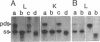Abstract
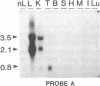
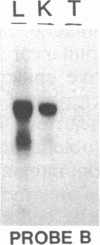
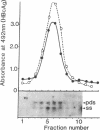
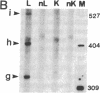
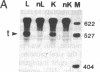
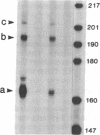
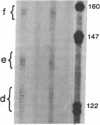
We produced transgenic mice by microinjecting a partial tandem duplication of the complete hepatitis B virus (HBV) genome into fertilized eggs of C57BL/6 mice. One of eight transgenic mice was a high producer for HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) and HBV e antigen (HBeAg) in the serum. The HBV genomes were transmitted to the next generation and these F1 mice also produced HBsAg and HBeAg. mRNAs of 3.5, 2.1, and 0.8 kilobases were detected in the livers and the kidneys of these mice. In addition, a 0.8-kilobase RNA was detected in the testis. Single-stranded and partially double-stranded HBV DNAs were shown to be produced in the cytoplasm of the liver and kidneys. These HBV DNAs were associated with the core particles, indistinguishable from nucleocapsid produced in an infected human liver. Viral genome DNA was detected in the serum. These results demonstrate that the HBV genome integrated into the mouse chromosome acted as a template for viral gene expression, allowing viral replication. Thus, these transgenic mice should be useful for detailed studies of the replication and expression of HBV and for pathological studies of hepatitis, including the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Full text
PDF

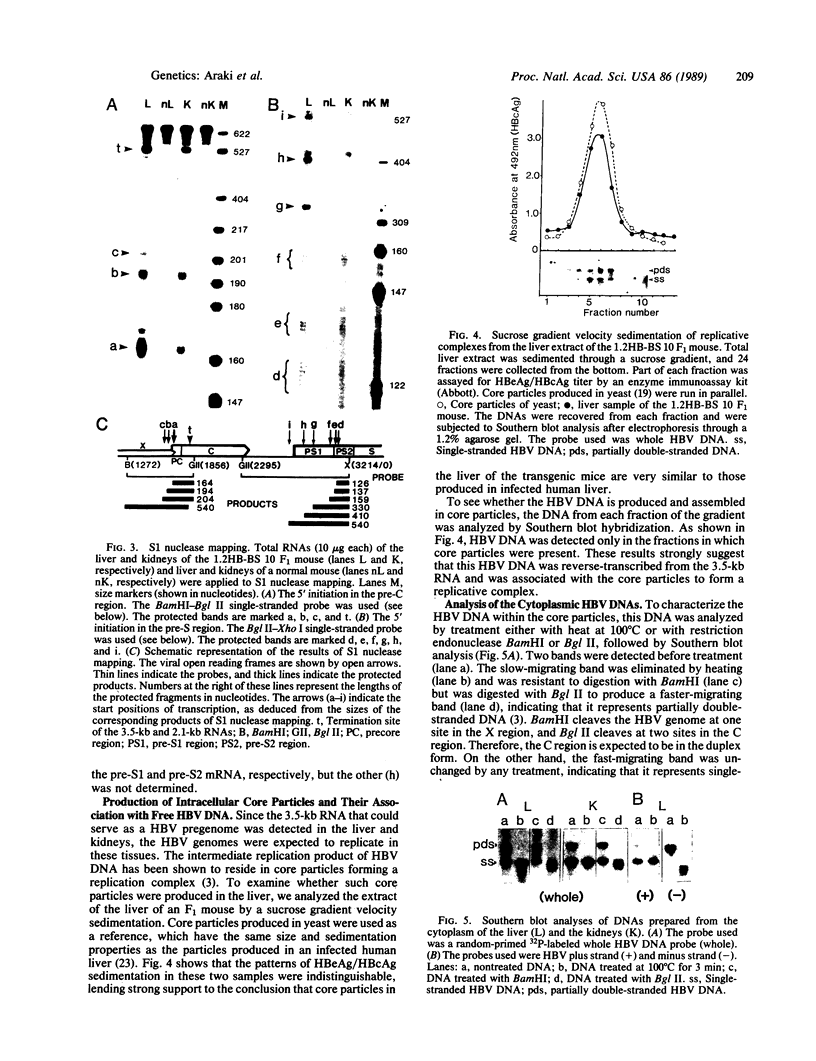


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babinet C., Farza H., Morello D., Hadchouel M., Pourcel C. Specific expression of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in transgenic mice. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1160–1163. doi: 10.1126/science.3865370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Lin C. C., Chien C. S. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk R. D., DeLoia J. A., elAwady M. K., Gearhart J. D. Tissue preferential expression of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen gene in two lines of HBV transgenic mice. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):649–654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.649-654.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. F. High-sensitivity S1 mapping with single-stranded [32P]DNA probes synthesized from bacteriophage M13mp templates. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Schaller H. Hepatitis B virus transcription in the infected liver. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2191–2196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Filippi P., Buras J., McLachlan A., Popper H., Pinkert C. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Structural and pathological effects of synthesis of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6909–6913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Pinkert C. A., Milich D. R., Filippi P., McLachlan A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A transgenic mouse model of the chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier state. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1157–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.3865369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Miyanohara A., Nozaki C., Yoneyama T., Ohtomo N., Matsubara K. Cloning and structural analyses of hepatitis B virus DNAs, subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4601–4610. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. W., Scangos G. A., Plotkin D. J., Barbosa J. A., Ruddle F. H. Genetic transformation of mouse embryos by microinjection of purified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7380–7384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern M. S., England J. M., Deery D. T., Petcu D. J., Mason W. S., Molnar-Kimber K. L. Viral nucleic acid synthesis and antigen accumulation in pancreas and kidney of Pekin ducks infected with duck hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4865–4869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameel S., Siddiqui A. The human hepatitis B virus enhancer requires trans-acting cellular factor(s) for activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):710–715. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Ford E. C., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. Demonstration of subpopulations of Dane particles. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):885–893. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.885-893.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyanohara A., Imamura T., Araki M., Sugawara K., Ohtomo N., Matsubara K. Expression of hepatitis B virus core antigen gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: synthesis of two polypeptides translated from different initiation codons. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):176–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.176-180.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sells M. A., Chen M. L., Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Rutter W. J., Laub O. A human hepatitis B viral enhancer element. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):427–430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Jameel S., Mapoles J. Expression of the hepatitis B virus X gene in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2513–2517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Jameel S., Mapoles J. Transcriptional control elements of hepatitis B surface antigen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):566–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Mullins J. I., Essex M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Mori W., Suwa K. Victoria blue-nuclear fast red stain for HBs antigen detection in paraffin section. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1981 Jan;31(1):93–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1981.tb00987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognoni A., Cattaneo R., Serfling E., Schaffner W. A novel expression selection approach allows precise mapping of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7457–7472. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh H., Hayashida H., Miyata T. Sequence homology between retroviral reverse transcriptase and putative polymerases of hepatitis B virus and cauliflower mosaic virus. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):827–829. doi: 10.1038/305827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Fujiyama A., Matsubara K. Stable expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in an integrated state in a human hepatoma cell line transfected with the cloned viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Shirakata Y., Kobayashi M., Koike K. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) particles are produced in a cell culture system by transient expression of transfected HBV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2678–2682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura K., Kikutani H., Takahashi N., Taga T., Akira S., Kawai K., Fukuchi K., Kumahara Y., Honjo T., Kishimoto T. Introduction of human gamma 1 immunoglobulin genes into fertilized mouse eggs. J Biochem. 1984 Aug;96(2):357–363. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura K., Tsurimoto T., Ebihara T., Kamino K., Fujiyama A., Ochiya T., Matsubara K. Methylation of hepatitis B virus DNA and liver-specific suppression of RNA production in transgenic mouse. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987 Jul;78(7):681–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]