Abstract
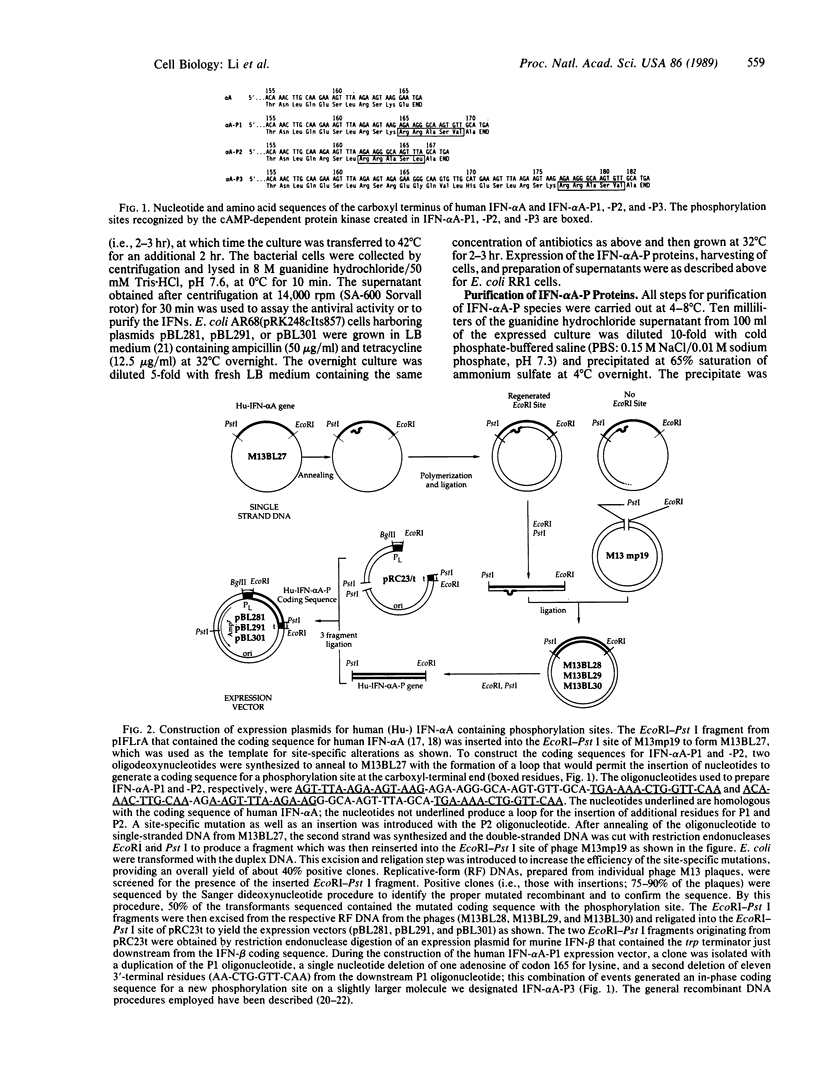
A phosphorylation site was introduced into human interferon alpha A (IFN-alpha A) by site-specific mutation of the coding sequence. Three slightly different phosphorylation sites were created by using the predicted amino acid consensus sequences for phosphorylation by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. The resultant modified interferons (IFN-alpha A-P) were expressed in Escherichia coli and purified. The purified proteins exhibit antiviral activity on bovine and human cells similar to that of the unmodified IFN-alpha A. The IFN-alpha A-P proteins can be phosphorylated by the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase with [gamma-32P]ATP to high specific activity (2000-5000 Ci/mmol; 1 Ci = 37 GBq) with retention of biological activity. The 32P-labeled IFN-alpha A-P proteins bind to cells and can be covalently bound to the IFN-alpha/beta receptor with a bifunctional reagent as can human IFN-alpha A. The introduction of phosphorylation sites into proteins provides a procedure to prepare a large variety of radioactive proteins for research and clinical use.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M. High-affinity binding of 125I-labelled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):459–461. doi: 10.1038/284459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa T., Parker C. G., Lai P. H. Sites of phosphorylation in recombinant human interferon-gamma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 29;136(2):679–684. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90494-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Evidence that types I and II interferons have different receptors. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):768–770. doi: 10.1038/294768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang N. T., Kung H. F., Pestka S. Synthesis of a human leukocyte interferon with a modified carboxy terminus in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):585–589. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R., Seamans C., Lomedico P., McAndrew S. Versatile expression vectors for high-level synthesis of cloned gene products in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarniecki C. W., Fennie C. W., Powers D. B., Estell D. A. Synergistic antiviral and antiproliferative activities of Escherichia coli-derived human alpha, beta, and gamma interferons. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.490-496.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Familletti P. C., Rubinstein S., Pestka S. A convenient and rapid cytopathic effect inhibition assay for interferon. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields R., Mariano T. M., Stein S., Pestka S. Recombinant rat and murine immune interferons are phosphorylated at a single site, Ser132. J Interferon Res. 1988 Aug;8(4):549–557. doi: 10.1089/jir.1988.8.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interferons. Part C. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:1–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A. R., Sarkar F. H., Gupta S. L. Interferon receptors. Cross-linking of human leukocyte interferon alpha-2 to its receptor on human cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13884–13887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Rashidbaigi A., Jones C., Tischfield J. A., Shows T. B., Pestka S. Human chromosomes 6 and 21 are required for sensitivity to human interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4151–4155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. A., Ortaldo J. R., Pestka S. Binding of human alpha-interferons to natural killer cells. J Interferon Res. 1986 Apr;6(2):97–105. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. A., Pestka S. Procedures for studying binding of interferon to human cells in suspension cultures. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:305–311. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. A., Rashidbaigi A., Pestka S. Preparation of 32P-labeled murine immune interferon and its binding to the mouse immune interferon receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9801–9804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., McCandliss R., Gross M., Sloma A., Familletti P. C., Tabor J. M., Evinger M., Levy W. P., Pestka S. Construction and identification of bacterial plasmids containing nucleotide sequence for human leukocyte interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7010–7013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariano T. M., Kozak C. A., Langer J. A., Pestka S. The mouse immune interferon receptor gene is located on chromosome 10. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5812–5814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen K. E., Bandu M. T., Vignaux F., Aguet M., Gressner I. Binding of 125I-labelled human alpha interferon to human lymphoid cells. Int J Cancer. 1981 Nov 15;28(5):575–582. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Interferon from 1981 to 1986. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:3–14. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. The human interferons--from protein purification and sequence to cloning and expression in bacteria: before, between, and beyond. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Feb 15;221(1):1–37. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90118-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Kung H. F., Pestka S. Characterization of receptors for immune interferon in U937 cells with 32P-labeled human recombinant immune interferon. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8514–8519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Langer J. A., Jung V., Jones C., Morse H. G., Tischfield J. A., Trill J. J., Kung H. F., Pestka S. The gene for the human immune interferon receptor is located on chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):384–388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Galliot B., Commoy-Chevalier M. J., Georges P., Chany C. Phosphorylation of recombinant interferon-gamma by kinases released from various cells. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1439–1448. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin T., Hobbs D. S., Kung H., Lai C. Y., Pestka S. Purification and characterization of recombinant human leukocyte interferon (IFLrA) with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9750–9754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R. A., Shatzman A. R., Rosenberg M. Expression and characterization of the human c-myc DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):448–456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonehara S. Radioactive human lymphoblastoid interferon. One-step purification, regulation of heterogeneous species production and its use for radioimmunoassay. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jul;125(3):529–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Arnheiter H. Studies of the interferon receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1984;24(2):259–278. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(84)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K., Zur Nedden D., Arnheiter H. Specific binding of human alpha interferon to a high affinity cell surface binding site on bovine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4695–4697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]