Abstract
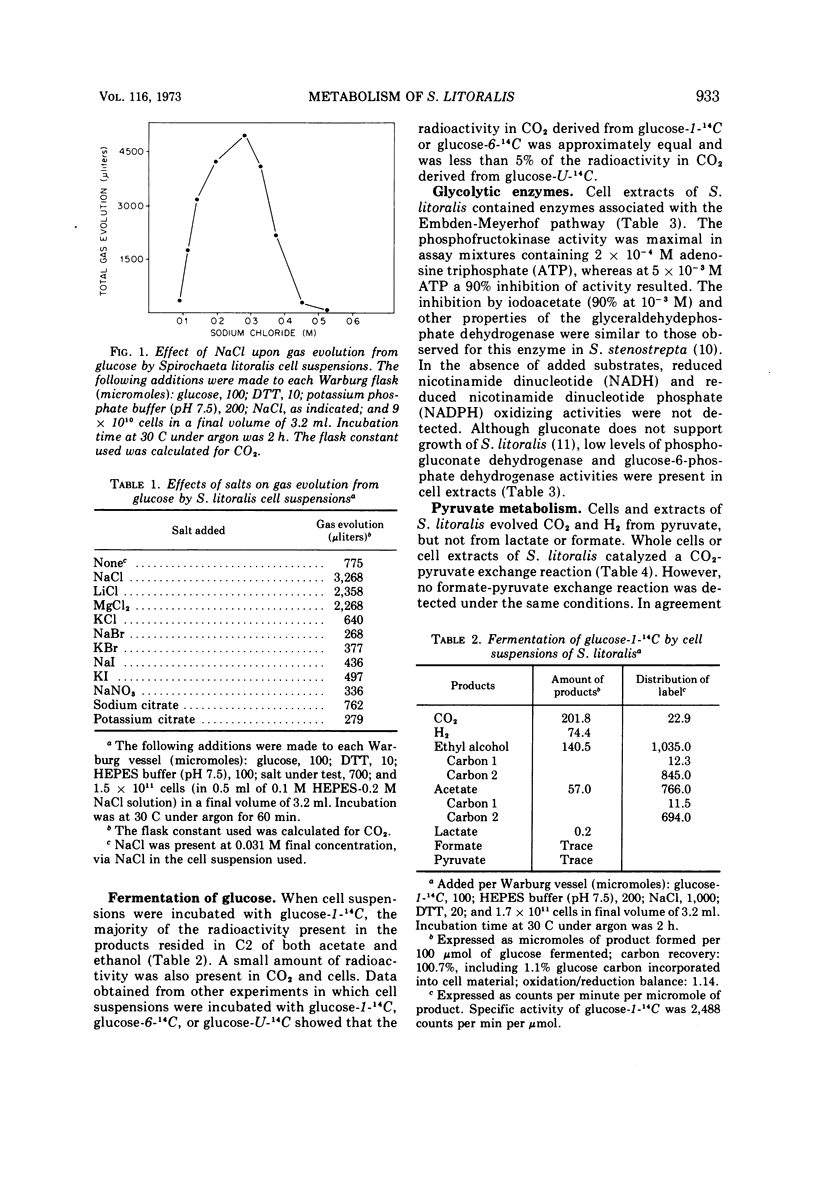
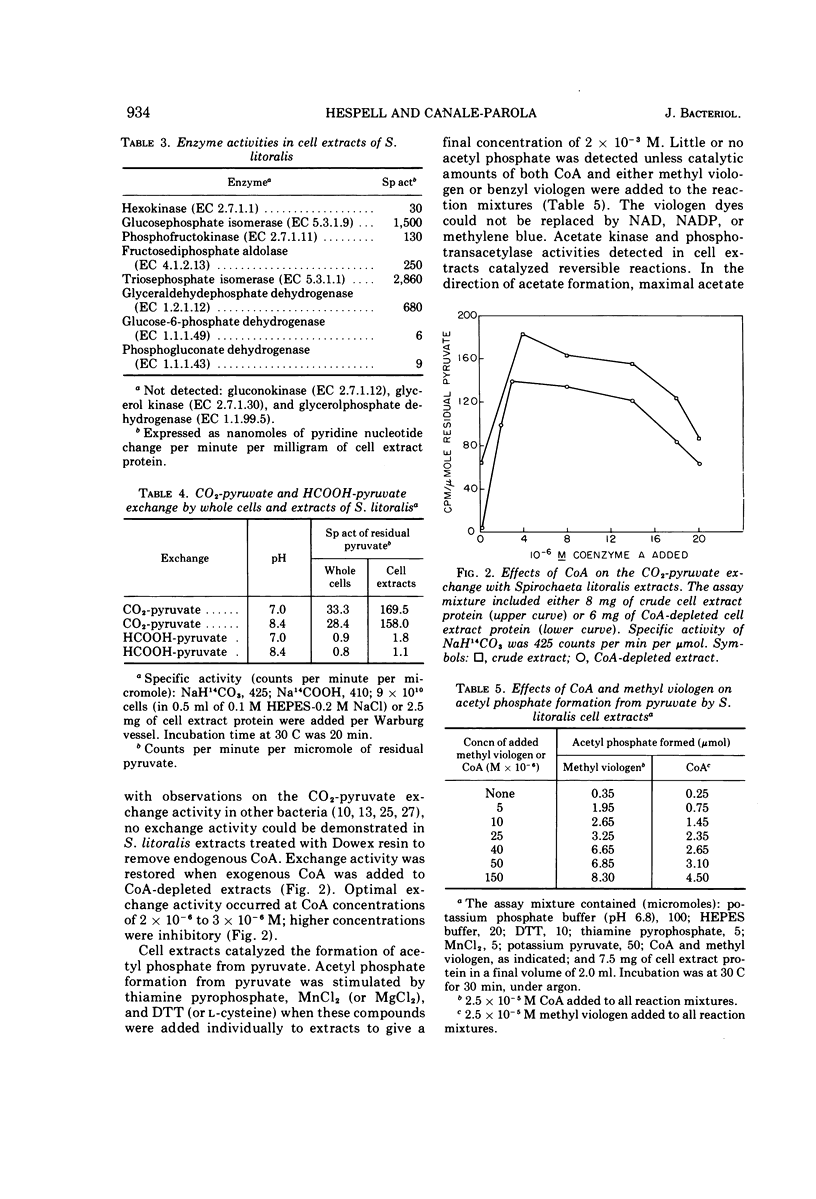
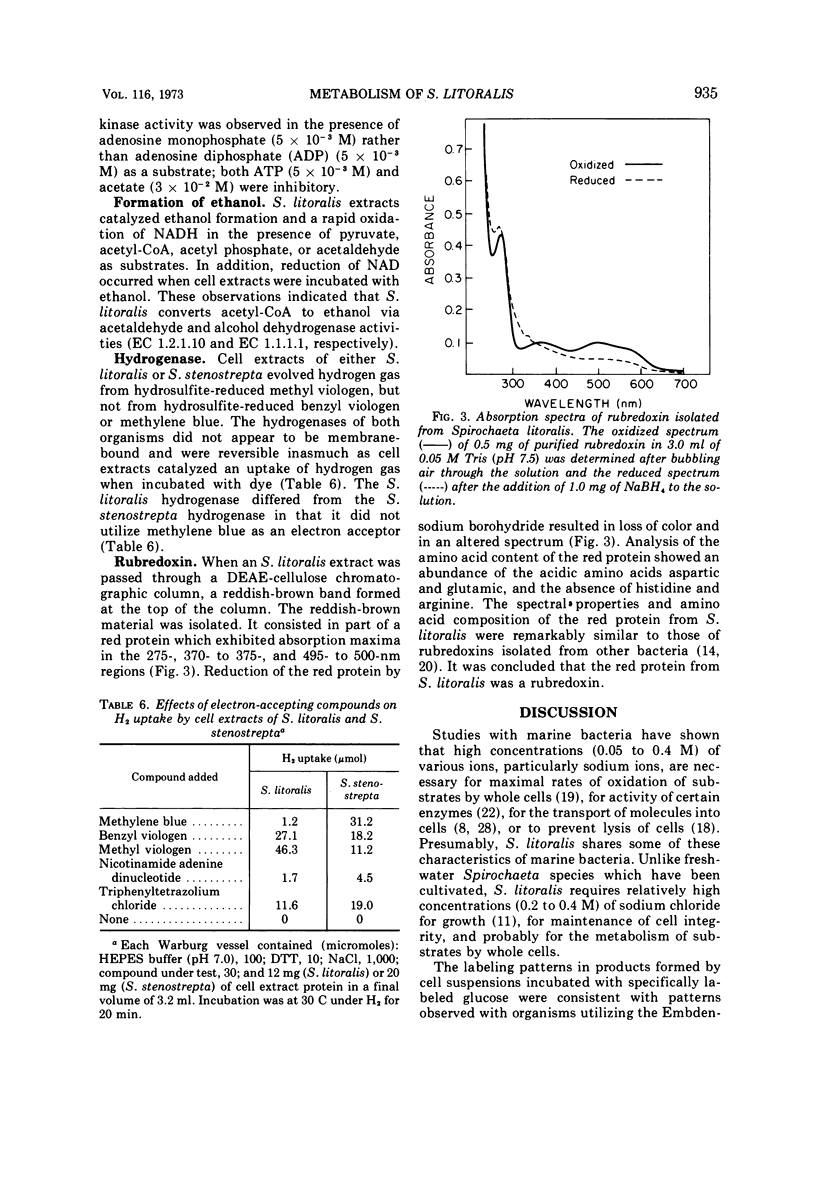
The pathways of glucose and pyruvate metabolism in Spirochaeta litoralis, a free-living, strictly anaerobic marine spirochete, were studied. Addition of 0.2 to 0.4 M NaCl (final concentration) to suspending buffers prevented cell lysis and was necessary for gas evolution from various substrates by cell suspensions. The organism fermented glucose mainly to ethanol, acetate, CO2, and H2. Determination of radioactivity in products formed from 14C-labeled glucose and assays of enzymatic activities in cell extracts indicated that S. litoralis catabolized glucose via the Embden-Meyerhof pathway. A clostridial-type clastic reaction was utilized by the spirochete to degrade pyruvate to acetyl-coenzyme A, CO2, and H2. Formation of acetate from acetyl-coenzyme A was catalyzed by phosphotransacetylase and acetate kinase. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent acetaldehyde and alcohol dehydrogenases converted acetyl-coenzyme A to ethanol. A reversible hydrogenase activity was detected in cell extracts. S. litoralis cell extracts contained a rubredoxin similar in spectral properties to other bacterial rubredoxins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baseman J. B., Cox C. D. Intermediate energy metabolism of Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):992–1000. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.992-1000.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznak J. A., Canale-Parola E. Metabolism of Spirochaeta aurantia. I. Anaerobic energy-yielding pathways. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;83(4):261–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00425239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznak J. A., Canale-Parola E. Metabolism of Spirochaeta aurantia. II. Aerobic oxidation oxidation of carbohydrates. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;83(4):278–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00425240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznak J. A., Canale-Parola E. Spirochaeta aurantia, a pigmented, facultatively anaerobic spirochete. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):386–395. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.386-395.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canale-Parola E., Holt S. C., Udris Z. Isolation of free-living, anaerobic spirochetes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):41–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00406315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canale-Parola E., Udris Z., Mandel M. The classification of free-living spirochetes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;63(4):385–397. doi: 10.1007/BF00412124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., Matula T. I., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XV. Relation of Na+-activated transport to the Na+ requirement of a marine pseudomonad for growth. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):63–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.63-71.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henneberry R. C., Cox C. D. Beta-oxidation of fatty acids by Leptospira. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;16(1):41–45. doi: 10.1139/m70-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., Canale-Parola E. Amino acid and glucose fermentation by Treponema denticola. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;78(3):234–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00424897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., Canale-Parola E. Carbohydrate metabolism in Spirochaeta stenostrepta. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):216–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.216-226.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., Joseph R., Mortlock R. P. Requirement for coenzyme A in the phosphoroclastic reaction of anaerobic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1328–1334. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1328-1334.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. W., Canale-Parola E. Properties of rubredoxin and ferredoxin isolated from spirochetes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;89(4):341–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00408901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer D. G., Canale-Parola E. Pyruvate metabolism in Sarcina maxima. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):984–990. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.984-990.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., CLARIDGE C. A., HORI A., MURRAY J. F. Observations on the function of sodium in the metabolism of a marine bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):829–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A. THE QUESTION OF THE EXISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MARINE BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:9–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman D. J., Postgate J. R. Rubredoxin from a nitrogen-fixing variety of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Dec;7(1):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb19571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R., NOVELLI G. D., LIPMANN F. Coenzyme A function in and acetyl transfer by the phosphotransacetylase system. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jul;191(1):365–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Green M. L., Happold F. C. Cation-activated nucleotidase in cell envelopes of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):834–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.834-841.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VELDKAMP H. Isolation and characteristics of Treponema zuelzerae nov. spec., and anaerobic, free-living spirochete. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1960;26:103–125. doi: 10.1007/BF02538999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITELEY H. R., McCORMICK N. G. Degradation of pyruvate by Micrococcus lactilyticus. III. Properties and cofactor requirements of the carbon dioxide-exchange reaction. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85:382–393. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.382-393.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE R. S., O'KANE D. J. Cofactors of the carbon dioxide exchange reaction of Clostridium butyricum. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):637–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE R. S., O'KANE D. J. Cofactors of the phosphoroclastic reaction of Clostridium butyricum. J Biol Chem. 1953 Dec;205(2):755–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Thompson J., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVII. Ion-dependent retention of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid and its relation to Na+ dependent transport in a marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1016–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


