Abstract
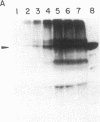
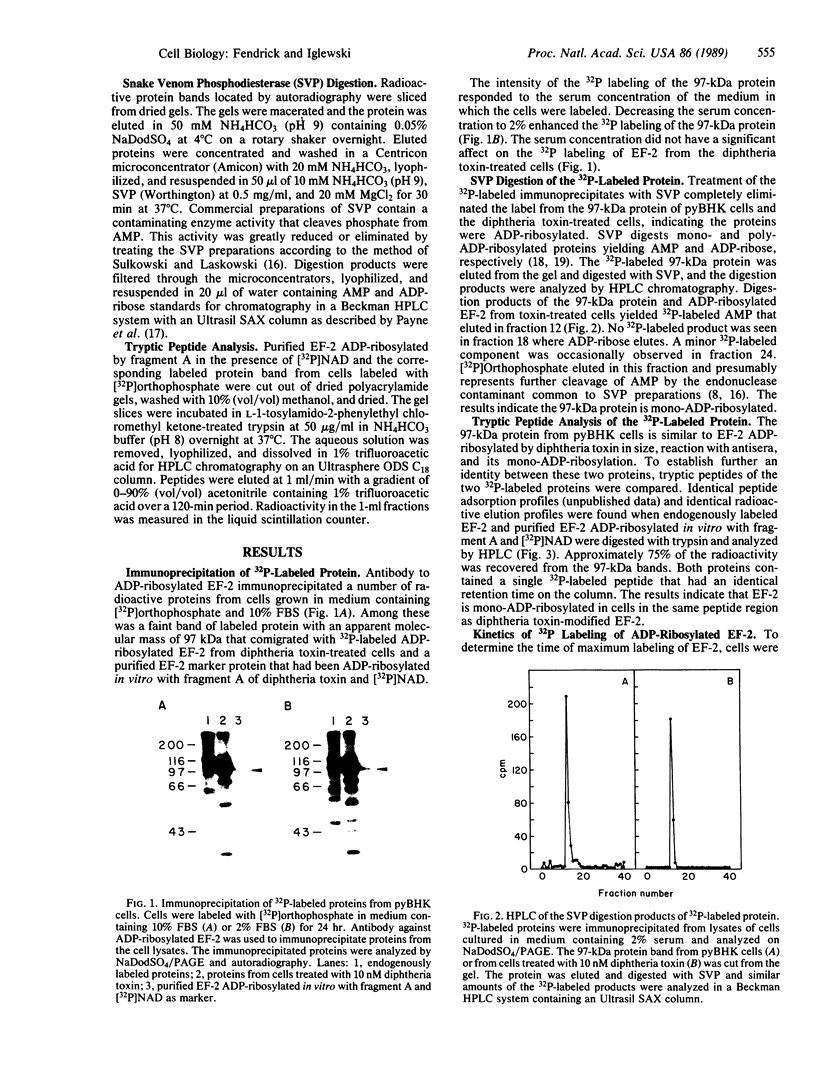
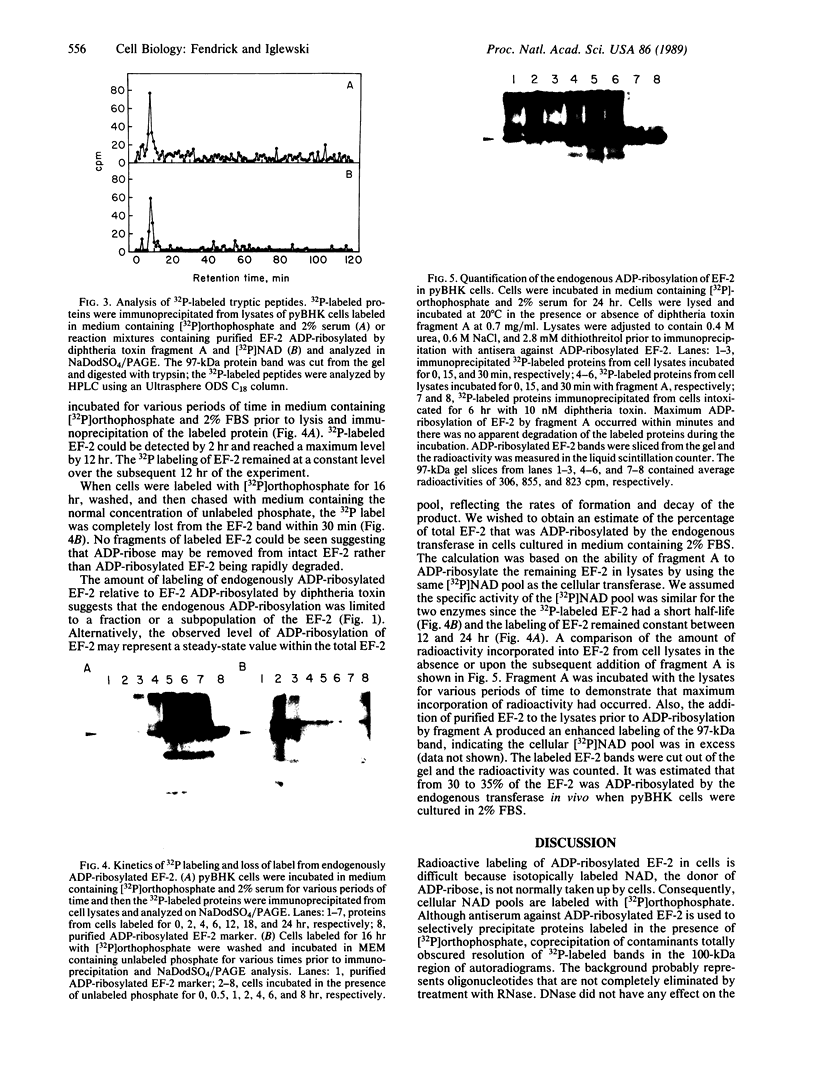
Polyoma virus-transformed baby hamster kidney (pyBHK) cells were cultured in medium containing [32P]orthophosphate and 10% (vol/vol) fetal bovine serum. A 32P-labeled protein with an apparent molecular mass of 97 kDa was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with antiserum to ADP-ribosylated elongation factor 2 (EF-2). The 32P labeling of the protein was enhanced by culturing cells in medium containing 2% serum instead of 10% serum. The 32P label was completely removed from the protein by treatment with snake venom phosphodiesterase and the digestion product was identified as [32P]AMP, indicating the protein was mono-ADP-ribosylated. HPLC analysis of tryptic peptides of the 32P-labeled 97-kDa protein and purified EF-2, which was ADP-ribosylated in vitro with diphtheria toxin fragment A and [32P]NAD, demonstrated an identical labeled peptide in the two proteins. The data strongly suggest that EF-2 was endogenously ADP-ribosylated in pyBHK cells. Maximum incorporation of radioactivity in EF-2 occurred by 12 hr and remained constant over the subsequent 12 hr. It was estimated that 30-35% of the EF-2 was ADP-ribosylated in cells cultured in medium containing 2% serum. When 32P-labeled cultures were incubated in medium containing unlabeled phosphate, the 32P label was lost from the EF-2 within 30 min.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown B. A., Bodley J. W. Primary structure at the site in beef and wheat elongation factor 2 of ADP-ribosylation by diphtheria toxin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):253–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Cole H. A. Diphtheria toxin subunit active in vitro. Science. 1969 Jun 6;164(3884):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3884.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassell J. A., Engelhardt D. L. The regulation of protein synthesis in animal cells by serum factors. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 6;15(7):1375–1381. doi: 10.1021/bi00652a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassell J. A., Engelhardt D. L. Translational inhibition in extracts from serum-deprived animal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 14;324(4):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen O., Smulson M. E. Function and properties of aminoacyl transferase II. II. Subcellular distribution during asynchronous and synchronous growth. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 May;150(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Mamont P., Shields R., Tomkins G. M. "Pleiotypic response". Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug;232(33):206–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3553–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski W. J., Lee H., Muller P. ADP-ribosyltransferase from beef liver which ADP-ribosylates elongation factor-2. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jul 23;173(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski W. J., Lee H. Purification and properties of an altered form of elongation factor 2 from mutant cells resistant to intoxication by diphtheria toxin. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):237–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski W. J., Lee H. Purification and properties of an altered form of elongation factor 2 from mutant cells resistant to intoxication by diphtheria toxin. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):237–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminskas E. Serum-mediated stimulation of protein synthesis in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5470–5476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Iglewski W. J. Cellular ADP-ribosyltransferase with the same mechanism of action as diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas toxin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2703–2707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldave K. Eukaryotic protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1109–1149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer N. J., Bodley J. W. Diphtheria toxin. Site and configuration of ADP-ribosylation of diphthamide in elongation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8579–8581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Levintow L., Bishop J. M. Uninfected vertebrate cells contain a protein that is closely related to the product of the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene (src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Jacobson E. L., Moss J., Jacobson M. K. Modification of proteins by mono(ADP-ribosylation) in vivo. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 17;24(26):7540–7549. doi: 10.1021/bi00347a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Henriksen O., Maxwell E. S. Elongation factor 2. Amino acid sequence at the site of adenosine diphosphate ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5088–5093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayhan O., Ozdemirli M., Nurten R., Bermek E. On the nature of cellular ADP-ribosyltransferase from rat liver specific for elongation factor 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1210–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitikov A. S., Davydova E. K., Ovchinnikov L. P. Endogenous ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 in polyribosome fraction of rabbit reticulocytes. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 15;176(1):261–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80953-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Amos H. Arrested protein synthesis in polysomes of cultured chick embryo cells. Science. 1966 Nov 4;154(3749):662–665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3749.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A., Iglewski B. H., Hager T. A., Sadoff J. C., Cross A. S., McManus A., Farber B. F., Iglewski W. J. Production of exoenzyme S by clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):147–153. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.147-153.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Hayaishi O. ADP-ribosylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:73–100. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Barrowclough B., Bodley J. W. Recognition of elongation factor 2 by diphtheria toxin is not solely defined by the presence of diphthamide. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 20;120(1):4–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Howard J. B., Bodley J. W. ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 by diphtheria toxin. NMR spectra and proposed structures of ribosyl-diphthamide and its hydrolysis products. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10710–10716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Kabat D., Iglewski B. H. Structure-activity relationships of an exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):353–361. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.353-361.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]