Abstract
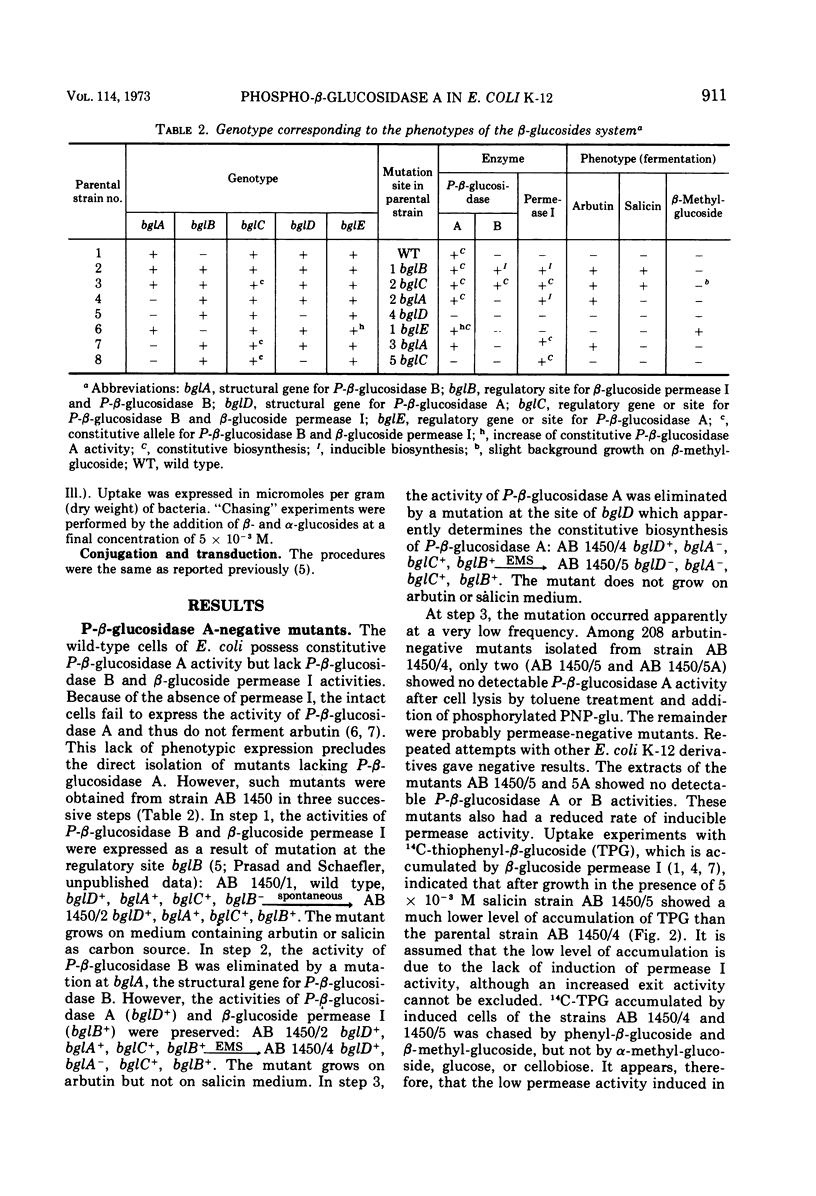
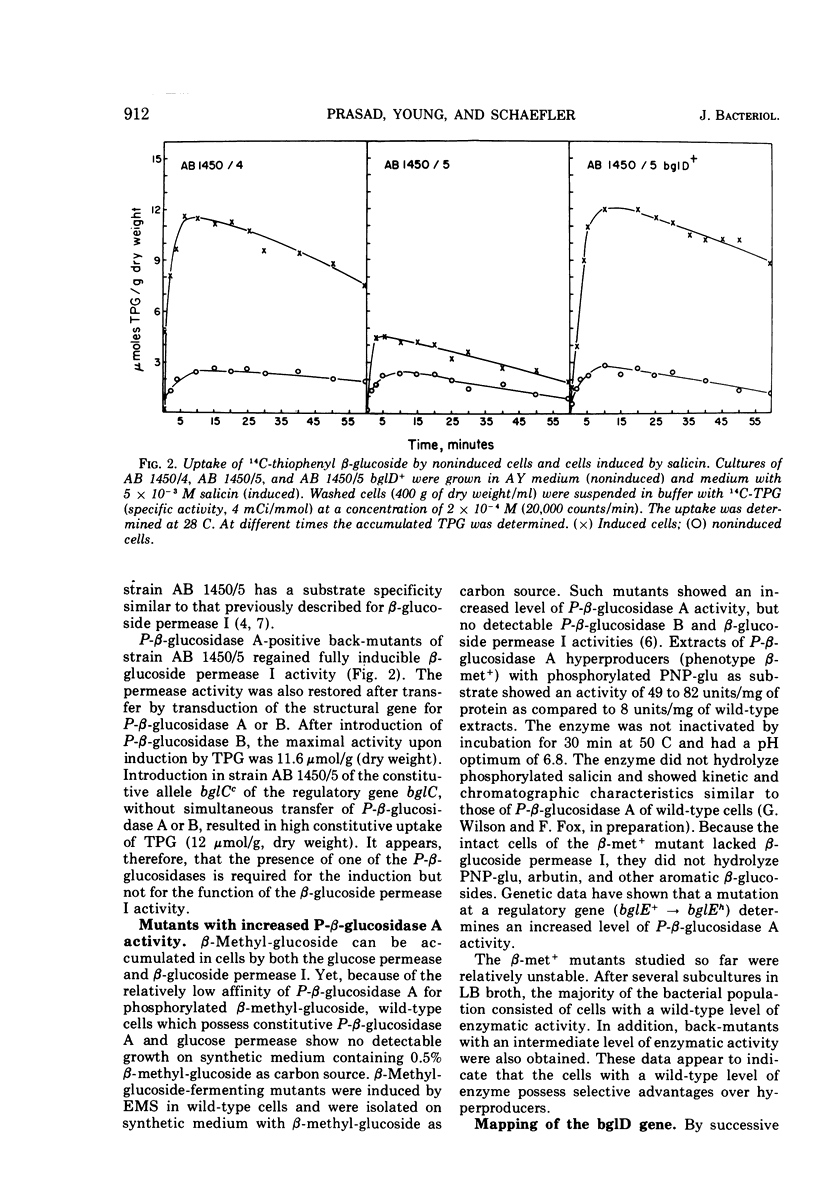
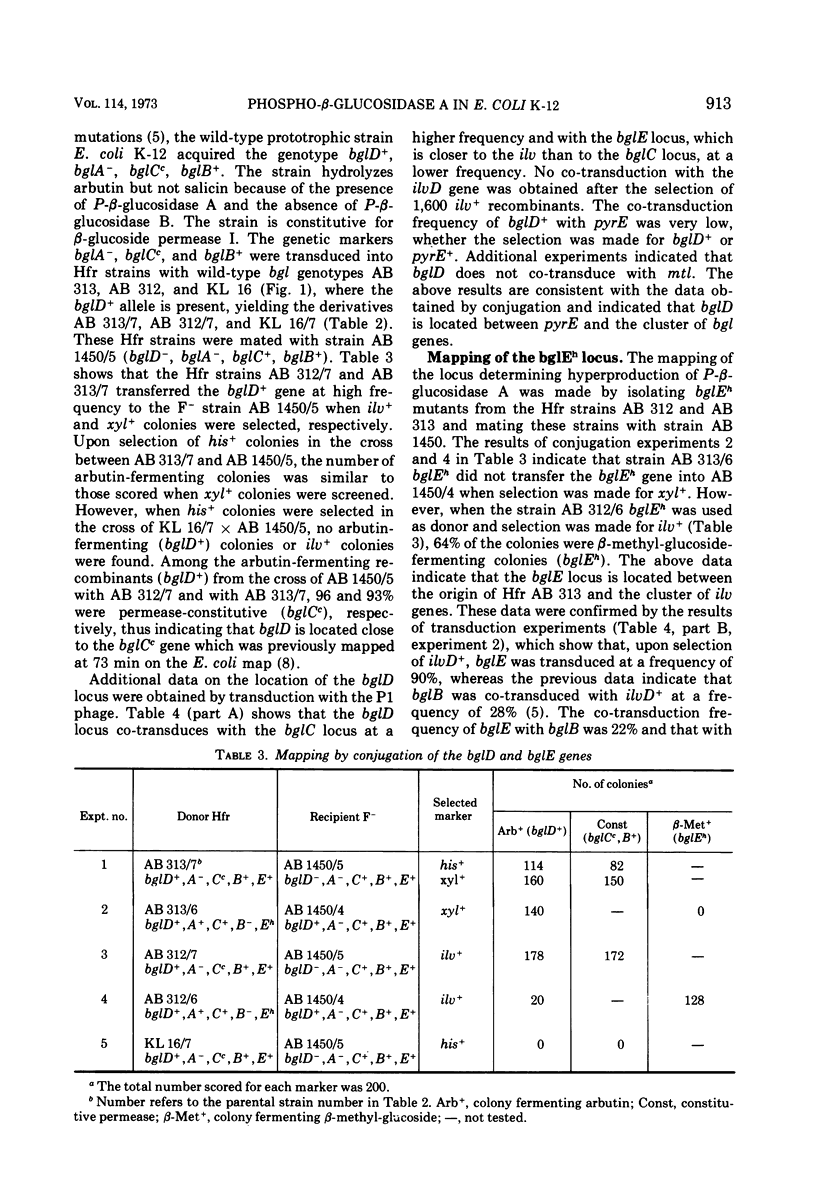
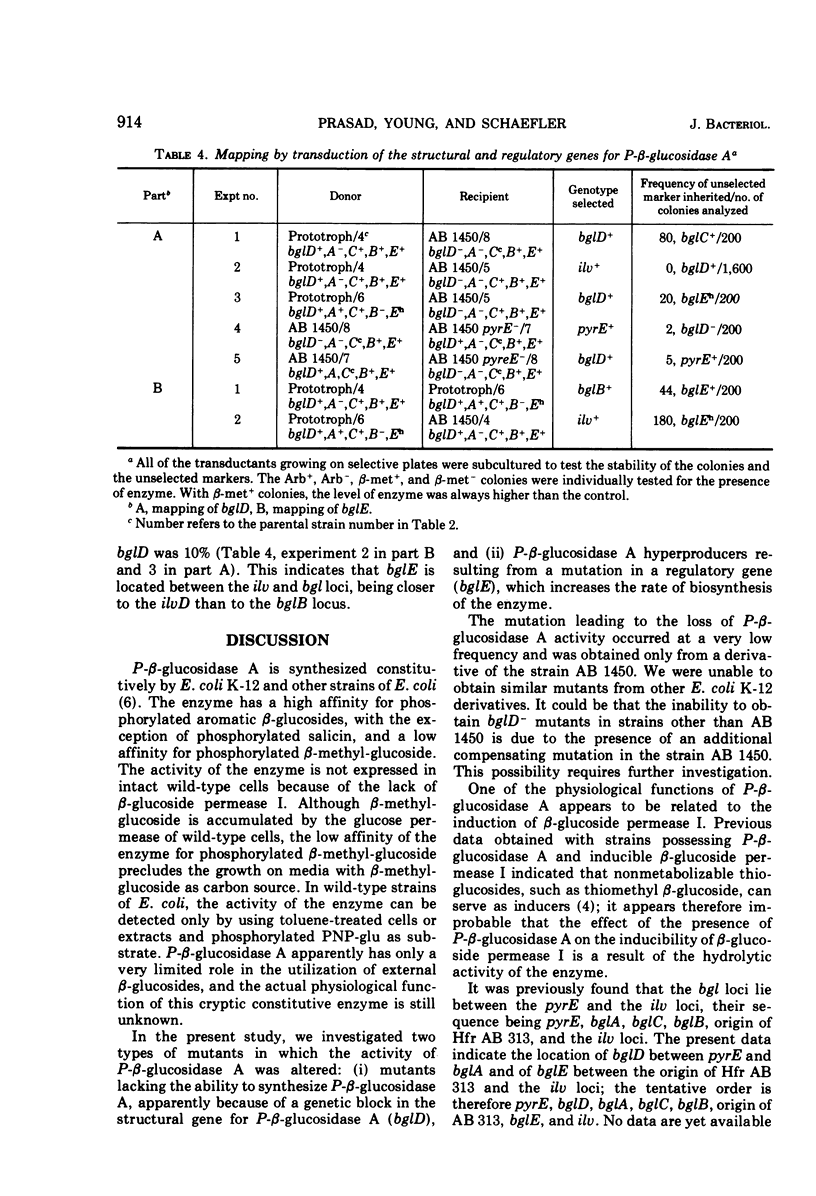
Escherichia coli wild-type cells form constitutively the enzyme phospho-β-glucosidase A, which has a high affinity for phosphorylated aromatic β-glucosides and a low affinity for phosphorylated β-methyl-glucoside. Phospho-β-glucosidase B and β-glucoside permease I are formed in aromatic β-glucoside-fermenting mutants. Mutants lacking phospho-β-glucosidases A and B have been isolated. These mutants showed a reduced rate of inducibility of the β-glucoside permease I. The restoration of phospho-β-glucosidase A or B activity resulted in an increased rate of induction of the β-glucoside permease I. The presence of the phospho-β-glucosidases was not required for the constitutive biosynthesis of the β-glucoside permease. Mutants selected for growth on β-methyl-glucoside as carbon source showed an increased level of constitutive phospho-β-glucosidase A activity. Gene bglD, the structural gene for phospho-β-glucosidase A, was mapped between the pyrE locus and the cluster bgl loci, whereas bglE, the regulatory site determining the hyperproduction of phospho-β-glucosidase A, was mapped between the bgl and ilv clusters. The bglE locus appears to have a regulatory effect on the expression of the bglD gene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fox C. F., Wilson G. The role of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent kinase system in beta-glucoside catabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):988–995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G., Banerjee S. A mutation increasing the amount of a constitutive enzyme in Escherichia coli, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 28;56(1):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S. Inducible system for the utilization of beta-glucosides in Escherichia coli. I. Active transport and utilization of beta-glucosides. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):254–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.254-263.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Maas W. K. Inducible system for the utilization of beta-glucosides in Escherichia coli. II. Description of mutant types and genetic analysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):264–272. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.264-272.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Malamy A. Taxonomic investigations on expressed and cryptic phospho-beta-glucosidases in Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):422–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.422-433.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S., Schenkein I. Beta-glucoside permeases and phospho beta-glucosidases in Aerobacter aerogenes: relationship with cryptic phospho beta-glucosidases in Enterobacteriaceae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):285–292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L. Current linkage map of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):155–175. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.155-175.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


