Abstract
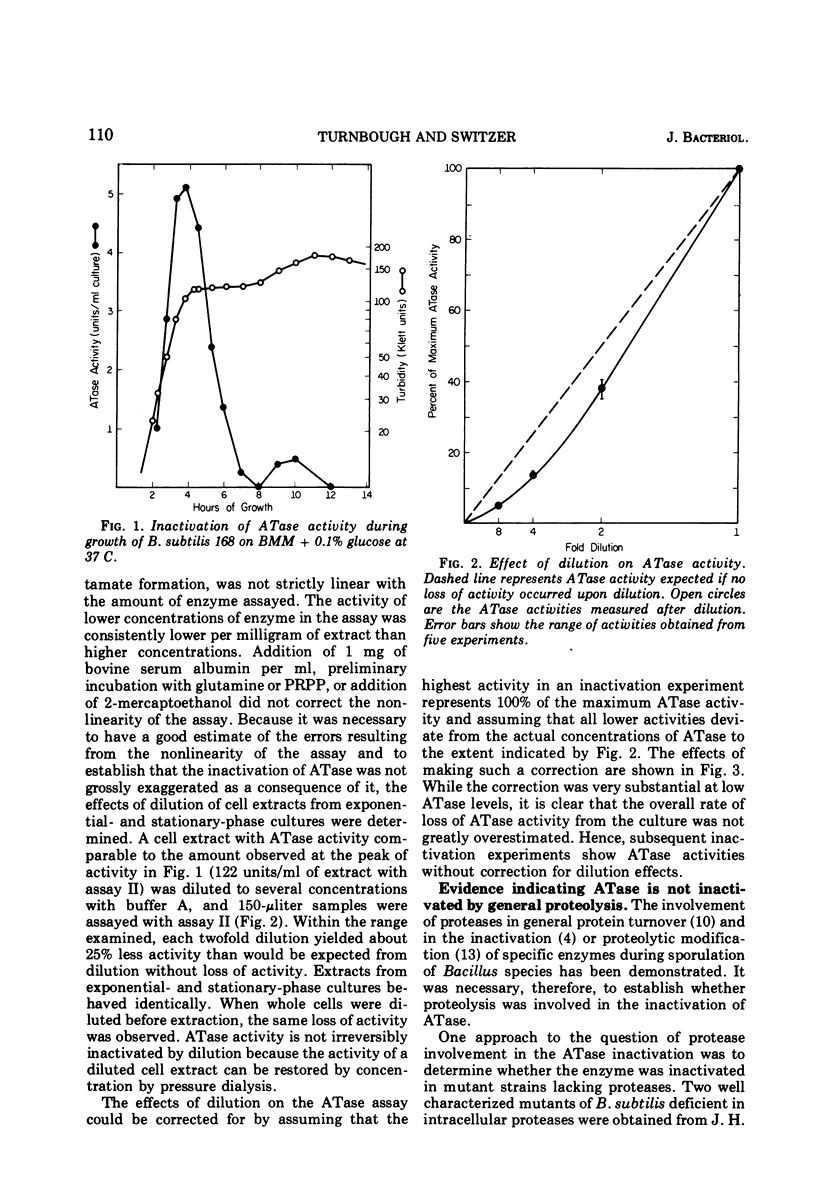
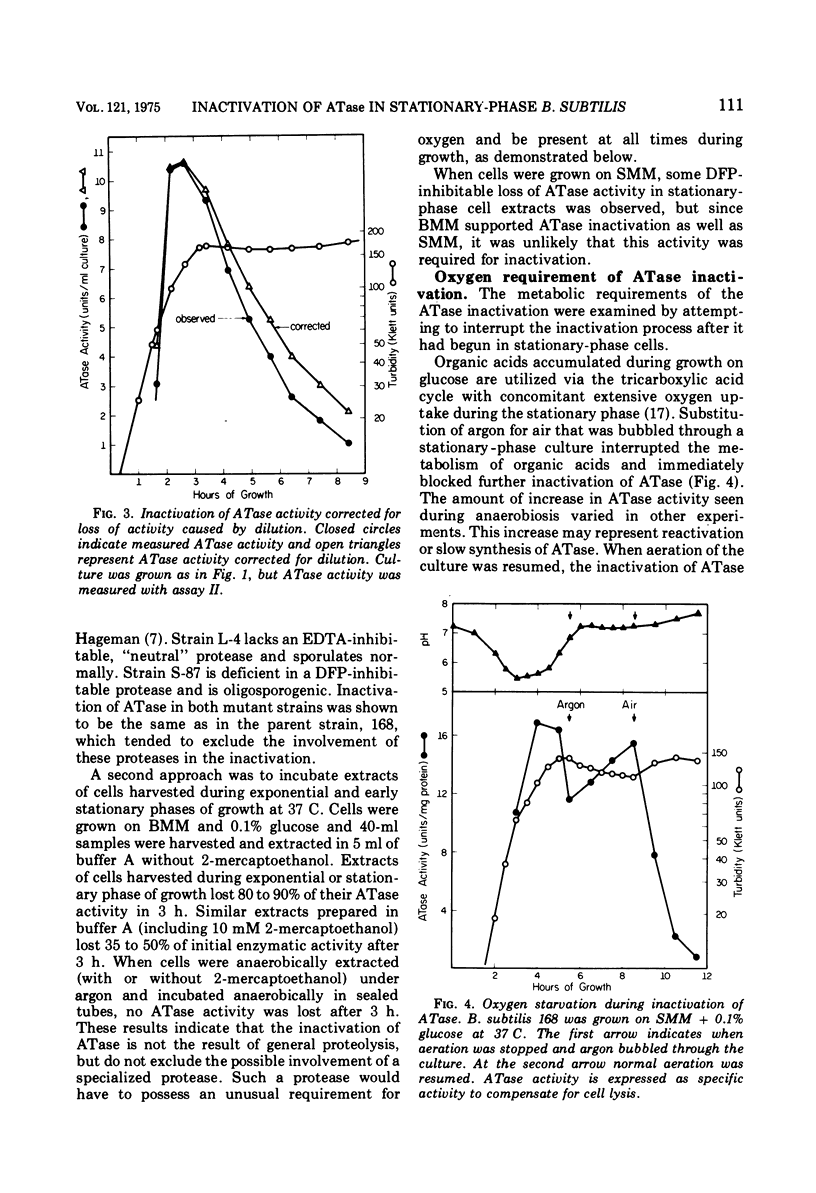
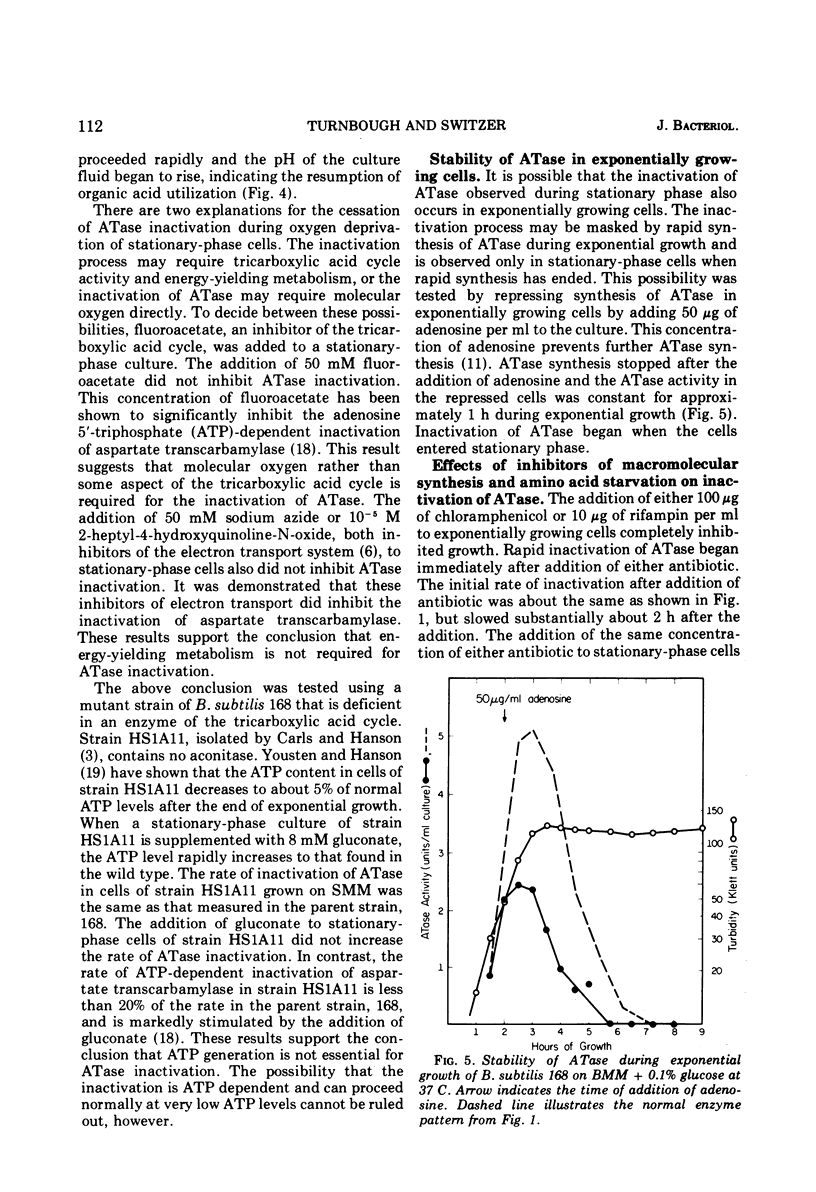
Glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase (ATase) activity is rapidly inactivated in stationary-phase cells of Bacillus subtilis. The inactivation of APase requires both the cessation of rapid cell growth and the presence of oxygen. ATase is inactivated in two protease-deficient mutant strains at a rate similar to that seen in the wild type, and is stable in anaerobic cell-free extracts of the parent strain. These results suggest that the inactivation of ATase is not the result of general proteolysis. The inactivation of ATase in stationary-phase cultures can be inhibited by oxygen starvation. This oxygen requirement does not reflect a dependence on the generation of metabolic energy, but appears to be a direct requirement for molecular oxygen. ATase synthesis is repressed by the addition of adenosine, and is inactivated only after the cessation of exponential growth. Addition of chloramphenicol or rifampin to exponential- and stationary-phase cells does not inhibit ATase inactivation, suggesting that protein or ribonucleic acid synthesis is not required for inactivation. ATase is inactivated at the end of exponential growth in cells that have exhausted a required amino acid.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagnara A. S., Mitchell A., Sin I. L., Finch L. R. A sensitive method for estimating 5-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate in Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):535–544. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90385-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carls R. A., Hanson R. S. Isolation and characterization of tricarboxylic acid cycle mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):848–855. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.848-855.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. 8. Patterns of enzyme development during growth and sporulation of Baccillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4653–4660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix J. A., Lundgren D. G. Electron transport system associated with membranes of Bacillus cereus during vegetative growth and sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):552–559. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.552-559.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman J. H., Carlton B. C. Effects of mutational loss of specific intracellular proteases on the sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):612–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.612-617.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG A., LIEBERMAN I., SIMMS E. S. Enzymatic synthesis and properties of 5-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jul;215(1):389–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelstam J., Waites W. M. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. The role of exoprotease. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):793–801. doi: 10.1042/bj1090793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momose H., Nishikawa H., Shiio I. Regulation of purine nucleotide synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. I. Enzyme repression by purine derivatives. J Biochem. 1966 Apr;59(4):325–331. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestidge L., Gage V., Spizizen J. Protease activities during the course of sporulation on Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):815–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.815-823.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoff H. L., Celikkol E., Engelbrecht H. L. Conversion of bacterial aldolase from vegetative to spore form by a sporulation-specific protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):844–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. 23. Nucleotide metabolism during spore germination. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3645–3652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiio I., Ishii K. Regulation of purine ribonucleotide synthesis by end product inhibition. II. Effect of purine nucleotides on phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase of Bacillus subtilis. J Biochem. 1969 Aug;66(2):175–181. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbough C. L., Jr, Switzer R. L. Oxygen-dependent inactivation of glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase in vitro inactivation. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):115–120. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.115-120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waindle L. M., Switzer R. L. Inactivation of aspartic transcarbamylase in sporulating Bacillus subtilis: demonstration of a requirement for metabolic energy. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):517–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.517-527.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousten A. A., Hanson R. S. Sporulation of tricarboxylic acid cycle mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):886–894. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.886-894.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


