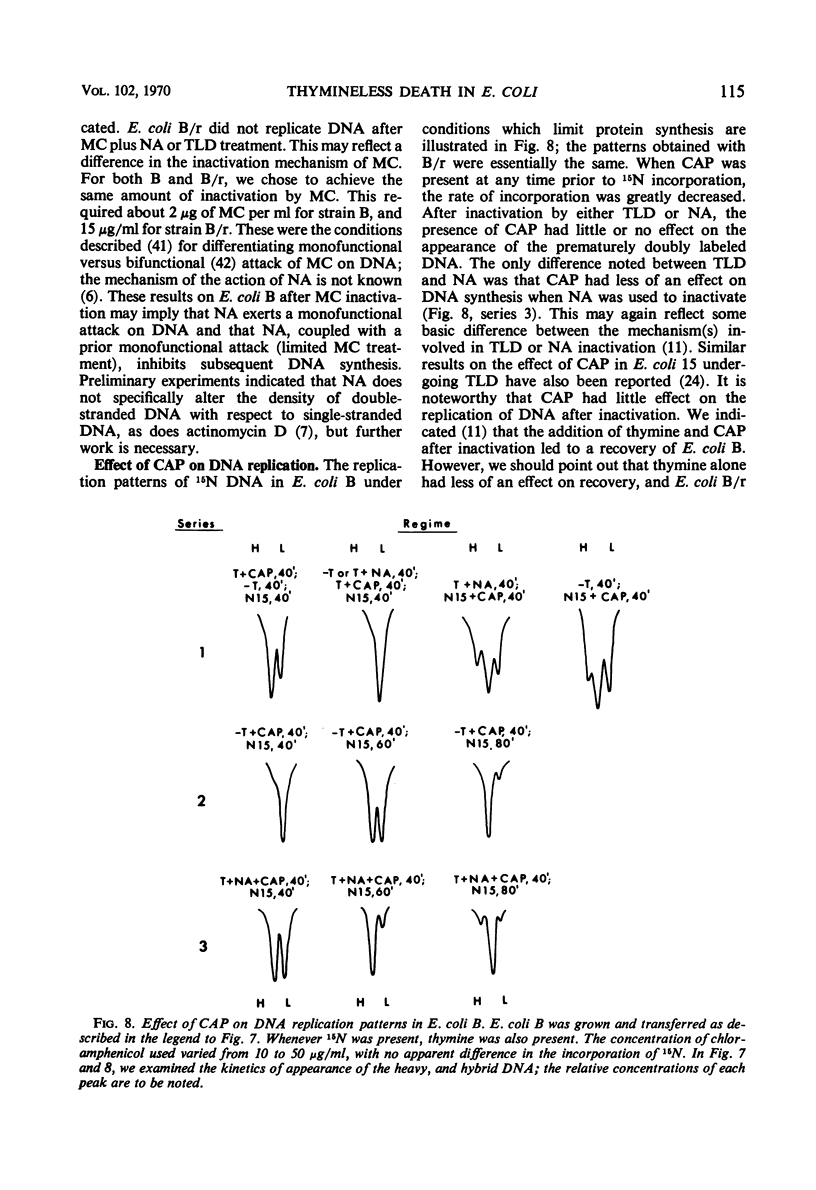
Thymineless death (TLD) and nalidixic acid (NA) inactivation were studied in multiple auxotrophic strains of Escherichia coli B and B/r. As expected, it was found that both E. coli B and B/r exhibited an “immune state,” i.e., a fraction of the population survived inactivation to both TLD and NA. With glucose as a carbon source in minimal medium, 0.1 to 0.3% of strain B and 0.2 to 0.5% of strain B/r survived inactivation; with acetate as the carbon source, the surviving fractions were increased to 1 to 2% and 5 to 7%, respectively. These immune fractions could be increased in magnitude by preincubation in minimal media containing thymine. Systematic analysis of the particular supplements necessary for the immune state indicated that the absence of the required amino acids was essential for the maximal expression of immunity. However, immunity was not abolished in acetate medium even in the presence of the required supplements. Further studies on the replication of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) during preincubation indicated that the degree of immunity did not necessarily correlate with the completion of a round of DNA replication. This finding was supported by examining the immune state in synchronous populations. In both glucose and acetate medium, there was no significant change in the degree of immunity to inactivation within the cell cycles of E. coli B and B/r. We concluded that some other event, possibly inhibition of protein synthesis, was necessary in determining the degree of the immune state. DNA replication was investigated after TLD and NA inactivation, and, as expected, it was found that both events led to premature initiation of replication. The only differences observed in the effects of these two processes on DNA synthesis were the following. (i) NA-induced replication was less sensitive to chloramphenicol than was TLD. (ii) TLD-induced replication was unaffected by pretreatment of the cells with mitomycin C, but this pretreatment prevented the replication of DNA after NA treatment. It was suggested that the mechanism of action of NA could involve a monofunctional attack on the DNA.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOREK E., RYAN A., ROCKENBACH J. Nucleic acid metabolism in relation to the lysogenic phenomenon. J Bacteriol. 1955 Apr;69(4):460–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.4.460-467.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas C., Hardy J., Beck W. S. Release of repressor control of ribonucleotide reductase by thymine starvation. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3631–3640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. V., Cook T. M., Goss W. A. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid on Escherichia coli. Vi. Cell-free studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):230–236. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.230-236.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. V., Goss W. A., Cook T. M. Induction of excessive deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli by nalidixic acid. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1664–1671. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1664-1671.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Reich E., Ward D. C., Goldberg I. H. The interaction of actinomycin with DNA: requirement for the 2-amino group of purines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1036–1042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S., Barner H. D. STUDIES ON UNBALANCED GROWTH IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1954 Oct;40(10):885–893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.10.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook T. M., Deitz W. H., Goss W. A. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid on Escherichia coli. IV. Effects on the stability of cellular constituents. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):774–779. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.774-779.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S., Helmstetter C. E. Chromosome replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):519–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J., Kusy A. R. Thymineless death in Escherichia coli: inactivation and recovery. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):558–566. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.558-566.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J., Mondale L. Density-gradient banding of denatured deoxyribonucleic acid in cesium sulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 13;120(3):448–453. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J., Mondale L. Thymineless death in Escherichia coli: strain specificity. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1917–1924. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1917-1924.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J., Taylor A. L. Thymineless death and its relation to UV sensitivity in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):171–176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitz W. H., Cook T. M., Goss W. A. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid on Escherichia coli. 3. Conditions required for lethality. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):768–773. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.768-773.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doudney C. O., White B. F., Ferguson M. J. Degradation of ribosomes and ribonucleic acid with bacteria starved for thymine and amino acids. Curr Mod Biol. 1967 May;1(2):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(67)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAMPTON E. W., BRINKLEY B. R. EVIDENCE OF LYSOGENY IN DERIVATIVES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:446–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.446-452.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAWALT P. C. Involvement of synthesis of RNA in thymineless death. Nature. 1963 Apr 20;198:286–286. doi: 10.1038/198286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAWALT P. C., RAY D. S. ISOLATION OF THE GROWING POINT IN THE BACTERIAL CHROMOSOME. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:125–132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMSTETTER C. E., CUMMINGS D. J. AN IMPROVED METHOD FOR THE SELECTION OF BACTERIAL CELLS AT DIVISION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 16;82:608–610. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90453-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMSTETTER C. E., CUMMINGS D. J. BACTERIAL SYNCHRONIZATION BY SELECTION OF CELLS AT DIVISION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:767–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor G. J., Deering R. A. Effect of nalidixic acid and hydroxyurea on division ability of Escherichia coli fil+ and lon- strains. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):520–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.520-530.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlström O., Larsson A. Significance of ribonucleotide reduction in the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Dec;3(2):164–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARK C., LARK K. G. EVIDENCE FOR TWO DISTINCT ASPECTS OF THE MECHANISM REGULATING CHROMOSOME REPLICATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:120–136. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARK K. G., REPKO T., HOFFMAN E. J. THE EFFECT OF AMINO ACID DEPRIVATION ON SUBSEQUENT DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID REPLICATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 17;76:9–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Forchhammer J. Evidence for reduced breakdown of messenger RNA during blocked transcription or translation in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 14;43(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzati D. Effect of thymine starvation on messenger ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1435–1446. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1435-1446.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAALOE O., HANAWALT P. C. Thymine deficiency and the normal DNA replication cycle. I. J Mol Biol. 1961 Apr;3:144–155. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., GREENBERG J. A new chemical mutagen for bacteria, 1-methyl-3-nitro-1-nitrosoguanidine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Dec;3:575–577. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennigmann H. D. Electron microscopy of the anti-bacterial agent produced by Escherichia coli 15. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):151–154. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M., OKAMOTO K., ASANO K. RNA metabolism in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4. Inhibition of host ribosomal and soluble RNA synthesis by phage and effect of chloromycetin. J Mol Biol. 1962 May;4:376–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhard J. Studies on the acid-soluble nucleotide pool in thymine-requiring mutants of Escherichia coli during thymine starvation. 3. On the regulation of the deoxyadenosine triphosphate and deoxycytidine triphosphate pools of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 24;129(1):104–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAZAKI R., OKAZAKIT, STROMINGER J. L., MICHELSON A. M. Thymidine diphosphate 4-keto-6-deoxy-d-glucose, an intermediate in thymidine diphosphate L-rhamnose synthesis in Escherichia coli strains. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3014–3026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRITCHARD R. H., LARK K. G. INDUCTION OF REPLICATION BY THYMINE STARVATION AT THE CHROMOSOME ORIGIN IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Aug;9:288–307. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REPASKE R. Lysis of gram-negative organisms and the role of versene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Nov;30(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S., BRENNER S. A genetic locus for the regulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Dec 15;47:2005–2014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.12.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZYBALSKI W., IYER V. N. CROSSLINKING OF DNA BY ENZYMATICALLY OR CHEMICALLY ACTIVATED MITOMYCINS AND PORFIROMYCINS, BIFUNCTIONALLY "ALKYLATING" ANTIBIOTICS. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:946–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaiberger G. E., Giegel J., Sallman B. Functional activity of DNA and DNA polymerase during thymine starvation of Escherichia coli 15T. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jul 10;28(1):30–37. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90401-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicard N., Simonnet G., Astrachan L. Base composition of rapidly-labelled RNA in E. coli undergoing thymineless death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Mar 9;26(5):532–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kilgore W. W. Effects of mitomycin C on macromolecular synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):675–682. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.675-682.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Revised linkage map of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):332–353. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.332-353.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


