Abstract
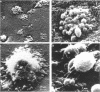
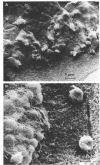
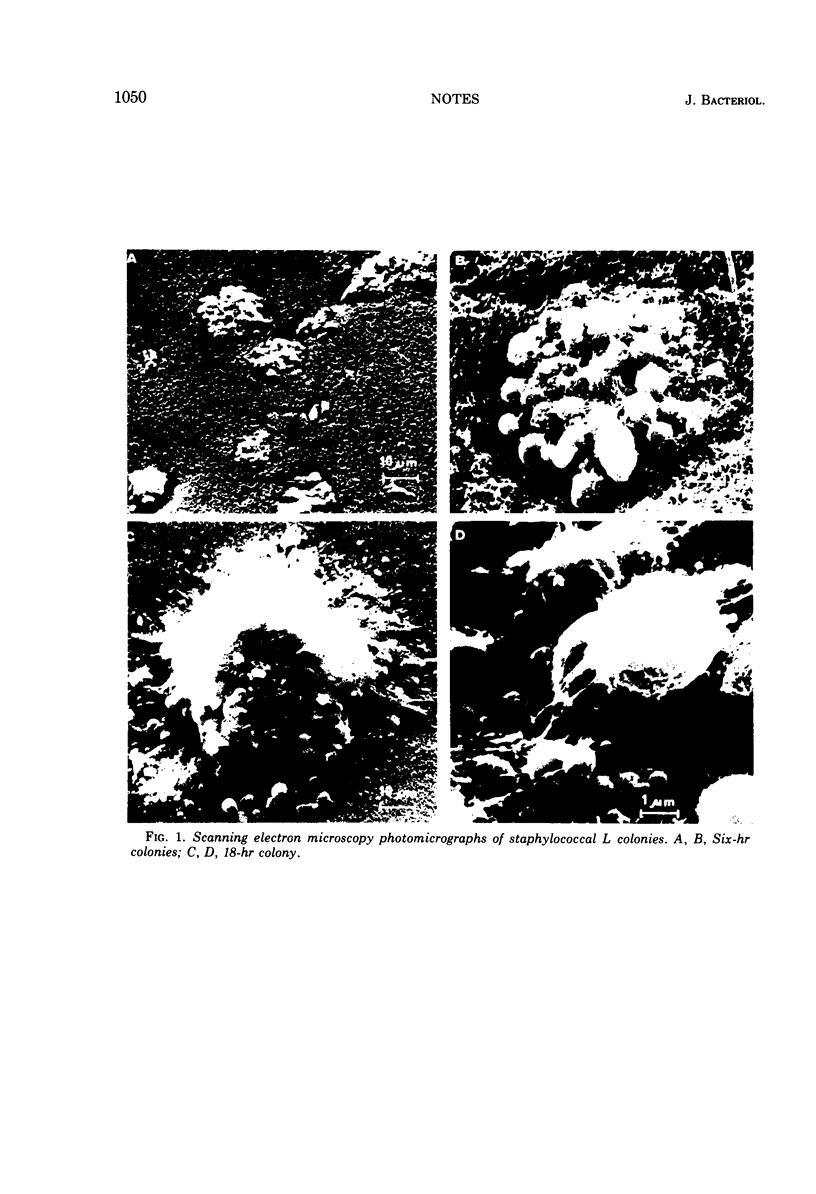
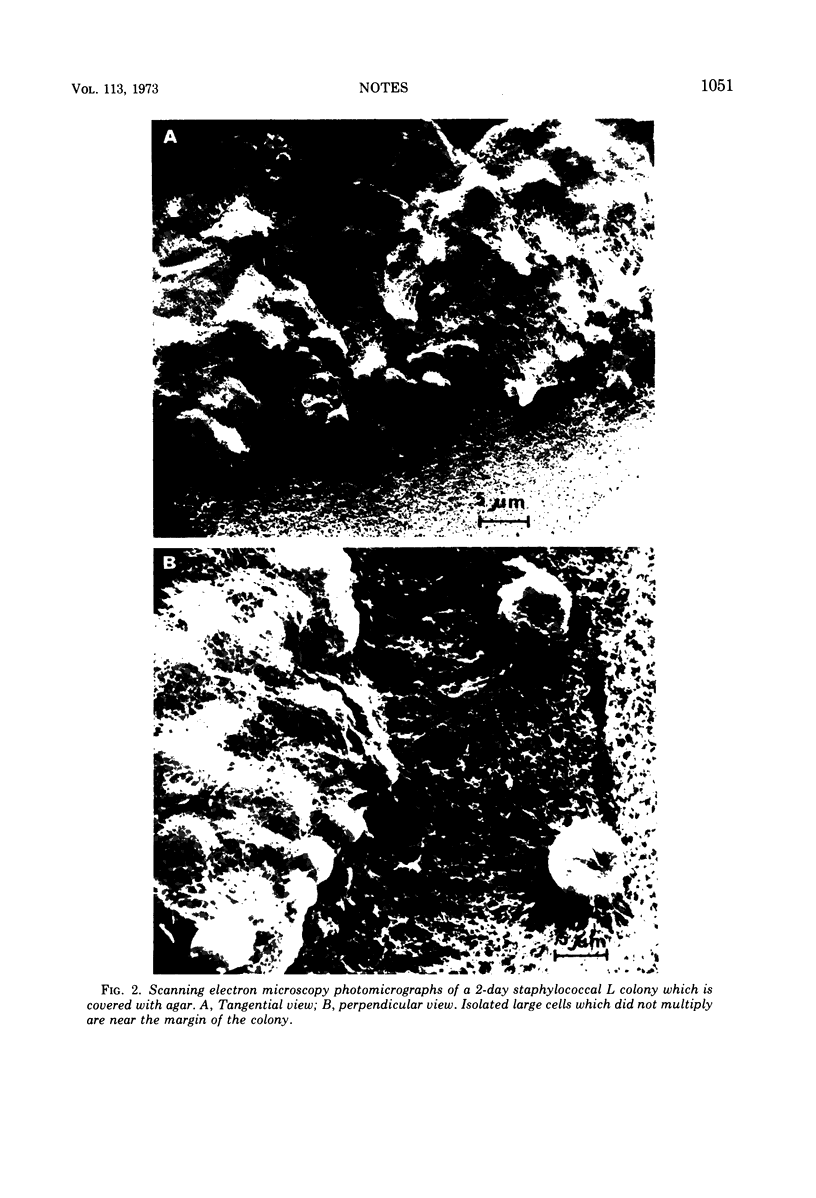
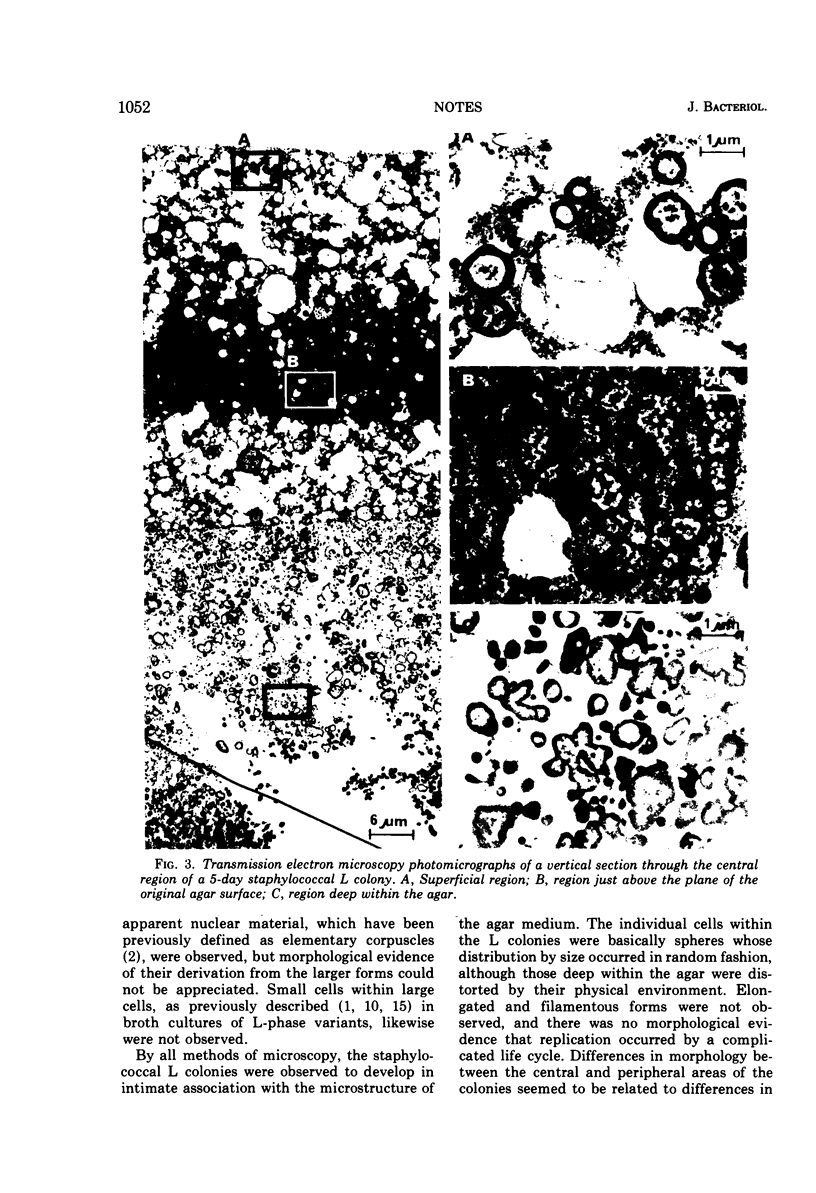
Scanning electron microscopy utilizing critical point drying was used in parallel with light and transmission electron microscopy to study L colonies produced by a stable L-phase variant of Staphylococcus aureus (AH24H).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dannis D. C., Marston J. H. Fine structure of staphylococcal L-forms. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Winter;23(4):729–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes L., Bullivant S. Comparison of the morphology of PPLO and L-forms of bacteria with light and electron microscopy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):719–733. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes L., Bullivant S. Morphology and reproductive processes of the L forms of bacteria. II. Comparative study of L forms and Mycoplasma with the electron microscope. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):672–687. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.672-687.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Carleton J., Watanakunakorn C., Klainer A. S., Hamburger M. Scanning-beam electron microscopy of cell wall-defective staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1970 Oct;2(4):504–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.4.504-515.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADOFF S. Isolation and identification of PPLO. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:383–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. I., Ashley C. A., Roberts L. Ultrastructure of meningococcal L forms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:127–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., LANDMAN O. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MESOSOME LOSS AND THE STABLE L STATE (OR PROTOPLAST STATE) IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:457–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.457-467.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORSSON K. G., WEIBULL C. Studies on the structure of bacterial L forms, protoplasts and protoplast-like bodies. J Ultrastruct Res. 1958 Aug;1(4):412–427. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(58)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C., Browder H. P. Effects of lysostaphin and its two active components on stable wall-defective forms of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):124–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C., Fass R. J., Klainer A. S., Hamburger M. Light and scanning-beam electron microscopy of wall-defective Staphylococcus aureus induced by lysostaphin. Infect Immun. 1971 Jul;4(1):73–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.1.73-78.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C., Goldberg L. M., Carleton J., Hamburger M. Staphylococcal spheroplasts and L-colonies. 3. Induction by lysostaphin. J Infect Dis. 1969 Jan;119(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibull C. Structure of bacterial L forms and their parent bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1467–1480. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1467-1480.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]