Abstract
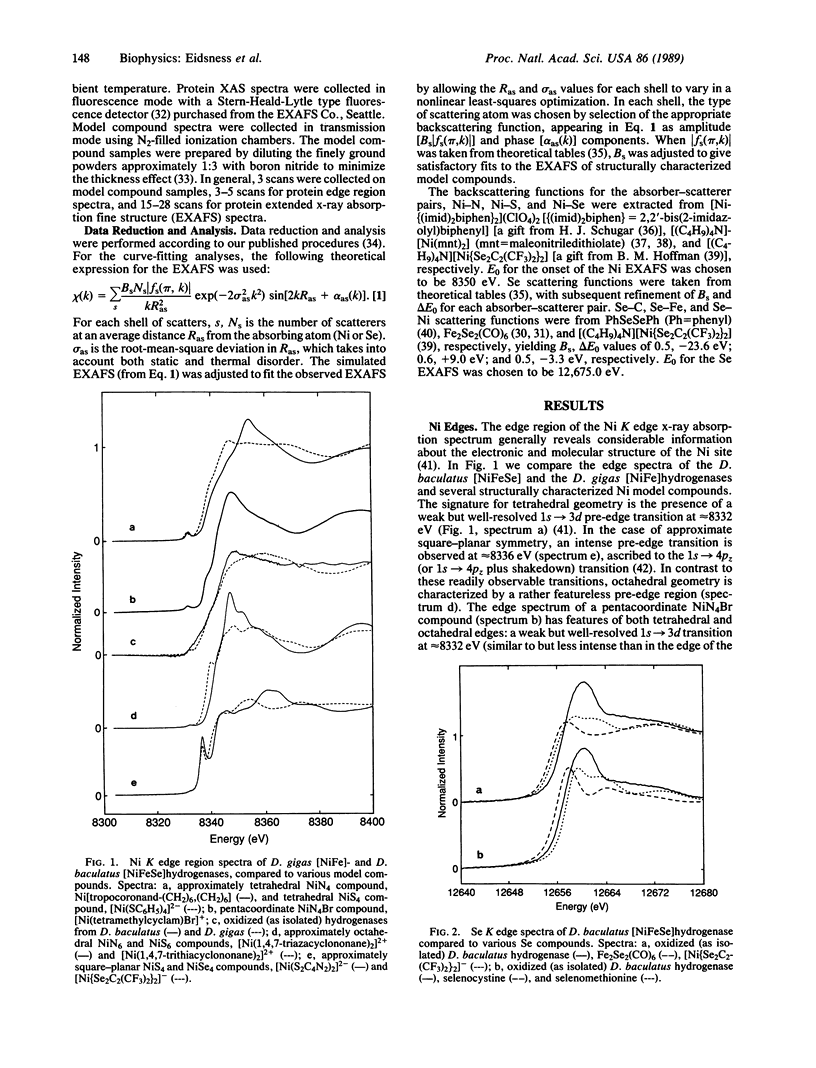
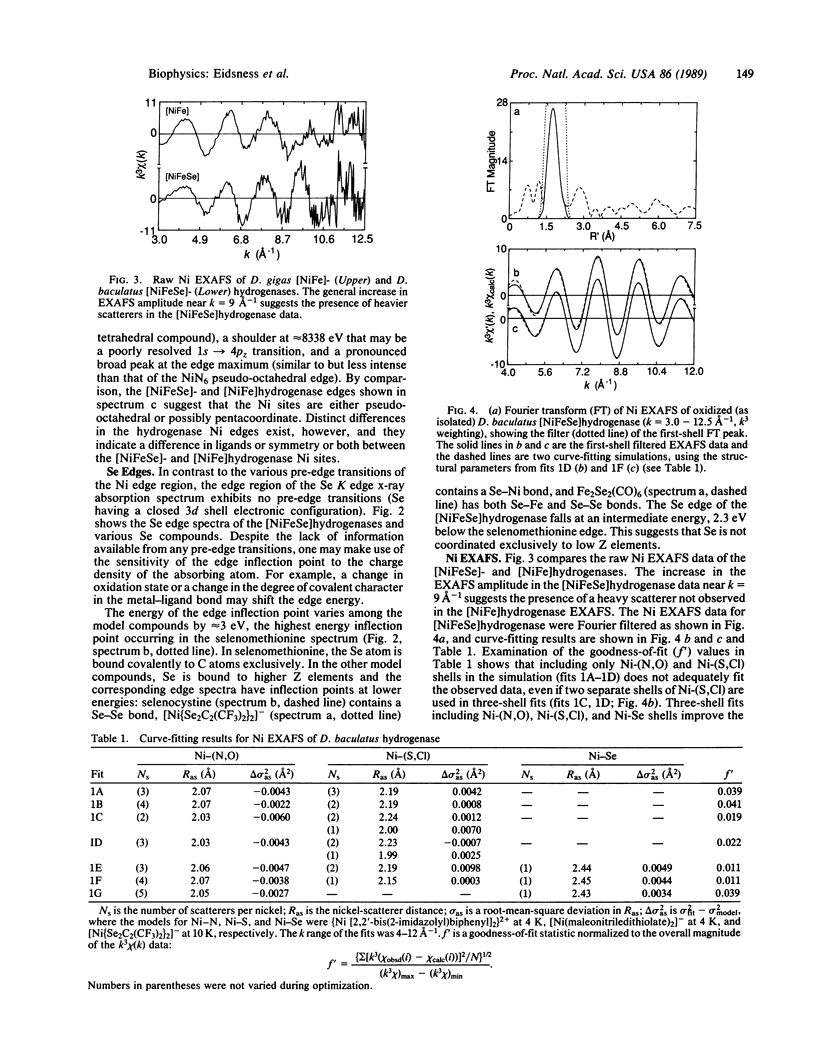
Ni and Se x-ray absorption spectroscopic studies of the [NiFeSe]hydrogenases from Desulfovibrio baculatus are described. The Ni site geometry is pseudo-octahedral with a coordinating ligand composition of 3-4 (N,O) at 2.06 A, 1-2 (S,Cl) at 2.17 A, and 1 Se at 2.44 A. The Se coordination environment consists of 1 C at 2.0 A and a heavy scatterer M (M = Ni or Fe) at approximately 2.4 A. These results are interpreted in terms of a selenocysteine residue coordinated to the Ni site. The possible role of the Ni-Se site in the catalytic activation of H2 is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. W., Mortenson L. E., Chen J. S. Hydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec;594(2-3):105–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(80)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlier Y., Fauque G. D., LeGall J., Choi E. S., Peck H. D., Jr, Lespinat P. A. Inhibition studies of three classes of Desulfovibrio hydrogenase: application to the further characterization of the multiple hydrogenases found in Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90703-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers I., Frampton J., Goldfarb P., Affara N., McBain W., Harrison P. R. The structure of the mouse glutathione peroxidase gene: the selenocysteine in the active site is encoded by the 'termination' codon, TGA. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1221–1227. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czechowski M. H., He S. H., Nacro M., DerVartanian D. V., Peck H. D., Jr, LeGall J. A cytoplasmic nickel-iron hydrogenase with high specific activity from Desulfovibrio multispirans sp. N., a new species of sulfate reducing bacterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91386-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER D. S., PRICE D. C. A SIMPLE SERUM IRON METHOD USING THE NEW SENSITIVE CHROMOGEN TRIPYRIDYL-S-TRIAZINE. Clin Chem. 1964 Jan;10:21–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. R., Martin W. G., Martin S. M. Purification and properties of the periplasmic hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Oct;26(10):1214–1223. doi: 10.1139/m80-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh B. H., Czechowski M. H., Krüger H. J., DerVartanian D. V., Peck H. D., Jr, LeGall J. Desulfovibrio vulgaris hydrogenase: a nonheme iron enzyme lacking nickel that exhibits anomalous EPR and Mössbauer spectra. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3728–3732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger H. J., Huynh B. H., Ljungdahl P. O., Xavier A. V., Der Vartanian D. V., Moura I., Peck H. D., Jr, Teixeira M., Moura J. J., LeGall J. Evidence for nickel and a three-iron center in the hydrogenase of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14620–14623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeGall J., Ljungdahl P. O., Moura I., Peck H. D., Jr, Xavier A. V., Moura J. J., Teixera M., Huynh B. H., DerVartanian D. V. The presence of redox-sensitive nickel in the periplasmic hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio gigas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):610–616. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinfelder W., Zehelein E., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Böck A. Gene for a novel tRNA species that accepts L-serine and cotranslationally inserts selenocysteine. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):723–725. doi: 10.1038/331723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Peck H. D., Jr, LeGall J., Przybyla A. E. Cloning, characterization, and sequencing of the genes encoding the large and small subunits of the periplasmic [NiFe]hydrogenase of Desulfovibrio gigas. DNA. 1987 Dec;6(6):539–551. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissolo T., Choi E. S., LeGall J., Peck H. D., Jr The presence of multiple intrinsic membrane nickel-containing hydrogenases in Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Hildenborough). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):701–708. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon N. K., Peck H. D., Jr, Gall J. L., Przybyla A. E. Cloning and sequencing of the genes encoding the large and small subunits of the periplasmic (NiFeSe) hydrogenase of Desulfovibrio baculatus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5401–5407. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5401-5407.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullenbach G. T., Tabrizi A., Irvine B. D., Bell G. I., Hallewell R. A. Sequence of a cDNA coding for human glutathione peroxidase confirms TGA encodes active site selenocysteine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5484–5484. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prickril B. C., He S. H., Li C., Menon N., Choi E. S., Przybyla A. E., DerVartanian D. V., Peck H. D., Jr, Fauque G., LeGall J. Identification of three classes of hydrogenase in the genus, Desulfovibrio. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90376-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder R., Cammack R., Hall D. O. Purification and properties of the soluble hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans (strain Norway 4). Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):637–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern E. A., Heald S. M. X-ray filter assembly for fluorescence measurements of x-ray absorption fine structure. Rev Sci Instrum. 1979 Dec;50(12):1579–1579. doi: 10.1063/1.1135763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira M., Fauque G., Moura I., Lespinat P. A., Berlier Y., Prickril B., Peck H. D., Jr, Xavier A. V., Le Gall J., Moura J. J. Nickel-[iron-sulfur]-selenium-containing hydrogenases from Desulfovibrio baculatus (DSM 1743). Redox centers and catalytic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 17;167(1):47–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira M., Moura I., Fauque G., Czechowski M., Berlier Y., Lespinat P. A., Le Gall J., Xavier A. V., Moura J. J. Redox properties and activity studies on a nickel-containing hydrogenase isolated from a halophilic sulfate reducer Desulfovibrio salexigens. Biochimie. 1986 Jan;68(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)81071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira M., Moura I., Xavier A. V., Dervartanian D. V., Legall J., Peck H. D., Jr, Huynh B. H., Moura J. J. Desulfovibrio Gigas hydrogenase: redox properties of the nickel and iron-sulfur centers. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;130(3):481–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira M., Moura I., Xavier A. V., Huynh B. H., DerVartanian D. V., Peck H. D., Jr, LeGall J., Moura J. J. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies on the mechanism of activation and the catalytic cycle of the nickel-containing hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio gigas. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8942–8950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voordouw G., Brenner S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Hildenborough). Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):515–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki S. A selenium-containing hydrogenase from Methanococcus vannielii. Identification of the selenium moiety as a selenocysteine residue. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7926–7929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Westen H. M., Mayhew S. G., Veeger C. Separation of hydrogenase from intact cells of Desulfovibrio vulgaris. Purification and properties. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


