Abstract
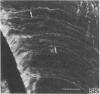
Immunocytochemical studies using monoclonal antibodies directed against oncogenic peptides revealed a heterogeneous distribution of the peptides within the ventricular zone of the embryonic day 18 rat forebrain. The sis-, src-, ras-, and myc-encoded peptides were concentrated in the same isolated clusters of 5-25 radial glial cells (also identified by vimentin staining), providing a transient columnar compartmentalization to the ventricular zone. An increased number of [3H]thymidine-labeled ventricular zone cells were observed within the protooncogene stained radial glial cell columns as compared to noncolumn areas. The columnar heterogeneity of radial glial cells reveals the mosaicism of the embryonic ventricular zone and the differential proliferation of its cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Nuclear location of the putative transforming protein of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Viral oncogenes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton P. C., Brugge J. S. Neural tissues express high levels of the cellular src gene product pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1157–1162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupouey P., Benjelloun S., Gomes D. Immunohistochemical demonstration of an organized cytoarchitecture of the radial glia in the CNS of the embryonic mouse. Dev Neurosci. 1985;7(2):81–93. doi: 10.1159/000112279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Mueckler M. M., Usher P., Lodish H. F. Elevated levels of glucose transport and transporter messenger RNA are induced by ras or src oncogenes. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1492–1495. doi: 10.1126/science.3103217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederiksen K., McKay R. D. Proliferation and differentiation of rat neuroepithelial precursor cells in vivo. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1144–1151. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01144.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fults D. W., Towle A. C., Lauder J. M., Maness P. F. pp60c-src in the developing cerebellum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Simon M. I., Teplow D. B., Robishaw J. D., Gilman A. G. Homologies between signal transducing G proteins and ras gene products. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.6436980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. G., Boyd S. R., van der Kooy D. Compartmentalization of the embryonic striatum after intraocular transplantation. Brain Res. 1987 Jun;430(2):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. M., Beasley L., Stallcup W. B. Localization of a neurectoderm-associated cell surface antigen in the developing and adult rat. Brain Res. 1986 Jun;392(1-2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(86)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. M., Beasley L., Stallcup W. B. The D1.1 antigen: a cell surface marker for germinal cells of the central nervous system. J Neurosci. 1984 Mar;4(3):820–831. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-03-00820.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt P., Cooper M. L., Rakic P. Coexistence of neuronal and glial precursor cells in the cerebral ventricular zone of the fetal monkey: an ultrastructural immunoperoxidase analysis. J Neurosci. 1981 Jan;1(1):27–39. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-01-00027.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misson J. P., Edwards M. A., Yamamoto M., Caviness V. S., Jr Mitotic cycling of radial glial cells of the fetal murine cerebral wall: a combined autoradiographic and immunohistochemical study. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 1;466(2):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niman H. L., Thompson A. M., Yu A., Markman M., Willems J. J., Herwig K. R., Habib N. A., Wood C. B., Houghten R. A., Lerner R. A. Anti-peptide antibodies detect oncogene-related proteins in urine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7924–7928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puelles L., Amat J. A., Martinez-de-la-Torre M. Segment-related, mosaic neurogenetic pattern in the forebrain and mesencephalon of early chick embryos: I. Topography of AChE-positive neuroblasts up to stage HH18. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Dec 8;266(2):247–268. doi: 10.1002/cne.902660210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Early developmental events: cell lineages, acquisition of neuronal positions, and areal and laminar development. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1982 Apr;20(4):439–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J Comp Neurol. 1972 May;145(1):61–83. doi: 10.1002/cne.901450105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Specification of cerebral cortical areas. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):170–176. doi: 10.1126/science.3291116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN R. L., MIALE I. L., FEDER N. Cell proliferation and migration in the primitive ependymal zone: an autoradiographic study of histogenesis in the nervous system. Exp Neurol. 1959 Oct;1:322–333. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Rakic P. A Golgi study of radial glial cells in developing monkey telencephalon: morphogenesis and transformation into astrocytes. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1979 Jun 5;156(2):115–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00300010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Rakic P. Arrested proliferation of radial glial cells during midgestation in rhesus monkey. Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):303–305. doi: 10.1038/277303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Cline M. J. Expression of cellular oncogenes during embryonic and fetal development of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7141–7145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield B. B., O'Leary D. D. Fetal occipital cortical neurones transplanted to the rostral cortex can extend and maintain a pyramidal tract axon. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):135–137. doi: 10.1038/313135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield M. D., Scrace G. T., Whittle N., Stroobant P., Johnsson A., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor is structurally related to the putative transforming protein p28sis of simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):35–39. doi: 10.1038/304035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Waechter R., Jaensch B. Generation times of the matrix cells during embryonic brain development: an autoradiographic study in rats. Brain Res. 1972 Nov 13;46:235–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]