Abstract
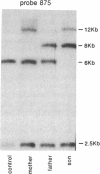
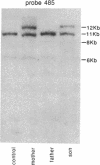
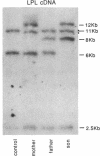
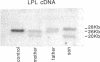
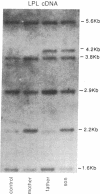
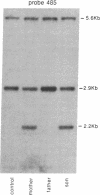
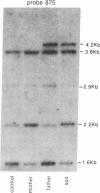
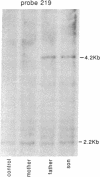
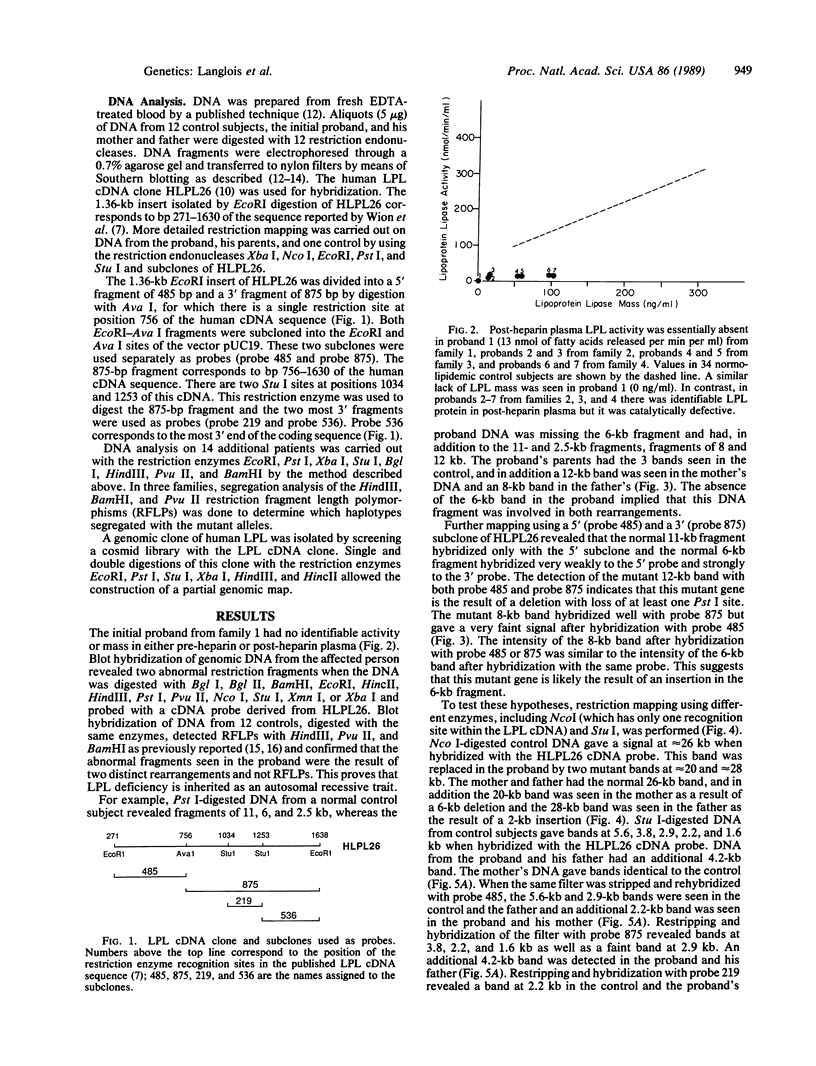
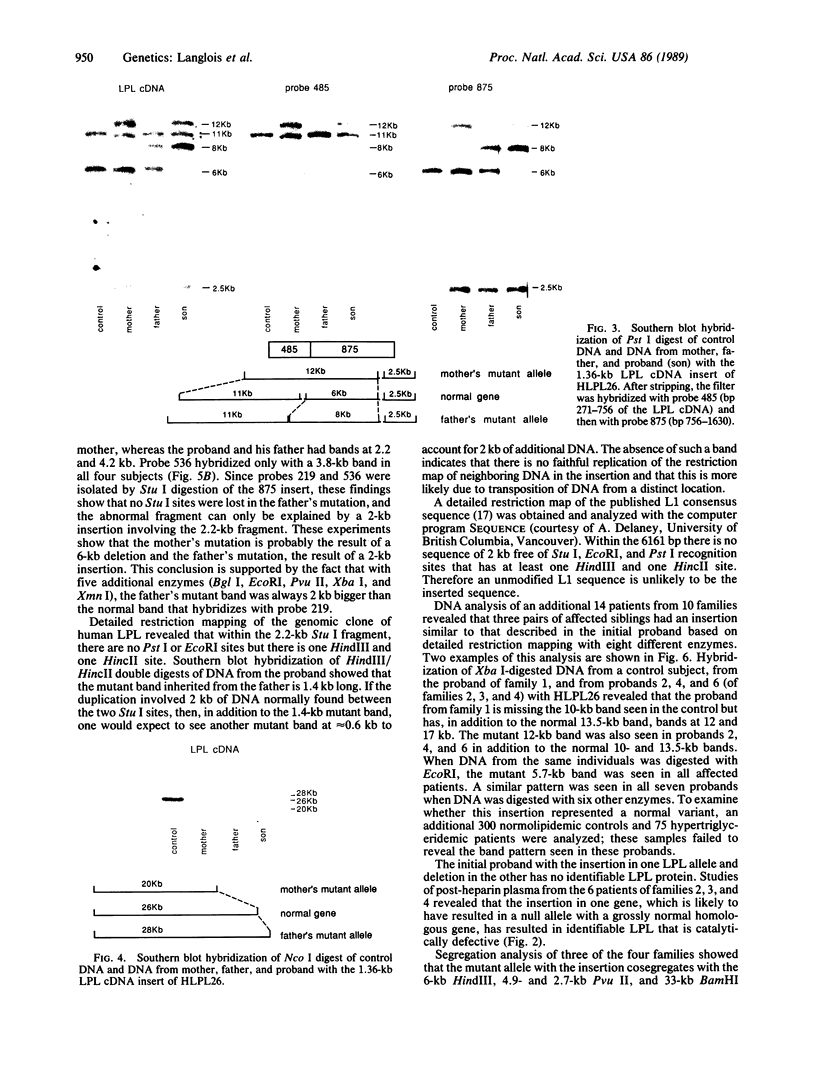
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL; triacylglyceroprotein acylhydrolase, EC 3.1.1.34) is an important enzyme involved in triacylglycerol metabolism. Primary LPL deficiency is a genetic disorder that is usually manifested by a severe elevation in triacylglycerol levels. We have used a recently isolated LPL cDNA clone to study 15 probands from 11 families with this inherited disorder. Surprisingly, 7 of the probands from 4 families, of different ancestries, had a similar insertion in their LPL gene. In contrast to other human genetic disorders, where insertions are rare causes of mutation, this insertion accounts for a significant proportion of the alleles causing LPL deficiency. Detailed restriction mapping of the insertion revealed that it was unlikely to be a duplication of neighboring DNA and that it was not similar to the consensus sequence of human L1 repetitive elements. This suggests that there must be other mechanisms of insertional mutagenesis in human genetic disease besides transposition of mobile L1 repetitive elements.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Youssoufian H., Kazazian H. H., Jr Molecular genetics of hemophilia A in man (factor VIII deficiency). Mol Biol Med. 1987 Apr;4(2):81–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J. H., Deeb S., Brunzell J. D., Peng R., Chait A. Transcriptional activation of the lipoprotein lipase and apolipoprotein E genes accompanies differentiation in some human macrophage-like cell lines. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2651–2655. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley L., Kelley R., Spradling A. Insertional mutagenesis of the Drosophila genome with single P elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1121–1128. doi: 10.1126/science.2830671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher K. L., FitzGerald G. A., Lawn R. M. Two polymorphisms in the human lipoprotein lipase (LPL) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7657–7657. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest S. M., Cross G. S., Speer A., Gardner-Medwin D., Burn J., Davies K. E. Preferential deletion of exons in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):638–640. doi: 10.1038/329638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funke H., Klug J., Assmann G. Hind III RFLP in the lipoprotein lipase gene, (LPL). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):9102–9102. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.9102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., GORDON R. S., Jr Idiopathic hyperlipemia: metabolic studies in an affected family. J Clin Invest. 1960 Dec;39:1777–1790. doi: 10.1172/JCI104202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan W. R., Jr, Winesett P. S., Wasserman A. J. Tissue lipoprotein lipase in normal individuals and in individuals with exogenous hypertriglyceridemia and the relationship of this enzyme to assimilation of fat. J Clin Invest. 1967 Feb;46(2):239–247. doi: 10.1172/JCI105526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden M. R., Kirk H., Clark C., Frohlich J., Rabkin S., McLeod R., Hewitt J. DNA polymorphisms in and around the Apo-A1-CIII genes and genetic hyperlipidemias. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 May;40(5):421–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverius P. H., Brunzell J. D. Human adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase: changes with feeding and relation to postheparin plasma enzyme. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 1):E107–E114. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.249.1.E107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverius P. H., Ostlund-Lindqvist A. M. Lipoprotein lipase from bovine milk. Isolation procedure, chemical characterization, and molecular weight analysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7791–7795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Wong C., Youssoufian H., Scott A. F., Phillips D. G., Antonarakis S. E. Haemophilia A resulting from de novo insertion of L1 sequences represents a novel mechanism for mutation in man. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):164–166. doi: 10.1038/332164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchgessner T. G., Svenson K. L., Lusis A. J., Schotz M. C. The sequence of cDNA encoding lipoprotein lipase. A member of a lipase gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8463–8466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Selective measurement of two lipase activities in postheparin plasma from normal subjects and patients with hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1107–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI107855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois S., Kastelein J. J., Hayden M. R. Characterization of six partial deletions in the low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene causing familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;43(1):60–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Alu-Alu recombination deletes splice acceptor sites and produces secreted low density lipoprotein receptor in a subject with familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3354–3361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. F., Schmeckpeper B. J., Abdelrazik M., Comey C. T., O'Hara B., Rossiter J. P., Cooley T., Heath P., Smith K. D., Margolet L. Origin of the human L1 elements: proposed progenitor genes deduced from a consensus DNA sequence. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90003-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senda M., Oka K., Brown W. V., Qasba P. K., Furuichi Y. Molecular cloning and sequence of a cDNA coding for bovine lipoprotein lipase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J. T., Caskey C. T. HPRT: gene structure, expression, and mutation. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:127–148. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wion K. L., Kirchgessner T. G., Lusis A. J., Schotz M. C., Lawn R. M. Human lipoprotein lipase complementary DNA sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1638–1641. doi: 10.1126/science.3823907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Dunnen J. T., Bakker E., Breteler E. G., Pearson P. L., van Ommen G. J. Direct detection of more than 50% of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations by field inversion gels. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):640–642. doi: 10.1038/329640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]