Abstract
Sporulation-specific mutations in Bacillus subtilis have been mapped by transduction and transformation. The mutations caused blocks at stages 0, II, III, and IV of sporulation; more than one phenotype was found for each of these stages. On the basis of the criteria used to define a sporulation operon, a minimum estimate could be made of the number of operons activated during sporulation. Nine operons were identified for stage 0, eight for stage II, five for stage III, and six for stage IV. It is probable that several of these 28 operons are activated in groups so that the number of steps in the dependent sequence of sporulation events should turn out to be less than the number of operons.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayad S. R., Barker G. R. The integration of donor and recipient deoxyribonucleic acid during transformation of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):167–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1130167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARAT M., ANAGNOSTOPOULOS C., SCHNEIDER A. M. LINKAGE RELATIONSHIPS OF GENES CONTROLLING ISOLEUCINE, VALINE, AND LEUCINE BIOSYNTHESIS IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:357–369. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.357-369.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BODMER W. F., GANESAN A. T. BIOCHEMICAL AND GENETIC STUDIES OF INTEGRATION AND RECOMBINATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS TRANSFORMATION. Genetics. 1964 Oct;50:717–738. doi: 10.1093/genetics/50.4.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
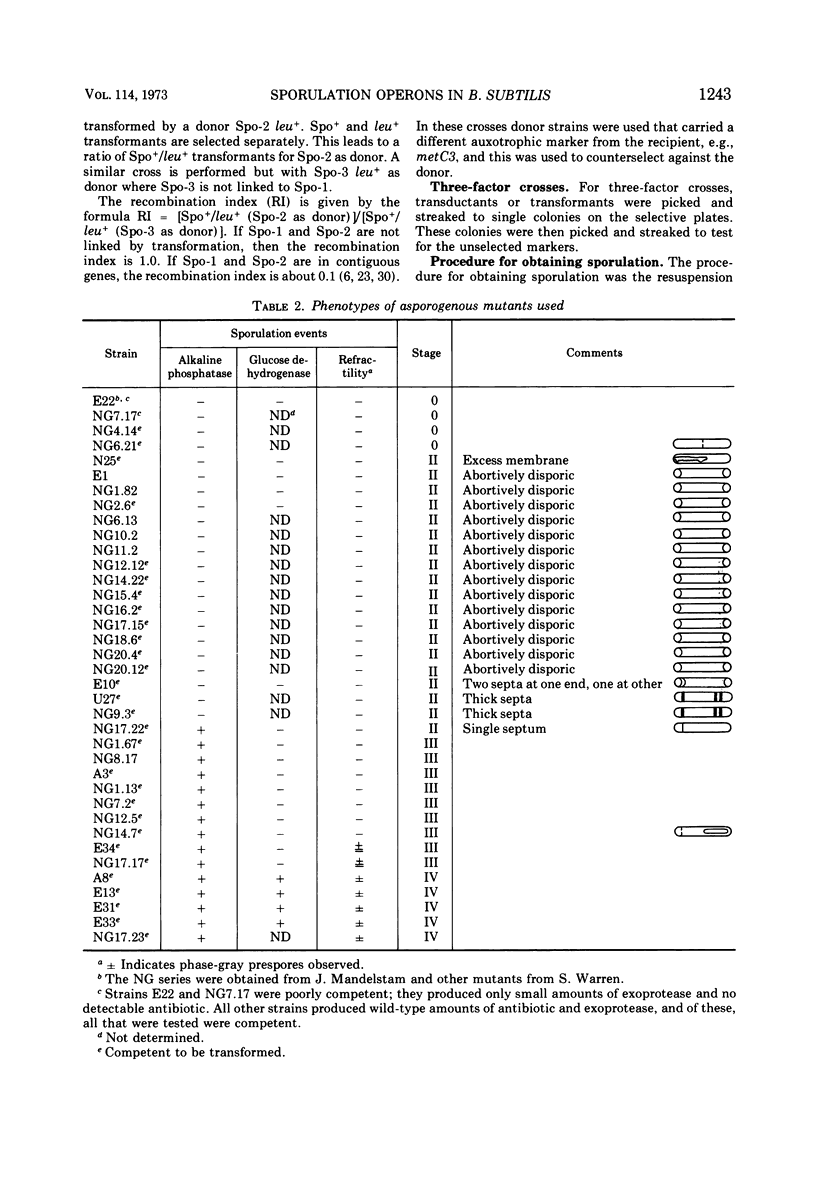
- Balassa G., Yamamoto T. Biochemical genetics of bacterial sporulation. 3. Correlation between morphological and biochemical properties of sporulation mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(1):1–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00343179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlton B. C. Fine-structure mapping by transformation in the tryptophan region of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1795–1803. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1795-1803.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. G., Mandelstam J. Use of constructed double mutants for determining the temporal order of expression of sporulation genes in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1254–1263. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1254-1263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
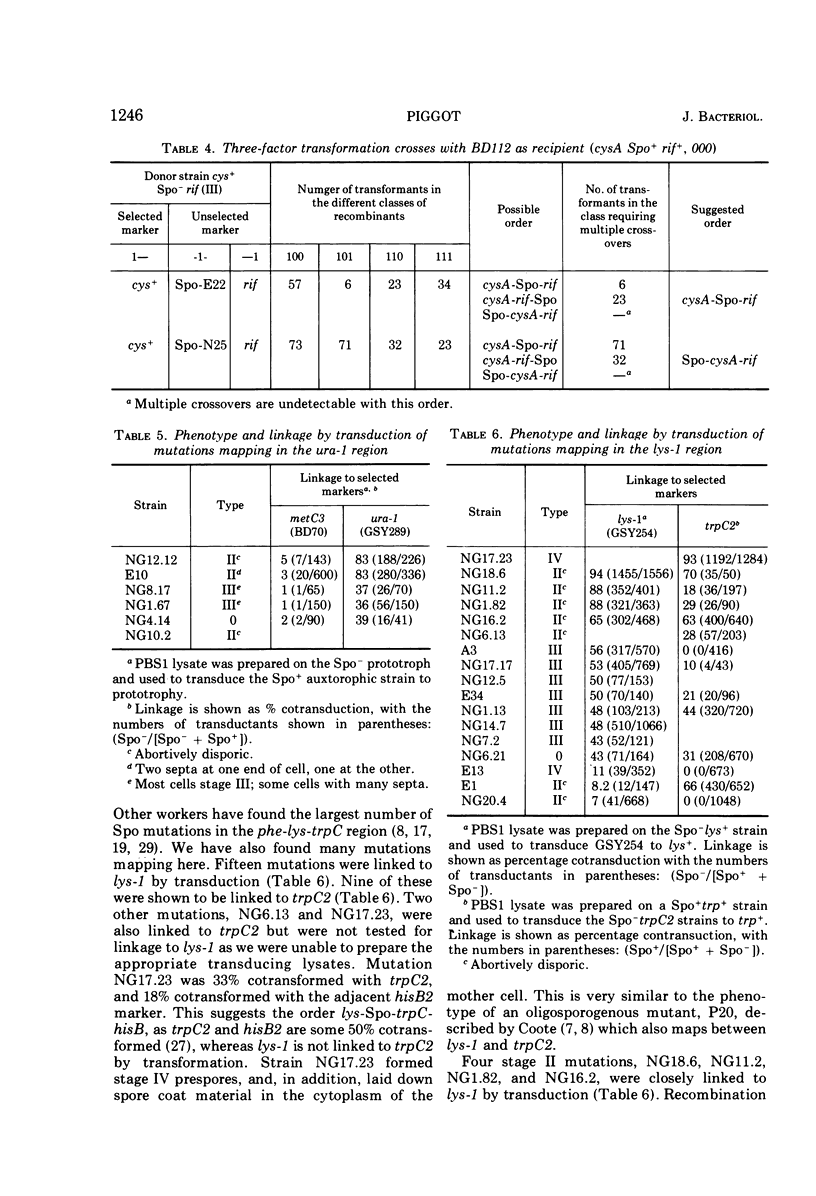
- Coote J. G. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Characterization of oligosporogenous mutants and comparison of their phenotypes with those of asporogenous mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. G. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Genetic analysis of oligosporogenous mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):17–27. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONNELLAN J. E., Jr, NAGS E. H., LEVINSON H. S. CHEMICALLY DEFINED, SYNTHETIC MEDIA FOR SPORULATION AND FOR GERMINATION AND GROWTH OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:332–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.332-336.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrati-Elizur E. Spontaneous transformation in Bacillus subtilis. Genet Res. 1968 Feb;11(1):83–96. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., GUNDERSEN W., BURGER M. Genetics of regulation of enzyme synthesis in the arginine biosynthetic pathway of Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:173–182. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harford N., Sueoka N. Chromosomal location of antibiotic resistance markers in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):267–286. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A. Genetic analysis of pleiotropic negative sporulation mutants in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):896–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.896-901.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A. Selection of cells transformed to prototrophy for sporulation markers. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1200–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1200-1201.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionesco H., Michel J., Cami B., Schaeffer P. Symposium on bacterial spores: II. Genetics of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis Marburg. J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;33(1):13–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb05230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karamata D., Gross J. D. Isolation and genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants of B. subtilis defective in DNA synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(3):277–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00283358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay D., Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Morphological changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):819–824. doi: 10.1042/bj1090819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACKS S., HOTCHKISS R. D. A study of the genetic material determining an enzyme in Pneumococcus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 22;39:508–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHLER I., NEUMANN I. M., MARMUR J. Studies of genetic-units controlling arginine biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 28;72:69–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelstam J., Waites W. M. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. The role of exoprotease. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):793–801. doi: 10.1042/bj1090793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nester E W, Schafer M, Lederberg J. Gene Linkage in DNA Transfer: A Cluster of Genes Concerned with Aromatic Biosynthesis in Bacillus Subtilis. Genetics. 1963 Apr;48(4):529–551. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.4.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M. Chromosomal regions which control sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jul;15(7):787–790. doi: 10.1139/m69-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyard J. F., Ionesco H., Schaeffer P. Classification génétique de certains mutants de sporulation de Bacillus subtilis, Marburg. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1967 Nov;113(5):675–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Schaeffer P., Ionesco H. Classification cytologique, par leur stade de blocage, des mutants de sporulation de Bacillus subtilis Marburg. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Mar;110(3):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEFFER P., IONESCO H. [Contribution to the genetic study of bacterial sporogenesis]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1960 Dec 19;251:3125–3127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P. Sporulation and the production of antibiotics, exoenzymes, and exotonins. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Mar;33(1):48–71. doi: 10.1128/br.33.1.48-71.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. A. S-amino acid metabolism and its regulation in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Adv Genet. 1971;16:141–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterlini J. M., Mandelstam J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1130029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI I. LOCALIZATION OF SPORE MARKERS ON THE CHROMOSOME OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1065–1067. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1065-1067.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI I. Transducing phages for Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 May;31:211–217. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waites W. M., Kay D., Dawes I. W., Wood D. A., Warren S. C., Mandelstam J. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Correlation of biochemical events with morphological changes in asporogenous mutants. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(4):667–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1180667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Biochemical changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj1090811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. A. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Properties and time of synthesis of alkali-soluble protein of the spore coat. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):505–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1300505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG I. E. CHARACTERISTICS OF AN ABORTIVELY DISPORIC VARIANT OF BACILLUS CEREUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:242–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.242-254.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Balassa G. Biochemical genetics of bacterial sporulation. II. Membrane development suring sporulation of B. subtilis and its mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;106(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00332816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E., Smith C., Reilly B. E. Chromosomal location of genes regulating resistance to bacteriophage in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1087–1097. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1087-1097.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


