Abstract
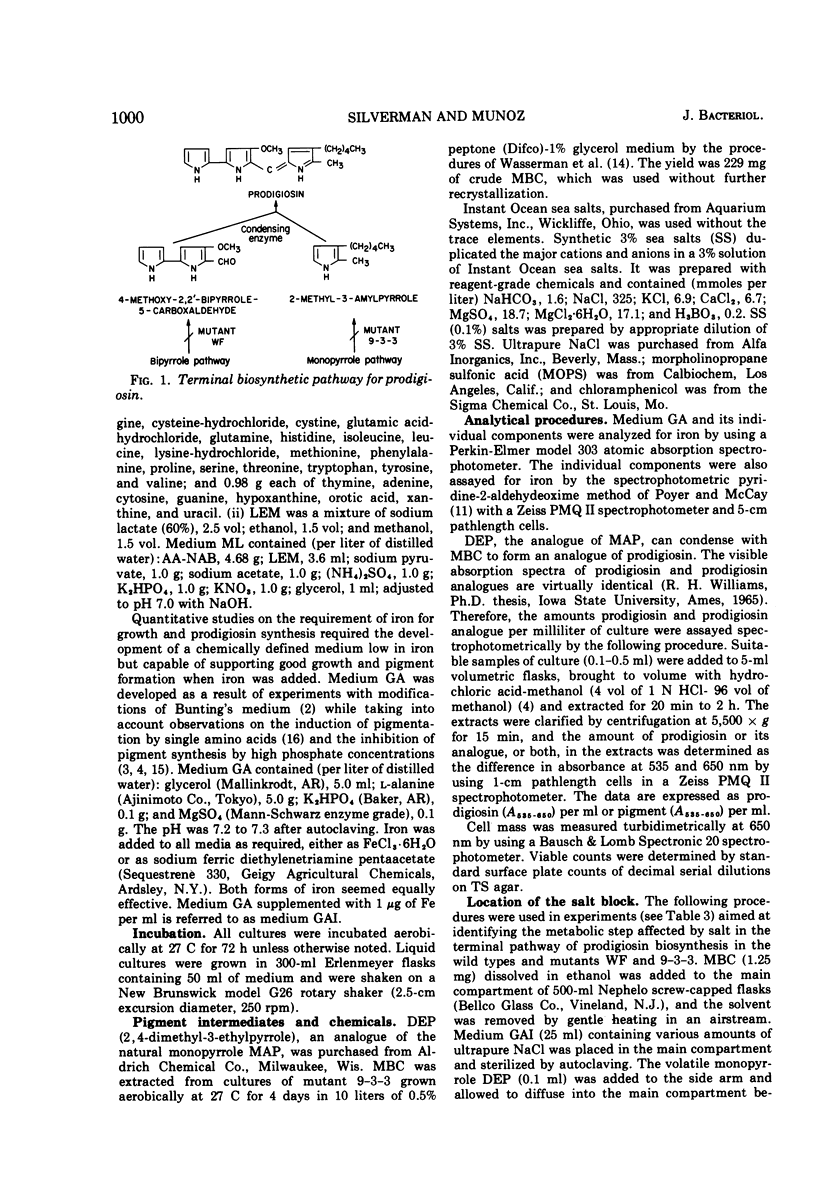
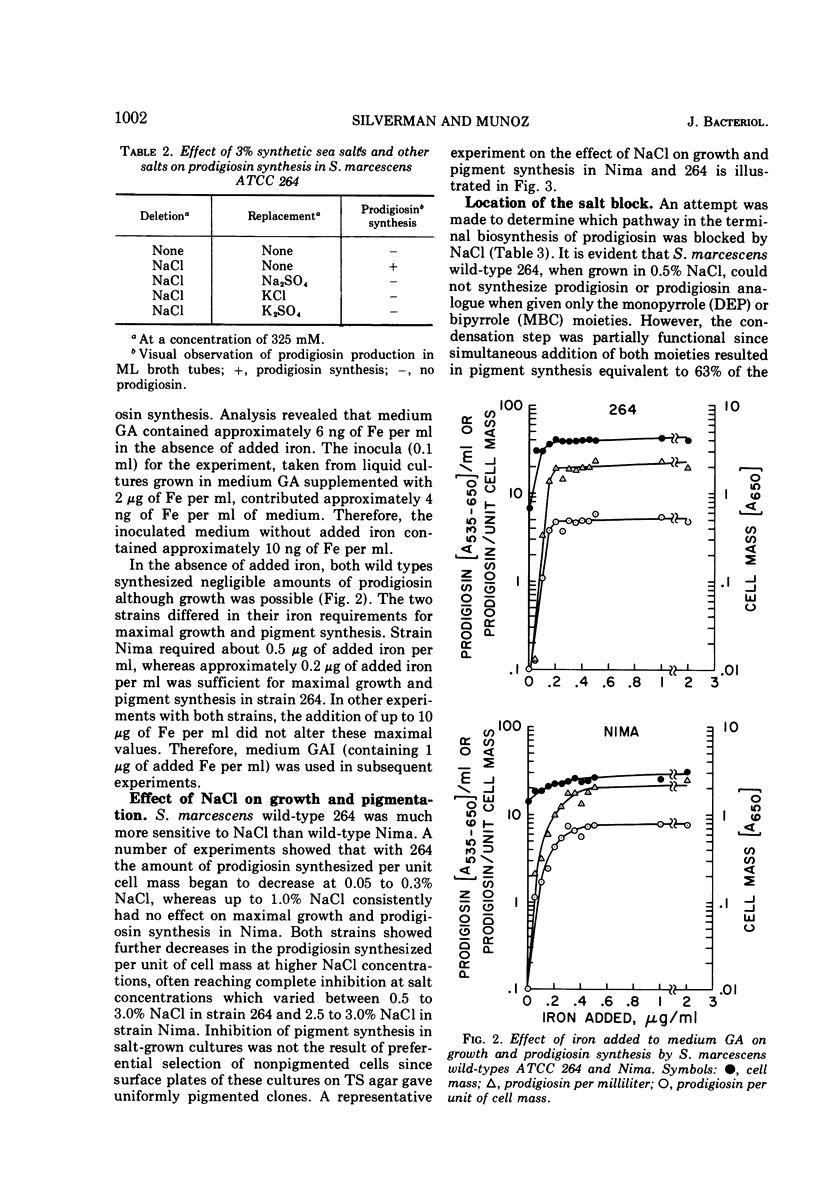
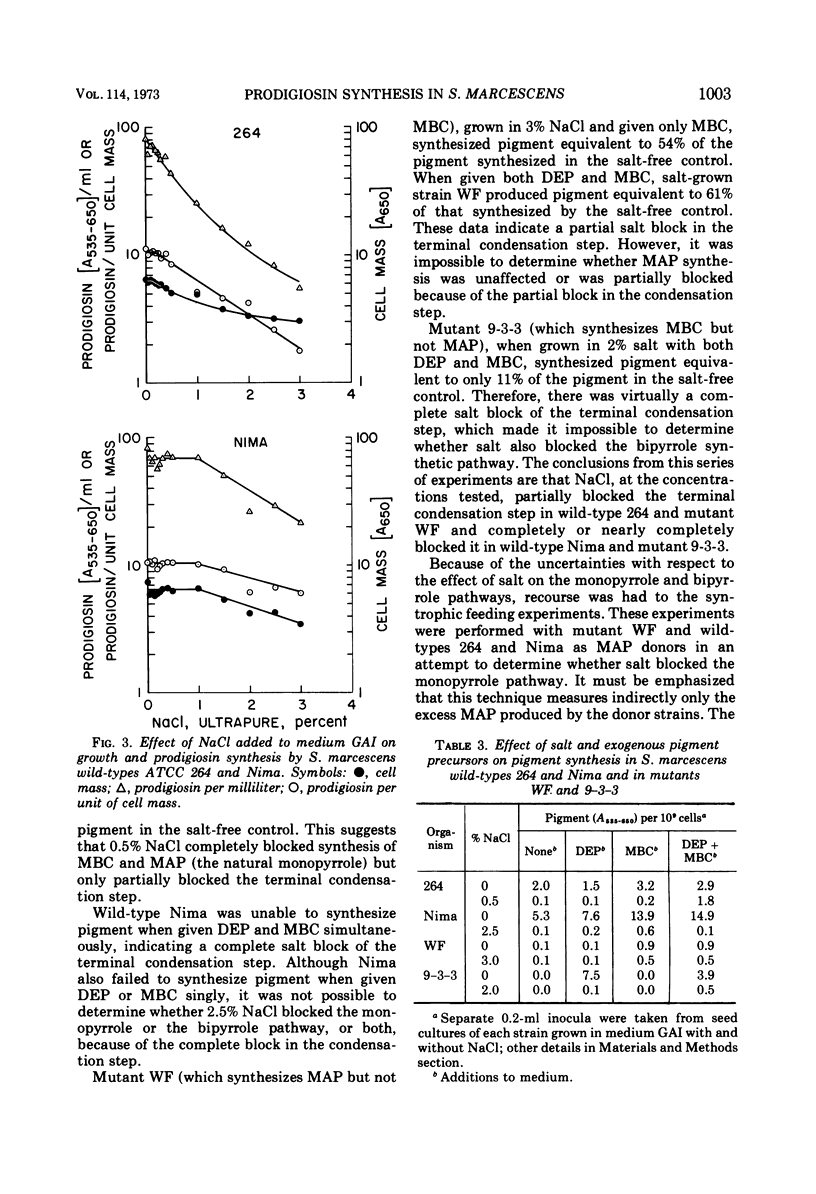
Serratia marcescens wild-types ATCC 264 and Nima grew but did not synthesize prodigiosin in a glycerol-alanine medium containing 10 ng of Fe per ml. Wild-type 264 required the addition of 0.2 μg of Fe per ml for maximal growth and prodigiosin synthesis; Nima required 0.5 μg of Fe per ml. Three percent, but not 0.1%, sea salts inhibited prodigiosin synthesis in a complex medium containing up to 10 μg of Fe per ml. NaCl was the inhibitory sea salt component. The inhibition was not specific for NaCl; equimolar concentrations of Na2SO4, KCl, and K2SO4 also inhibited prodigiosin synthesis. Experiments with strains 264 and Nima and with mutant WF which cannot synthesize 4-methoxy-2-2′-bipyrrole-5-carboxyaldehyde (MBC), the bipyrrole moiety of prodigiosin, and with mutant 9-3-3 which cannot synthesize the monopyrrole moiety 2-methyl-3-amylpyrrole (MAP) showed that both MBC synthesis and the reaction condensing MAP and MBC to form prodigiosin were relatively more sensitive to NaCl inhibition than the MAP-synthesizing step. The capacity of whole cells to condense MAP and MBC was present, but inactive, in cells grown in NaCl; removal of the NaCl from non-proliferating salt-grown cells restored the activity. Other evidence suggests the existence of a common precursor to the MAP- and MBC-synthesizing pathways.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunting M. I. A Description of Some Color Variants Produced by Serratia marcescens, Strain 274. J Bacteriol. 1940 Jul;40(1):57–68. doi: 10.1128/jb.40.1.57-68.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunting M. I., Robinow C. F., Bunting H. FACTORS AFFECTING THE ELABORATION OF PIGMENT AND POLYSACCHARIDE BY SERRATIA MARCESCENS. J Bacteriol. 1949 Jul;58(1):114–115. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt M. C., Williams R. P. Thiamine-induced formation of the monopyrrole moiety of prodigiosin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):609–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.609-616.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS S. M., CORPE W. A. PRODIGIOSIN-PRODUCING BACTERIA FROM MARINE SOURCES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jan;12:13–17. doi: 10.1128/am.12.1.13-17.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Prodigiosin synthesis in mutants of Serratia marcesens. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1599–1604. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1599-1604.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee P. P., Goldschmidt M. E., Williams R. P. Enzymic formation of prodigiosin analog by a cell-free preparation from Serratia marcescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 7;136(1):182–184. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90342-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyama V. I., Merek E. L., Silverman M. P. A search for viable organisms in a lunar sample. Science. 1970 Jan 30;167(3918):773–775. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3918.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poyer J. L., McCay P. B. Reduced triphosphopyridine nucleotide oxidase-catalyzed alterations of membrane phospholipids. IV. Dependence on Fe3+. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M. P., Munoz E. F., Oyama V. I. Effect of Apollo 11 lunar samples on terrestrial microorganisms. Nature. 1971 Mar 19;230(5290):169–170. doi: 10.1038/230169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. P., GOLDSCHMIDT M. E., GOTT C. L. INHIBITION BY TEMPERATURE OF THE TERMINAL STEP IN BIOSYNTHESIS OF PRODIGIOSIN. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Apr 9;19:177–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90500-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. P., Gott C. L., Qadri S. M. Induction of pigmentation in nonproliferating cells of Serratia marcescens by addition of single amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.444-448.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


