Abstract
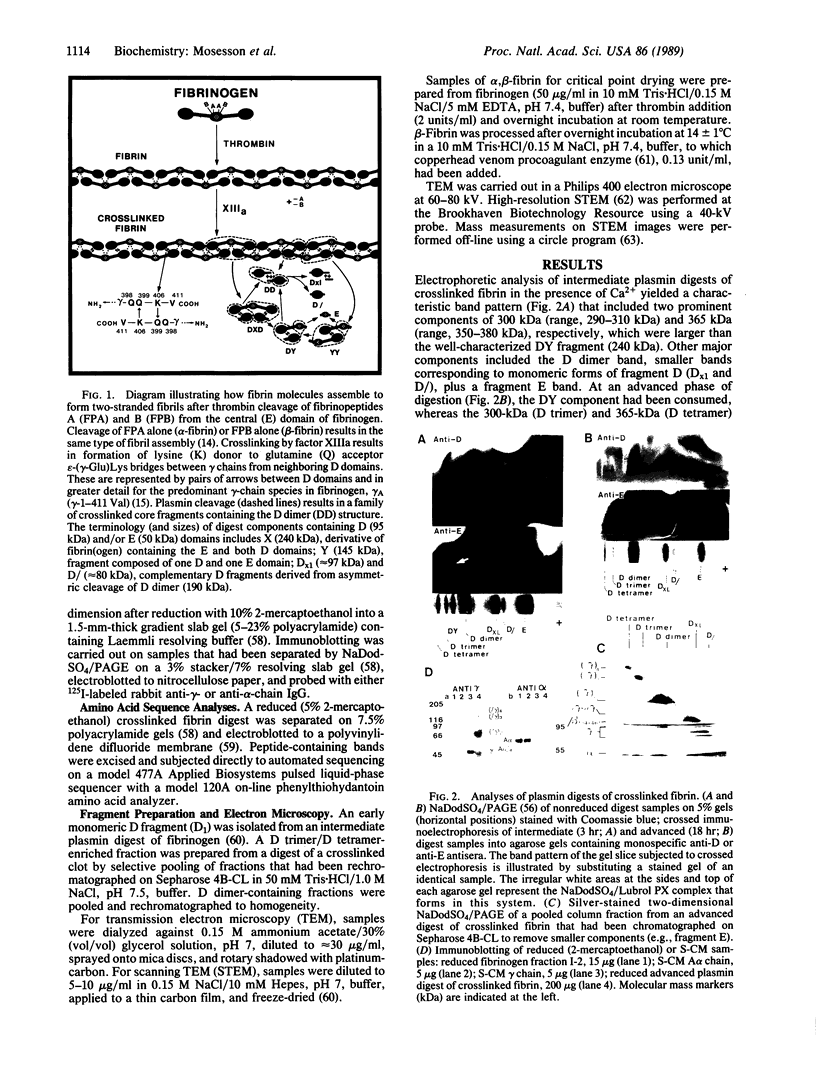
Following proteolytic conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, clot assembly commences with formation of double-stranded fibrils that subsequently branch extensively in forming a three-dimensional network. Plasmin digests of fibrin clots that had first been covalently crosslinked by plasma transglutaminase (factor XIIIa) contained multimeric proteolytic fragments composed of crosslinked outer (D) domains of neighboring fibrin molecules. Two of these were larger than the well-known "D dimer" fragment and corresponded to D trimers and D tetramers, respectively. Whereas D dimers originate from crosslinked D domains at bimolecular junctions within two-stranded fibrils, D trimers and D tetramers evidently arise through crosslinking of contiguous D domains at trimolecular and tetramolecular junctions or at fibril branch points, respectively. Measurement of the widths of fibrils comprising trifunctional branches in thin fiber networks revealed tetramolecular branch points, which are formed by bifurcation of two double-stranded fibrils. In addition, another type of trifunctional structure, which we term the trimolecular branch point, was composed of three double-stranded fibrils. Crosslinking of D domains to form trimers may occur at this type of junction. These findings add to our understanding of the crosslinking arrangements that stabilize fibrin clot structure and the ways that fibrin molecules polymerize to form branches in the clot matrix.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkjaersig N., Davies A., Fletcher A. Fibrin and fibrinogen proteolysis products: comparison between gel filtration and SDS polyacrylamide electrophoresis analysis. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Aug 31;38(2):524–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Hessel B., Hogg D., Therkildsen L. A two-step fibrinogen--fibrin transition in blood coagulation. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):501–505. doi: 10.1038/275501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. E., Jr, Shen L. L., Hermans J. Mass-length ratio of fibrin fibers from gel permeation and light scattering. Biopolymers. 1977 Jan;16(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Doolittle R. F. - cross-linking sites in human and bovine fibrin. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4487–4491. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Doolittle R. F. Identification of the polypeptide chains involved in the cross-linking of fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):420–427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Converse C. A., Papermaster D. S. Membrane protein analysis by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Science. 1975 Aug 8;189(4201):469–472. doi: 10.1126/science.1154021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Chen R., Lau F. Hybrid fibrin: proof of the intermolecular nature of - crosslinking units. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):94–100. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Watt K. W., Cottrell B. A., Strong D. D., Riley M. The amino acid sequence of the alpha-chain of human fibrinogen. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):464–468. doi: 10.1038/280464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P., Fowler W. E. Electron microscopy of fibrinogen, its plasmic fragments and small polymers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:146–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry J. D. The Mechanism of Polymerization of Fibrinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Jul;38(7):566–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.7.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson J. S., Mosesson M. W., Bronzert T. J., Pisano J. J. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. II. Cross-linking capacity of high solubility catabolic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5220–5222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler W. E., Erickson H. P., Hantgan R. R., McDonagh J., Hermans J. Cross-linked fibrinogen dimers demonstrate a feature of the molecular packing in fibrin fibers. Science. 1981 Jan 16;211(4479):287–289. doi: 10.1126/science.6108612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler W. E., Hantgan R. R., Hermans J., Erickson H. P. Structure of the fibrin protofibril. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4872–4876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Marder V. J., Barlow G. H. Plasmic degradation of crosslinked fibrin. Characterization of new macromolecular soluble complexes and a model of their structure. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1033–1043. doi: 10.1172/JCI109931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Marder V. J., Martin S. E. Plasmic degradation of crosslinked fibrin. I. Structural analysis of the particulate clot and identification of new macromolecular-soluble complexes. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):456–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney P. J., Brasher M. Subunit structure of the plasmin-induced degradation products of crosslinked fibrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 25;295(1):308–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney P. J., Joe F., Mahmoud M. Giant fibrin fragments derived from crosslinked fibrin: structure and clinical implication. Thromb Res. 1980 Dec 1;20(5-6):647–662. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90153-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney P. J. The occurrence and clinical relevance of fibrin fragments in blood. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:407–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman J. J., Folk J. E. Structural features of glutamine substrates for human plasma factor XIIIa (activated blood coagulation factor XIII). J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):419–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainfeld J. F., Wall J. S., Desmond E. J. A small computer system for micrograph analysis. Ultramicroscopy. 1982;8(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(82)90242-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantgan R. R., Hermans J. Assembly of fibrin. A light scattering study. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11272–11281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantgan R., Fowler W., Erickson H., Hermans J. Fibrin assembly: a comparison of electron microscopic and light scattering results. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Dec 19;44(3):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantgan R., McDonagh J., Hermans J. Fibrin assembly. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:344–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkate F., Timan G. Protective effect of calcium in the plasmin degradation of fibrinogen and fibrin fragments D. Thromb Res. 1977 Jun;10(6):803–812. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henschen A., Lottspeich F., Kehl M., Southan C. Covalent structure of fibrinogen. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:28–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans J., McDonagh J. Fibrin: structure and interactions. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1982 Jan;8(1):11–24. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzig R. H., Ratnoff O. D., Shainoff J. R. Studies on a procoagulant fraction of southern copperhead snake venom: the preferential release of fibrinopeptide B. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Sep;76(3):451–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewat E. A., Tranqui L., Wade R. H. Electron microscope structural study of modified fibrin and a related modified fibrinogen aggregate. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):203–222. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow W., Endres G. F., Siegel B. M., Scheraga H. A. An electron microscopic investigation of the polymerization of bovine fibrin monomer. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 28;71(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Studies on synthetic peptides that bind to fibrinogen and prevent fibrin polymerization. Structural requirements, number of binding sites, and species differences. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):1013–1019. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Synthetic peptide derivatives that bind to fibrinogen and prevent the polymerization of fibrin monomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3085–3089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Budzynski A. Z., Barlow G. H. Comparison of the physicochemical properties of fragment D derivatives of fibrinogen and fragment D-D of cross-linked fibrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 18;427(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matacić S., Loewy A. G. The identification of isopeptide crosslinks in insoluble fibrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 26;30(4):356–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90750-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh R. P., McDonagh J., Blombäck M., Blombäck B. Crosslinking of human fibrin: Evidence for intermolecular crosslinking involving alpha-chains. FEBS Lett. 1971 Apr 12;14(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. A., Mattock P., Hill R. L. Subunit structure of human fibrinogen, soluble fibrin, and cross-linked insoluble fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):738–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
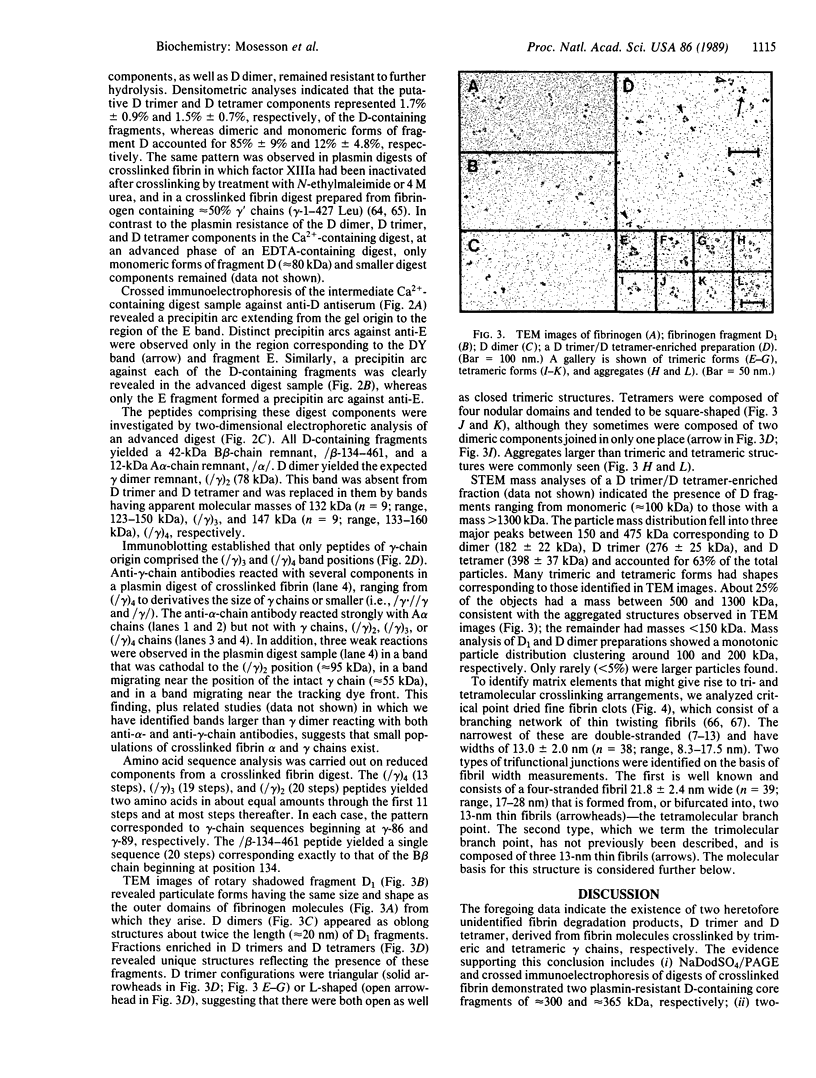
- Mosesson M. W., DiOrio J. P., Müller M. F., Shainoff J. R., Siebenlist K. R., Amrani D. L., Homandberg G. A., Soria J., Soria C., Samama M. Studies on the ultrastructure of fibrin lacking fibrinopeptide B (beta-fibrin). Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1073–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S. The search for the structure of fibrinogen. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:61–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Umfleet R. A. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. 3. Identification of chain variants. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5223–5227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Hainfeld J., Wall J., Haschemeyer R. H. Identification and mass analysis of human fibrinogen molecules and their domains by scanning transmission electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):695–718. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. F., Ris H., Ferry J. D. Electron microscopy of fine fibrin clots and fine and coarse fibrin films. Observations of fibers in cross-section and in deformed states. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 5;174(2):369–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90343-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuizen W., Vermond A., Haverkate F. Factors influencing the structure of terminal plasmin degradation products of human fibrinogen and fibrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 27;667(2):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
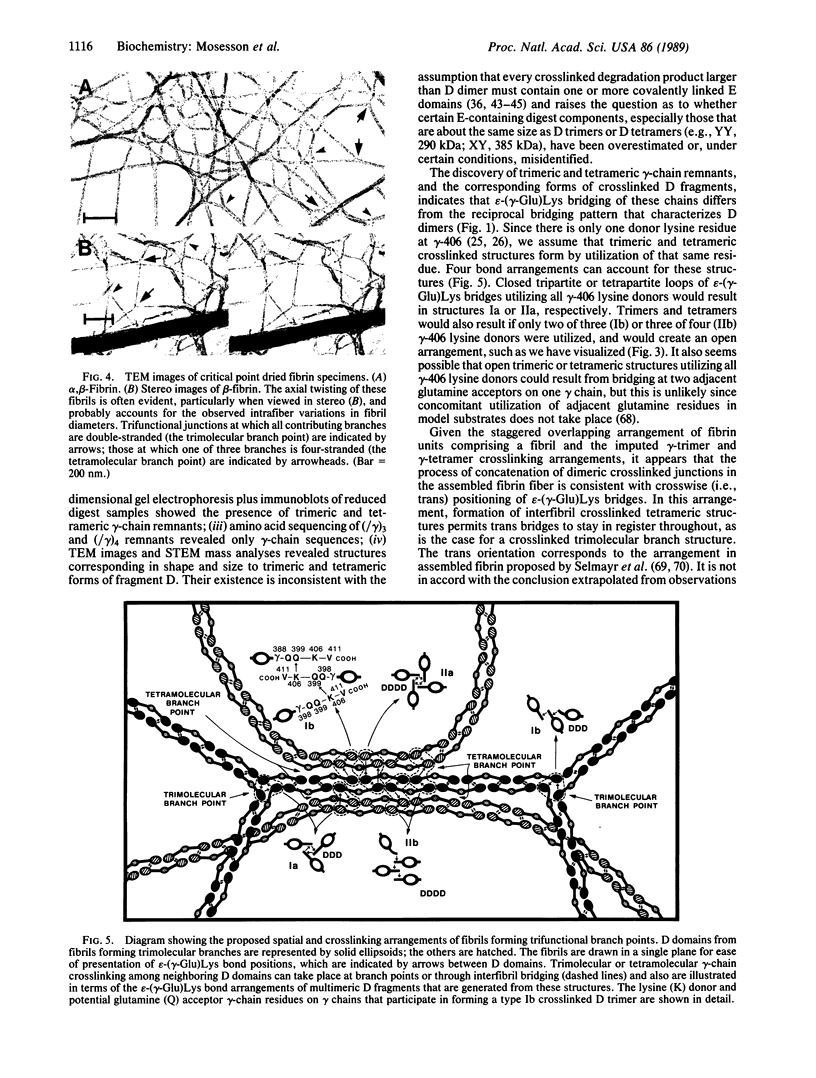
- Nieuwenhuizen W., Voskuilen M., Vermond A., Haverkate F., Hermans J. A fibrinogen fragment D (D intermediate) with calcium binding but without anticlotting properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 5;707(2):190–192. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90349-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olexa S. A., Budzynski A. Z. Evidence for four different polymerization sites involved in human fibrin formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Finlayson J. S., Peyton M. P. [Cross-link in fibrin polymerized by factor 13: epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine]. Science. 1968 May 24;160(3830):892–893. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3830.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo S. V., Schwartz M. L., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of plasmin on the subunit structure of human fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4574–4583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo S. V., Taylor L. M., Jr, Schwartz M. L., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. Subunit structure of fragment D from fibrinogen and cross-linked fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4584–4590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves L. R., Lindsey G. G., Brown G., Franks J. Stabilization of the plasmin digestion products of fibrinogen and fibrin by calcium ions. Thromb Res. 1978 Mar;12(3):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves L., Purves M., Brandt W. Cleavage of fibrin-derived D-dimer into monomers by endopeptidase from puff adder venom (Bitis arietans) acting at cross-linked sites of the gamma-chain. Sequence of carboxy-terminal cyanogen bromide gamma-chain fragments. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4640–4646. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regañon E., Vila V., Aznar J. Identification of high molecular weight derivatives of plasmic digests of cross-linked human fibrin. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Oct 31;40(2):368–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of fibrin-stabilizing factor on the subunit structure of human fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1506–1513. doi: 10.1172/JCI106636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmayr E., Deffner M., Bachmann L., Müller-Berghaus G. Chromatography and electron microscopy of cross-linked fibrin polymers--a new model describing the cross-linking at the DD-trans contact of the fibrin molecules. Biopolymers. 1988 Nov;27(11):1733–1748. doi: 10.1002/bip.360271104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmayr E., Thiel W., Müller-Berghaus G. Crosslinking of fibrinogen to immobilized DesAA-fibrin. Thromb Res. 1985 Aug 15;39(4):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Dardik B. N. Fibrinopeptide B and aggregation of fibrinogen. Science. 1979 Apr 13;204(4389):200–202. doi: 10.1126/science.155308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Dardik B. N. Fibrinopeptide B in fibrin assembly and metabolism: physiologic significance in delayed release of the peptide. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:254–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt K. W., Takagi T., Doolittle R. F. Amino acid sequence of the beta chain of human fibrinogen. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):68–76. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C. Morphology of bovine fibrinogen monomers and fibrin oligomers. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 15;150(3):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90555-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C. Morphology of fibrinogen monomers and of fibrin protofibrils. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:180–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenstein-Todel C., Mosesson M. W. Carboxy-terminal amino acid sequence of a human fibrinogen gamma-chain variant (gamma'). Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6146–6149. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenstein-Todel C., Mosesson M. W. Human plasma fibrinogen heterogeneity: evidence for an extended carboxyl-terminal sequence in a normal gamma chain variant (gamma'). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]