Abstract
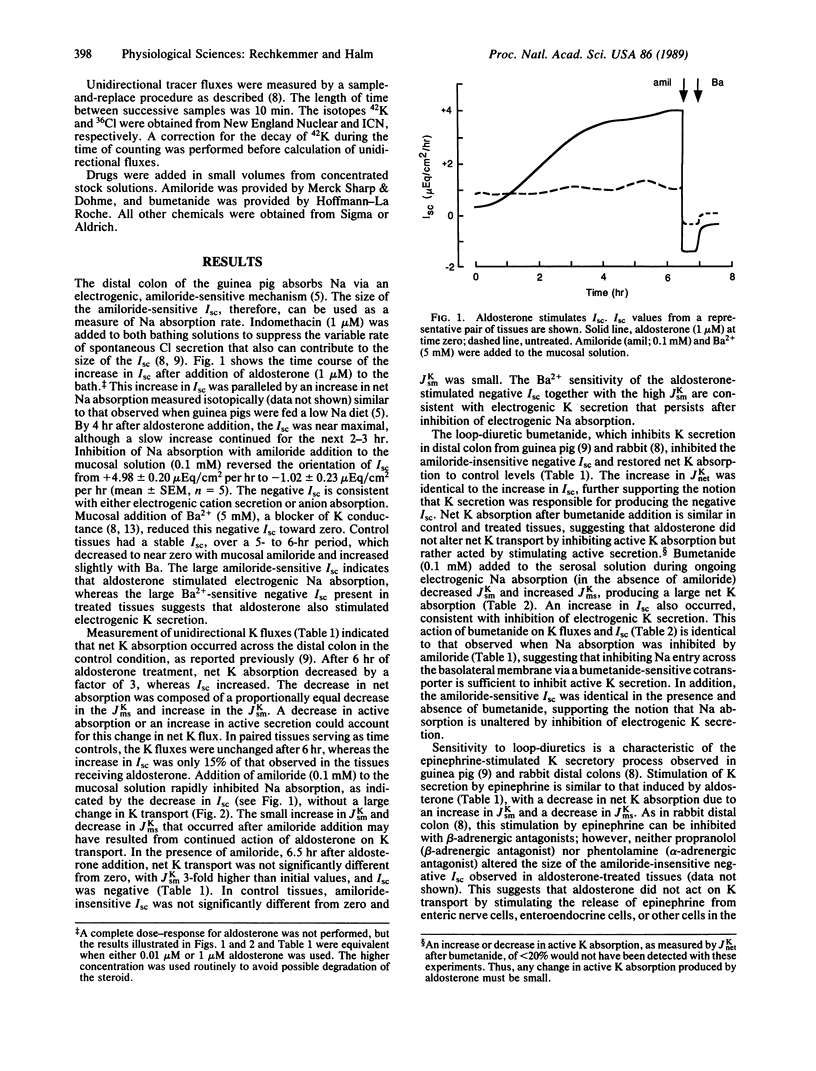
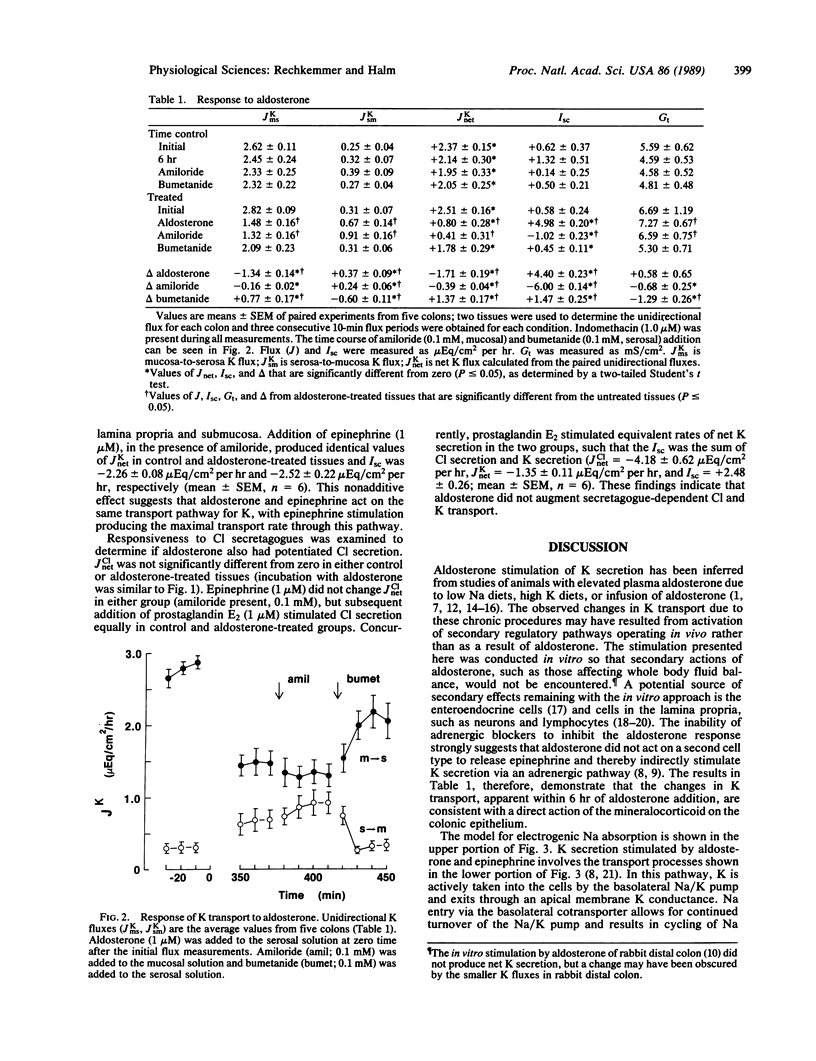
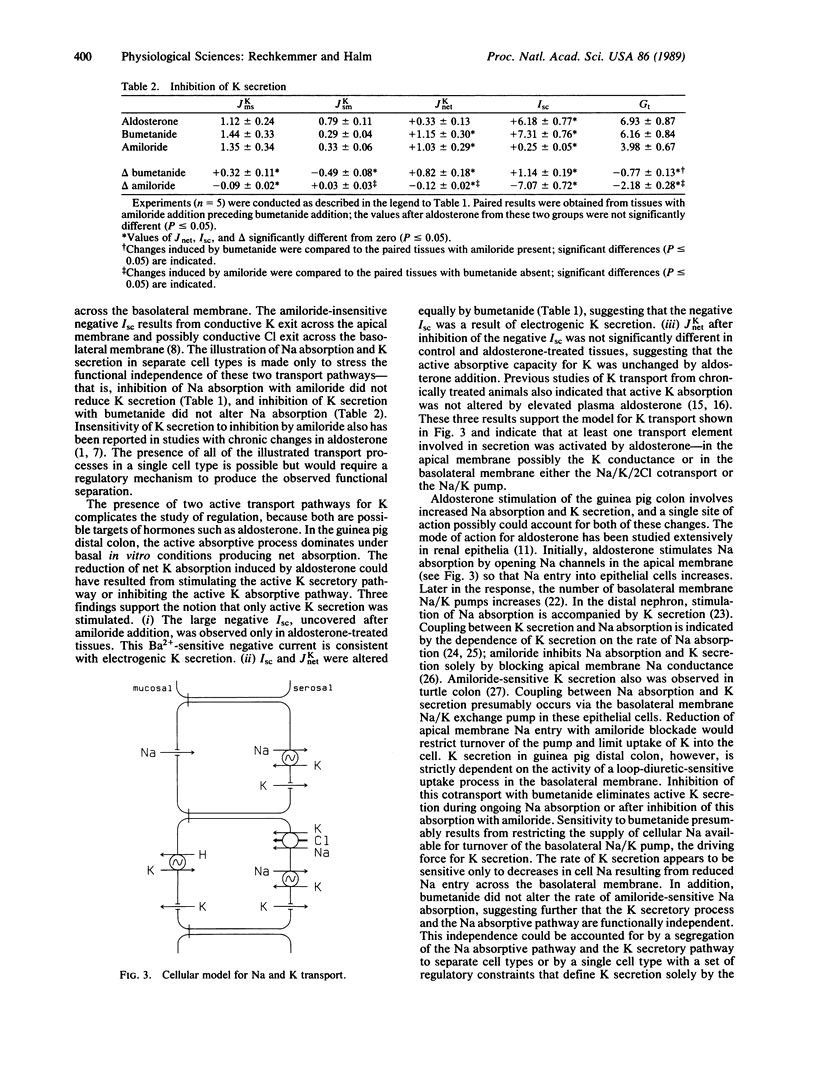
K transport across guinea pig (Cavia porcellus) distal colon was measured in vitro using isotopically determined unidirectional fluxes. Aldosterone stimulated electrogenic Na absorption, as measured by amiloride-sensitive short-circuit current (Isc), and reduced net K absorption from +2.5 +/- 0.2 microEq/cm2 per hr to +0.8 +/- 0.3 microEq/cm2 per hr (mean +/- SEM). Amiloride addition to the mucosal solution did not enhance net K absorption, as expected if inhibiting active Na absorption would reduce active K secretion as in the distal nephron. The amiloride-insensitive Isc was -1.0 +/- 0.2 microEq/cm2 per hr (mean +/- SEM) and was inhibited by mucosal addition of Ba, a K channel blocker. Addition of bumetanide to the serosal solution also inhibited this negative Isc, and K transport returned to the control level of net absorption. Thus, the amiloride-insensitive, negative Isc is consistent with active K secretion stimulated by aldosterone. This stimulation of an active K secretory pathway by aldosterone occurred without altering the active K absorption pathway that also is present. These results indicate that the aldosterone-stimulated K secretory pathway operates independently of the amiloride-sensitive Na absorption pathway, which also is stimulated by aldosterone.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bridges R. J., Rack M., Rummel W., Schreiner J. Mucosal plexus and electrolyte transport across the rat colonic mucosa. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:531–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W. W., Leblond C. P. Renewal of the epithelium in the descending colon of the mouse. I. Presence of three cell populations: vacuolated-columnar, mucous and argentaffin. Am J Anat. 1971 May;131(1):73–99. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001310105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clauss W., Dürr J., Rechkemmer G. Characterization of conductive pathways in guinea pig distal colon in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 1):G176–G183. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.2.G176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster E. S., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Mechanism of active potassium absorption and secretion in the rat colon. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):G611–G617. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.5.G611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster E. S., Jones W. J., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Role of aldosterone and dietary potassium in potassium adaptation in the distal colon of the rat. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster E. S., Sandle G. I., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Dietary potassium modulates active potassium absorption and secretion in rat distal colon. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):G619–G626. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.5.G619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Koch M. J., Schultz S. G. Ion transport by rabbit colon. I. Active and passive components. J Membr Biol. 1976;27(3):297–316. doi: 10.1007/BF01869142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Effect of aldosterone on ion transport by rabbit colon in vitro. J Membr Biol. 1978 Feb 6;39(1):1–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01872752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H. Mechanisms of aldosterone action in tight epithelia. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(3):193–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01870126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geering K., Girardet M., Bron C., Kraehenbühl J. P., Rossier B. C. Hormonal regulation of (Na+,K+)-ATPase biosynthesis in the toad bladder. Effect of aldosterone and 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10338–10343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebisch G., Stanton B. Potassium transport in the nephron. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:241–256. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy J., Budinger M. E., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Role of aldosterone in the regulation of sodium and chloride transport in the distal colon of sodium-depleted rats. Gastroenterology. 1986 Nov;91(5):1227–1233. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(86)80021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halm D. R., Dawson D. C. Potassium transport by turtle colon: active secretion and active absorption. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 1):C315–C322. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.3.C315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halm D. R., Frizzell R. A. Active K transport across rabbit distal colon: relation to Na absorption and Cl secretion. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 1):C252–C267. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.2.C252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M., Biagi B. A., Giebisch G. H. Intracellular microelectrode characterization of the rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F35–F47. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Miller C. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):11–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01870671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. D., Smith P. L., Sullivan L. P. Ion transport by rabbit descending colon: mechanisms of transepithelial potassium transport. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):G594–G602. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.5.G594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R., Cooke H. J., Sullivan L. P. Potassium transport by rabbit descending colon. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):C81–C86. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.1.C81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil R. G., Helman S. I. Transport characteristics of renal collecting tubules: influences of DOCA and diet. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):F544–F558. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.6.F544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechkemmer G., Krause M., Becker G., von Engelhardt W. Konzentrationen von Elektrolyten und kurzkettigen Fettsäuren im Magen-Darm-Trakt des Meerschweinchens bei Normaldiät und bei natriumarmer Diät. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1987 Jan 8;94(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Potassium secretion by cortical collecting tubule: relation to sodium absorption, luminal sodium concentration, and transepithelial voltage. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F395–F402. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannen R. L., Marino R., Dawson D. C. K+ transport by rat colon: adaptation to a low potassium diet. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 2):F483–F487. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.3.F483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper E. J. Local modulation of intestinal ion transport by enteric neurons. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):G457–G468. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.5.G457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnheim K., Plass H., Grasl M., Krivanek P., Wiener H. Sodium absorption and potassium secretion in rabbit colon during sodium deficiency. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 2):F235–F245. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.2.F235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will P. C., Cortright R. N., DeLisle R. C., Douglas J. G., Hopfer U. Regulation of amiloride-sensitive electrogenic sodium transport in the rat colon by steroid hormones. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):G124–G132. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.1.G124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


