Abstract
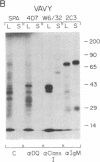
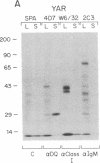
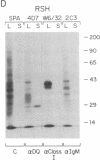
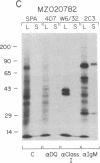
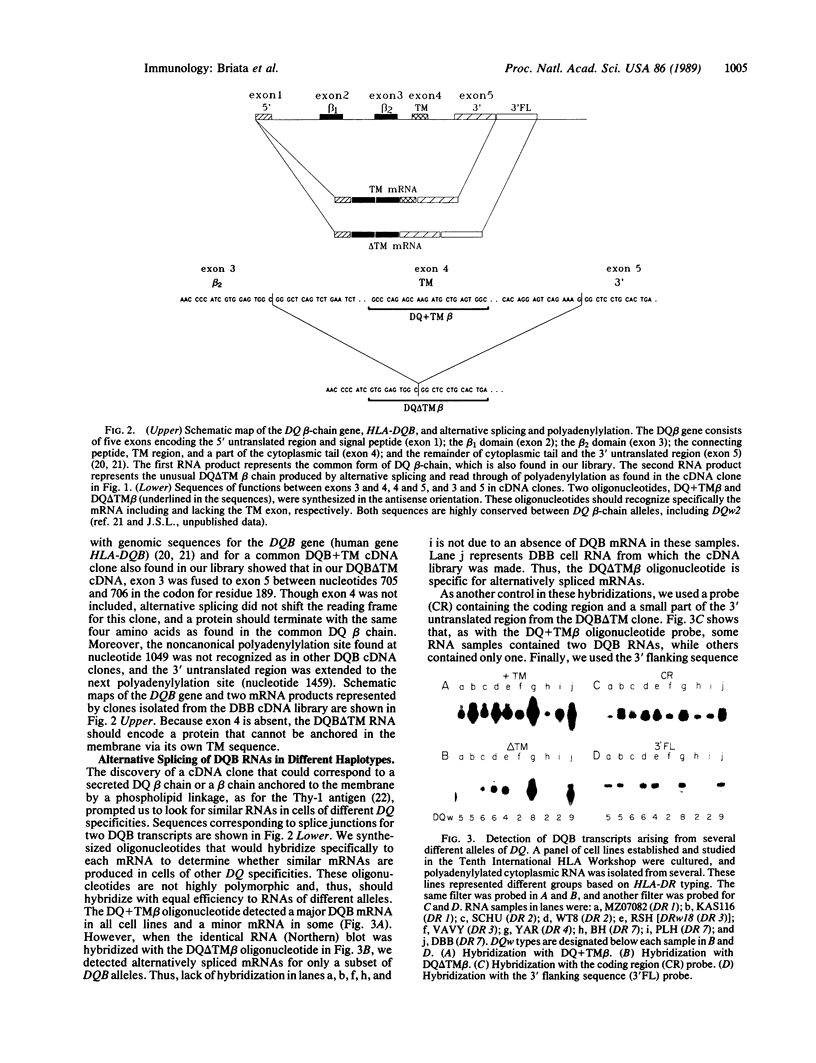
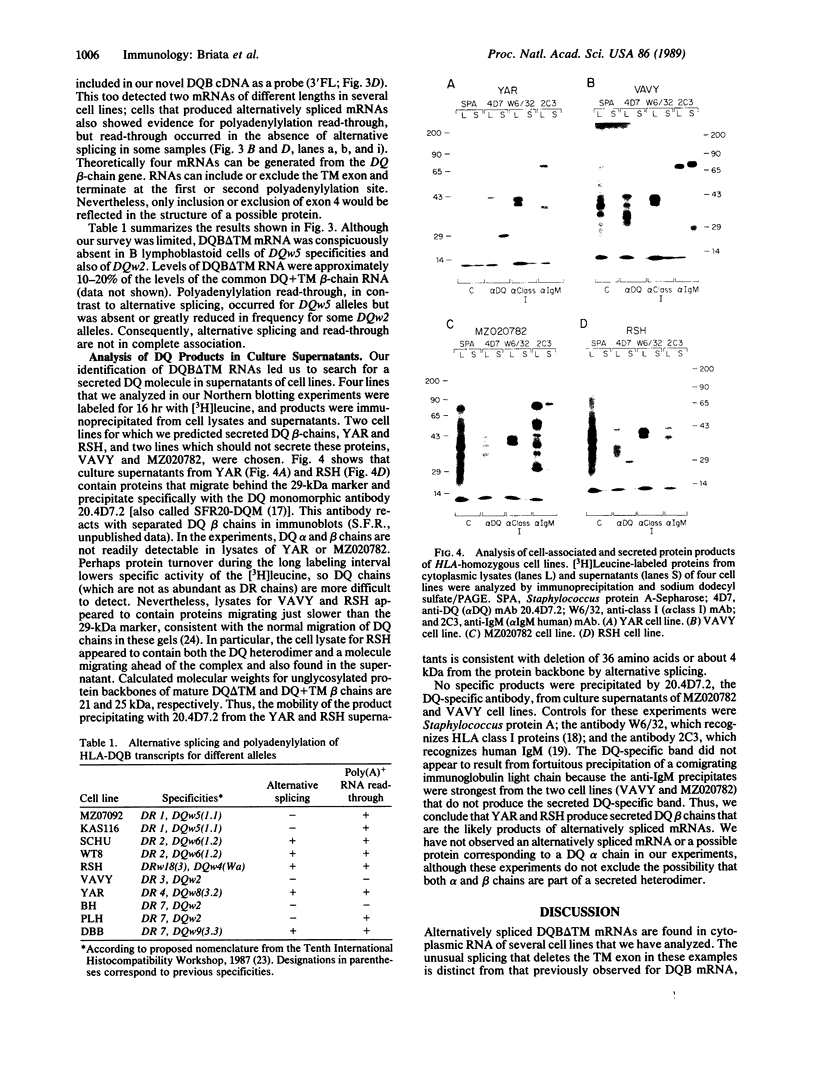
HLA class II antigens are highly polymorphic cell-surface proteins involved in initiation and regulation of the immune response. Allelic sequence variation primarily affects the structure of the first external domains of alpha and beta component chains. Here we provide evidence for other types of allelic polymorphism for the genes encoding these chains. Sequences of two cDNA clones corresponding to HLA-DQB mRNAs from an HLA-homozygous cell line exhibit both alternative splicing and read-through of polyadenylylation. Furthermore, alternative splicing that deletes the transmembrane exon is associated with only a subset of HLA-DQB alleles, while the polyadenylylation-site read-through is found in a larger subset. This suggest that polymorphic cis-acting elements within the HLA-DQB gene control both processing steps. Proteins, presumably encoded by alternatively spliced mRNAs lacking transmembrane exons, are immunoprecipitated with a monomorphic monoclonal antibody directed against HLA-DQ. These proteins are found in supernatants of cultured cell lines for which secretion is predicted, but not in those of cell lines that do not contain alternatively spliced mRNAs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Lillie J. W., Korman A. J., Boss J. M., Fréchin N., Guillemot F., Cooper J., Mulligan R. C., Strominger J. L. Structure and expression of HLA-DQ alpha and -DX alpha genes: interallelic alternate splicing of the HLA-DQ alpha gene and functional splicing of the HLA-DQ alpha gene using a retroviral vector. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(1-2):63–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00345456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. I., Denney D., Jr, Foster L., Belt T., Todd J. A., McDevitt H. O. Allelic variation in the DR subregion of the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6234–6238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Strominger J. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human major histocompatibility complex gene DC-3 beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5199–5203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns J. S., Curtsinger J. M., Dahl C. A., Freeman S., Alter B. J., Bach F. H. Sequence polymorphism of HLA DR beta 1 alleles relating to T-cell-recognized determinants. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):166–168. doi: 10.1038/317166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A., Holly R. C., Dinndorf P. A., Shu G. Polypeptides on human B lymphocytes associated with cell activation. Hum Immunol. 1986 May;16(1):100–113. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume C. R., Accolla R. S., Lee J. S. Defective HLA class II expression in a regulatory mutant is partially complemented by activated ras oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8603–8607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappes D. J., Arnot D., Okada K., Strominger J. L. Structure and polymorphism of the HLA class II SB light chain genes. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2985–2993. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Auffray C., Korman A. J., Shackelford D. A., Strominger J. The class II molecules of the human and murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Boss J. M., Spies T., Sorrentino R., Okada K., Strominger J. L. Genetic complexity and expression of human class II histocompatibility antigens. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:45–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S. Secretion of HLA-A and -B antigens via an alternative RNA splicing pathway. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1173–1190. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Wiman K., Claesson L., Peterson P. A., Dobberstein B. Membrane insertion and oligomeric assembly of HLA-DR histocompatibility antigens. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Hyldig-Nielsen J. J., Servenius B., Andersson G., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Exon-intron organization and complete nucleotide sequence of a human major histocompatibility antigen DC beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7313–7317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Jones P. P., Loken M. R., McDevitt H. O. Interaction between I region loci influences the expression of a cell surface Ia antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5404–5408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartoris S., Cohen E. B., Lee J. S. A rapid and improved method for generating cDNA libraries in plasmid and phage lambda vectors. Gene. 1987;56(2-3):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenning L., Larhammar D., Bill P., Wiman K., Jonsson A. K., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Both alpha and beta chains of HLA-DC class II histocompatibility antigens display extensive polymorphism in their amino-terminal domains. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):447–452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A., Buus S., Colon S., Smith J. A., Miles C., Grey H. M. Structural characteristics of an antigen required for its interaction with Ia and recognition by T cells. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):395–399. doi: 10.1038/328395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Kaufman J. F., Korman A. J., Strominger J. L. HLA-DR antigens: structure, separation of subpopulations, gene cloning and function. Immunol Rev. 1982;66:133–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Platz P., Ryder L. P. HLA and disease 1982--a survey. Immunol Rev. 1983;70:193–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DQ beta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):599–604. doi: 10.1038/329599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers P., Blundell T. L., Sternberg M. J., Bodmer W. F. Structural and evolutionary analysis of HLA-D-region products. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):235–238. doi: 10.1038/310235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto K., Yasunami M., Kimura A., Inoko H., Ando A., Hirose T., Inayama S., Sasazuki T. DQw1 beta gene from HLA-DR2-Dw12 consists of six exons and expresses multiple DQw1 beta polypeptides through alternative splicing. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(5):343–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00404428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Gagnon J. Neuronal cell Thy-1 glycoprotein: homology with immunoglobulin. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):696–703. doi: 10.1126/science.6177036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]