Abstract
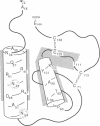
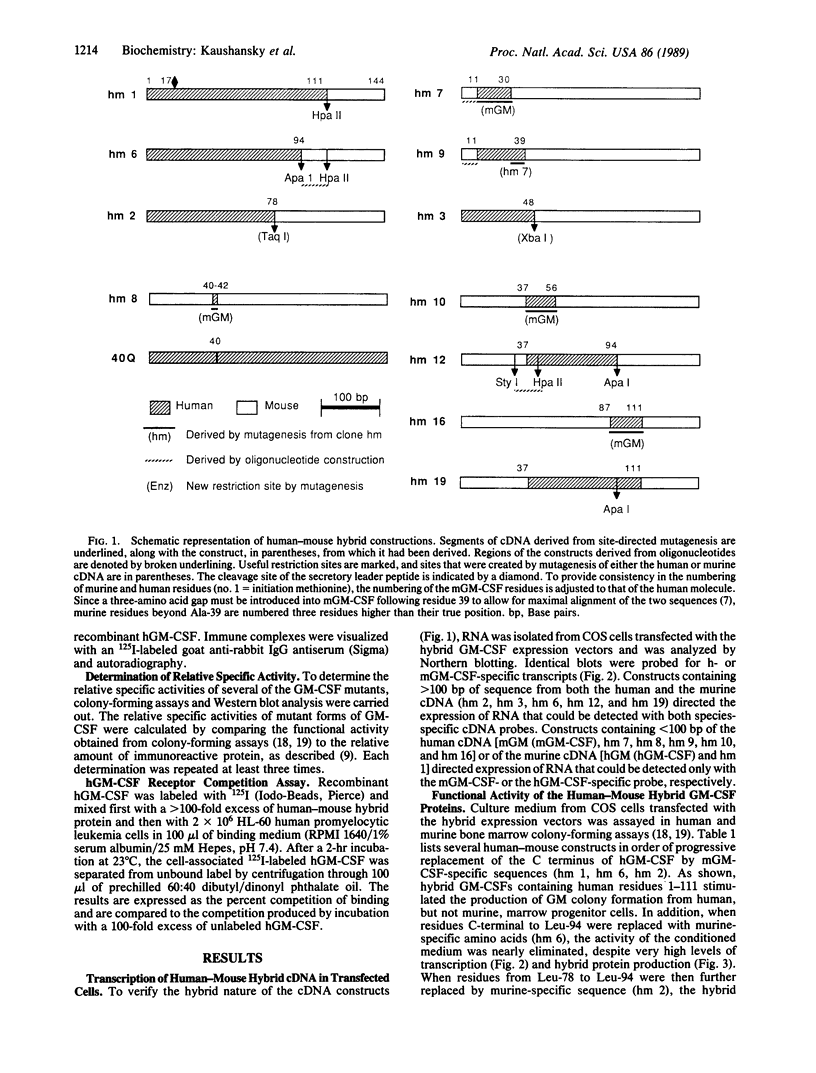
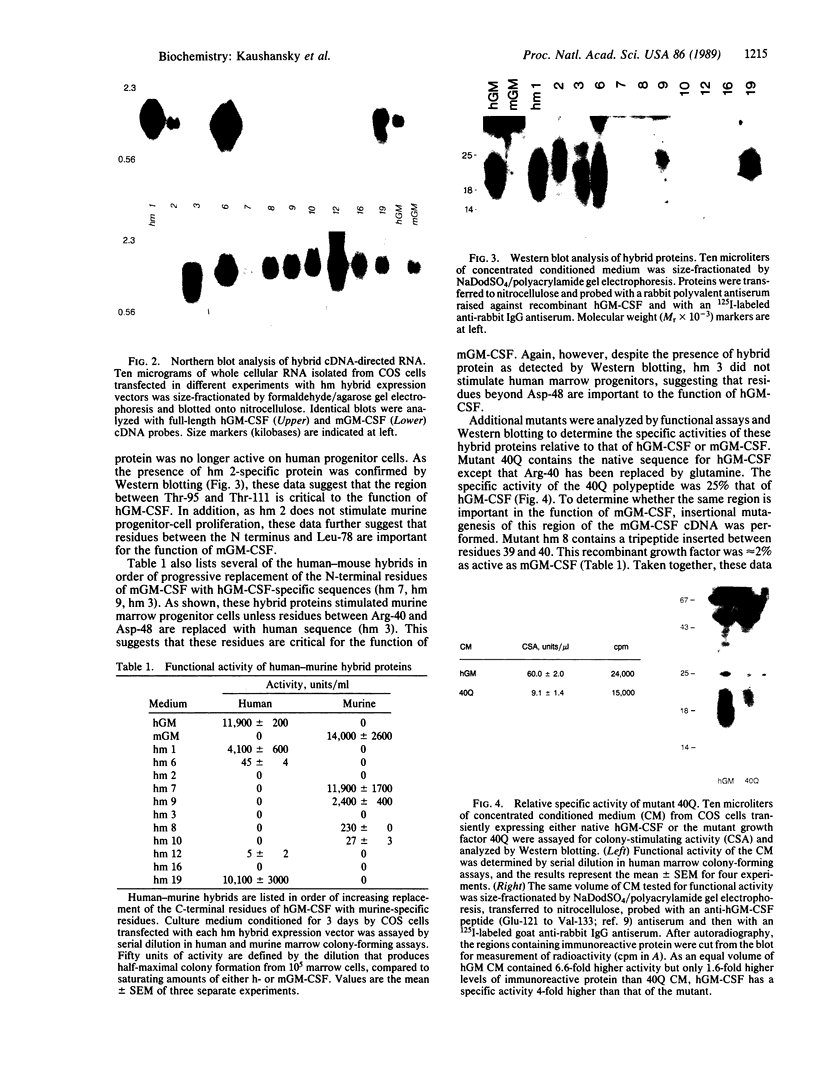
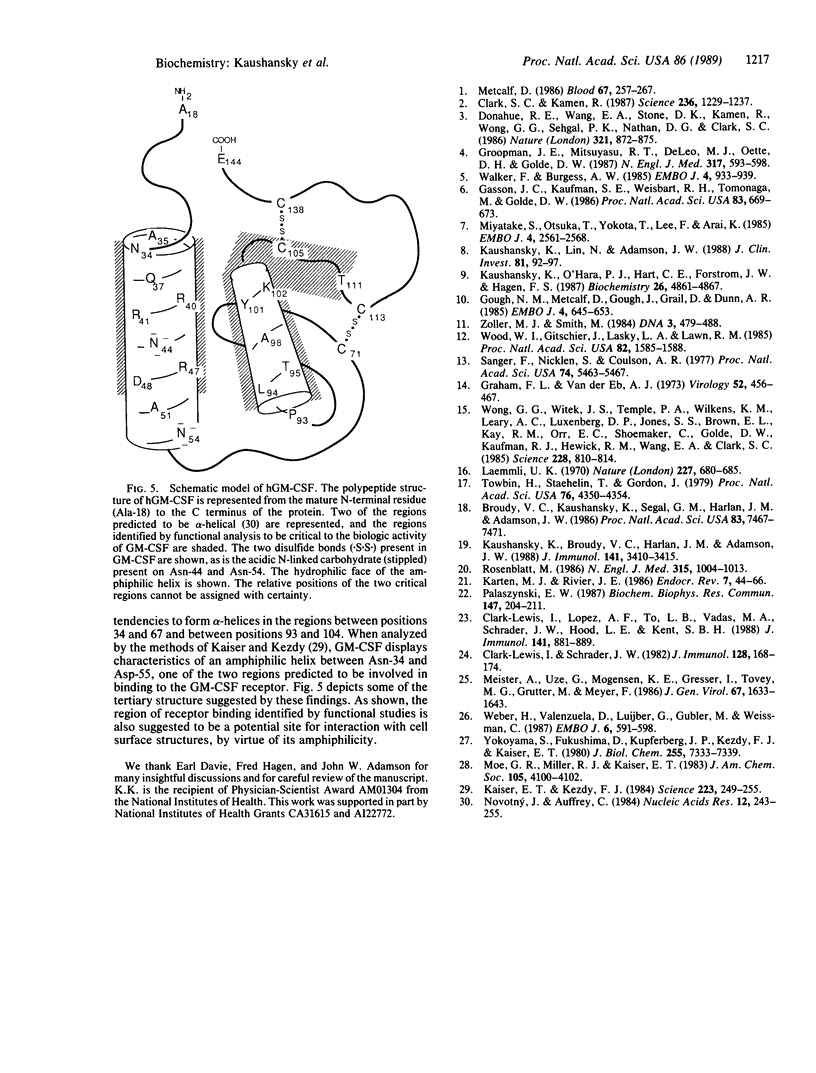
Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is an acidic glycoprotein that stimulates hematopoiesis in vitro and in vivo. Despite a high degree of sequence homology, the GM-CSFs from human and murine sources fail to crossreact in their respective colony-forming assays. On the basis of this finding, a series of hybrid molecules containing various proportions of human- and murine-specific amino acid sequences were generated by recombinant DNA techniques and assayed for species-specific activity against human and murine marrow target cells. Two regions of GM-CSF, residues 38-48 and residues 95-111, were found to be critical for hematopoietic function. These regions are structurally characterized by an amphiphilic helix and by a disulfide-bonded loop, respectively, and are homologous in position in the human and murine growth factors. In addition, competition assays suggested that, together, these regions bind to the GM-CSF receptor.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broudy V. C., Kaushansky K., Segal G. M., Harlan J. M., Adamson J. W. Tumor necrosis factor type alpha stimulates human endothelial cells to produce granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7467–7471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Lopez A. F., To L. B., Vadas M. A., Schrader J. W., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Structure-function studies of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Identification of residues required for activity. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):881–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Schrader J. W. Biochemical characterization of regulatory factors derived from T cell hybridomas and spleen cells. I. Separation of T cell growth factor and T cell replacing factor from granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):168–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. C., Kamen R. The human hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1229–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3296190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue R. E., Wang E. A., Stone D. K., Kamen R., Wong G. G., Sehgal P. K., Nathan D. G., Clark S. C. Stimulation of haematopoiesis in primates by continuous infusion of recombinant human GM-CSF. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):872–875. doi: 10.1038/321872a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Kaufman S. E., Weisbart R. H., Tomonaga M., Golde D. W. High-affinity binding of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to normal and leukemic human myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Metcalf D., Gough J., Grail D., Dunn A. R. Structure and expression of the mRNA for murine granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):645–653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groopman J. E., Mitsuyasu R. T., DeLeo M. J., Oette D. H., Golde D. W. Effect of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on myelopoiesis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 3;317(10):593–598. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709033171003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J. Amphiphilic secondary structure: design of peptide hormones. Science. 1984 Jan 20;223(4633):249–255. doi: 10.1126/science.6322295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karten M. J., Rivier J. E. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analog design. Structure-function studies toward the development of agonists and antagonists: rationale and perspective. Endocr Rev. 1986 Feb;7(1):44–66. doi: 10.1210/edrv-7-1-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushansky K., Broudy V. C., Harlan J. M., Adamson J. W. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and tumor necrosis factor-beta (lymphotoxin) stimulate the production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and IL-1 in vivo. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3410–3415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushansky K., Lin N., Adamson J. W. Interleukin 1 stimulates fibroblasts to synthesize granulocyte-macrophage and granulocyte colony-stimulating factors. Mechanism for the hematopoietic response to inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):92–97. doi: 10.1172/JCI113316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushansky K., O'Hara P. J., Hart C. E., Forstrom J. W., Hagen F. S. Role of carbohydrate in the function of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4861–4867. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Uzé G., Mogensen K. E., Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Grütter M., Meyer F. Biological activities and receptor binding of two human recombinant interferons and their hybrids. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1633–1643. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The molecular biology and functions of the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):257–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Otsuka T., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor: comparison of the mouse and human genes. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2561–2568. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03971.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Auffray C. A program for prediction of protein secondary structure from nucleotide sequence data: application to histocompatibility antigens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):243–255. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palaszynski E. W. Synthetic C-terminal peptide of IL-1 functions as a binding domain as well as an antagonist for the IL-1 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):204–211. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt M. Peptide hormone antagonists that are effective in vivo. Lessons from parathyroid hormone. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 16;315(16):1004–1013. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610163151606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F., Burgess A. W. Specific binding of radioiodinated granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to hemopoietic cells. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):933–939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03721.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber H., Valenzuela D., Lujber G., Gubler M., Weissmann C. Single amino acid changes that render human IFN-alpha 2 biologically active on mouse cells. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):591–598. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Fukushima D., Kupferberg J. P., Kézdy F. J., Kaiser E. T. The mechanism of activation of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase by apolipoprotein A-I and an amphiphilic peptide. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7333–7339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]