Abstract
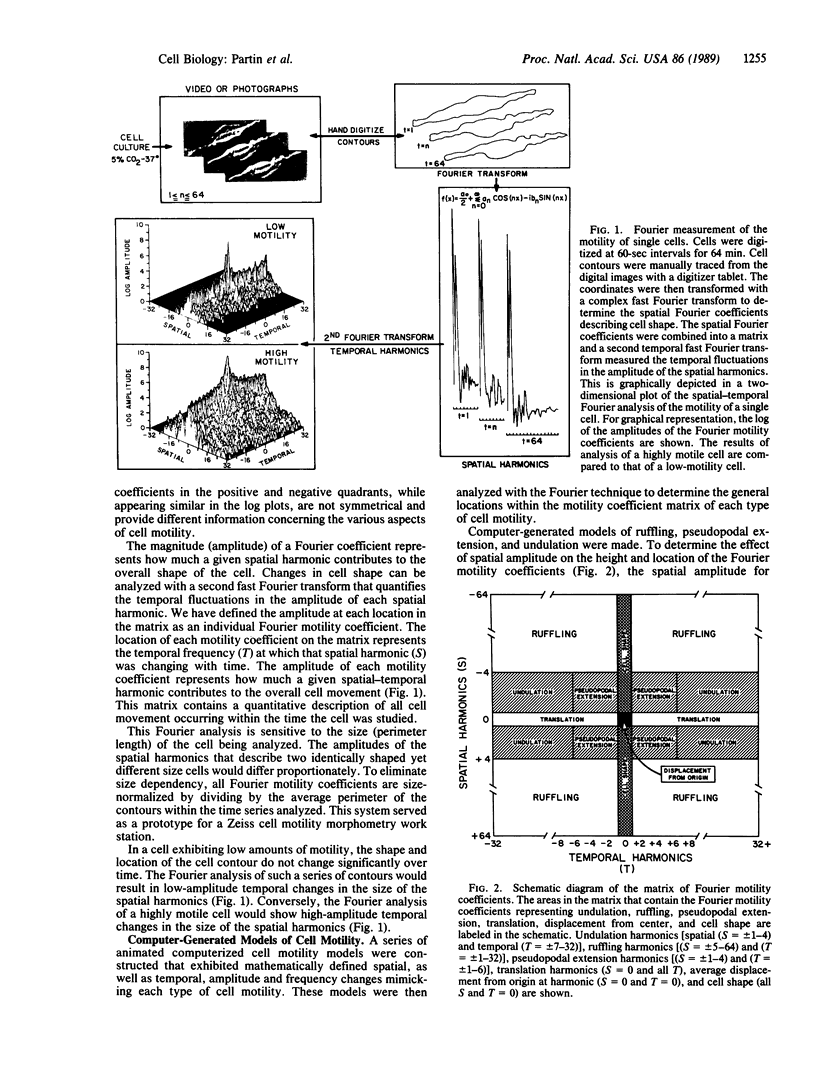
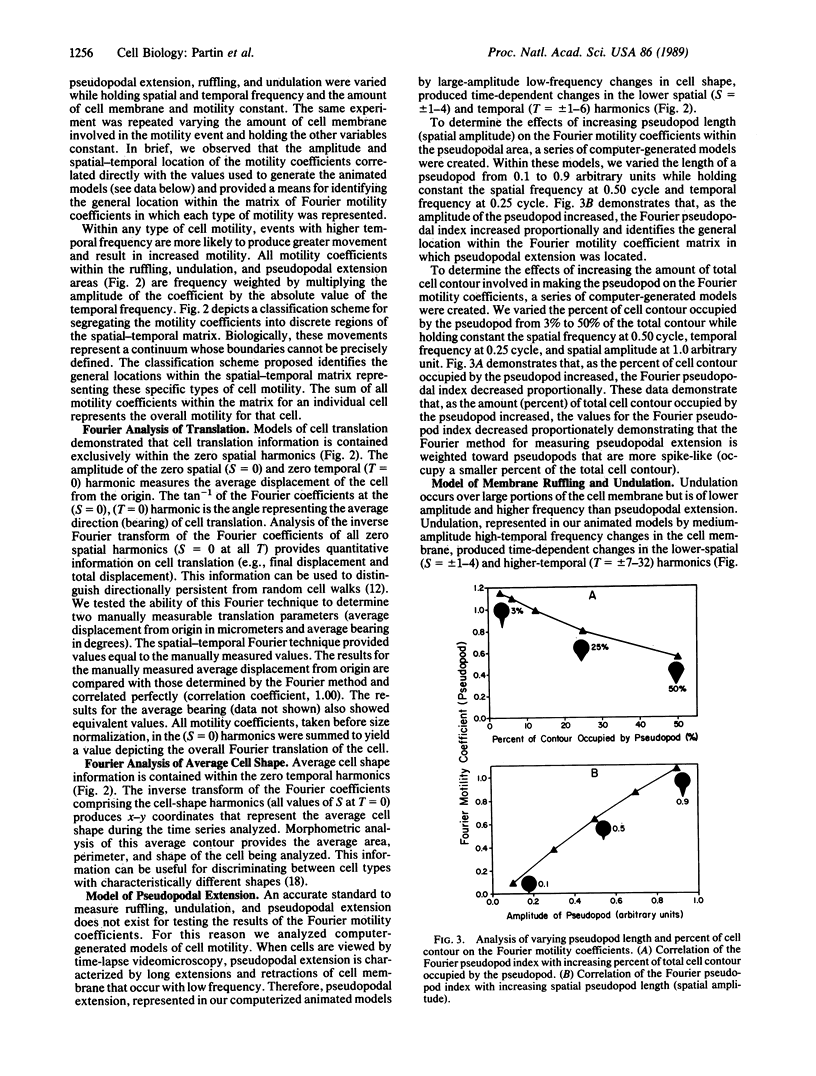
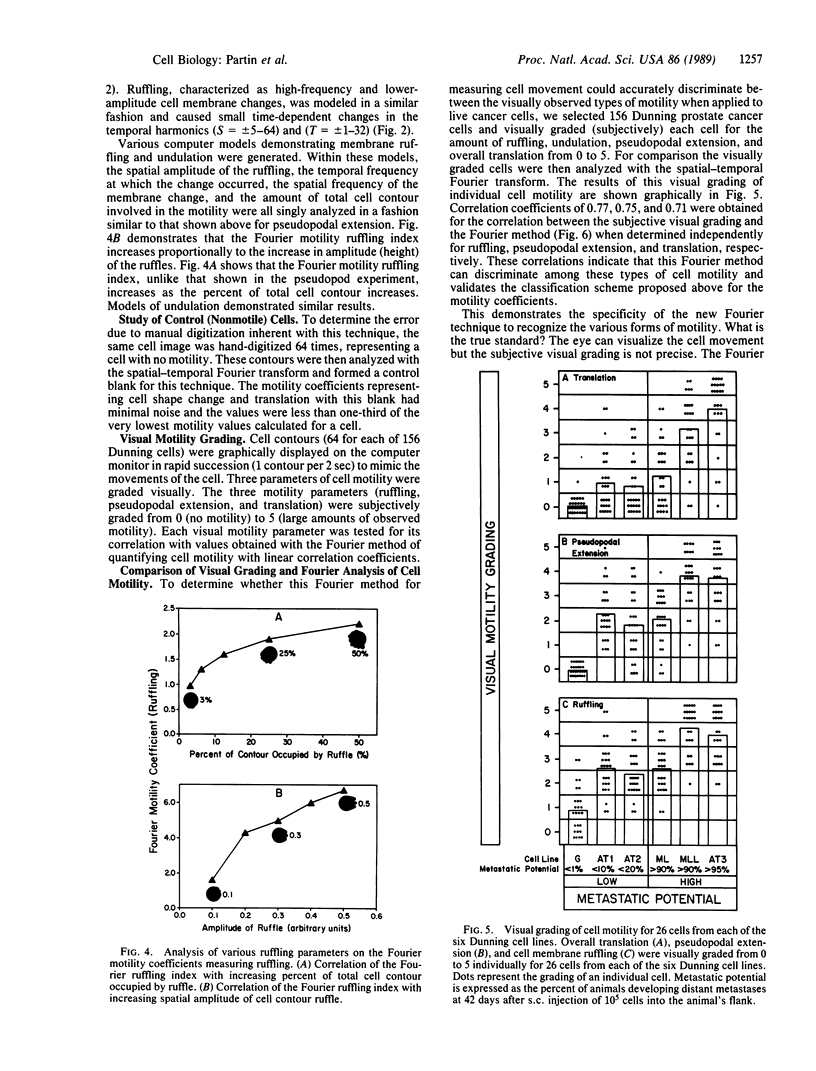
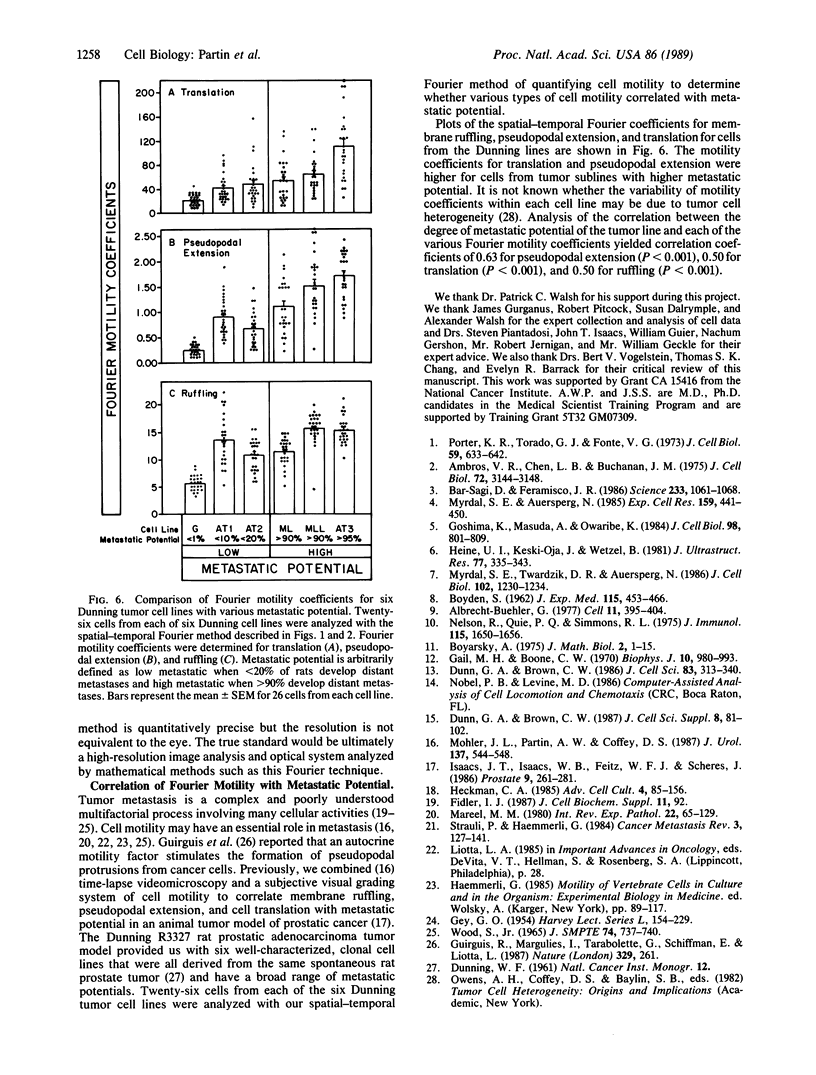
We report the development of a computerized, mathematical system for quantitating the various types of cell motility. This Fourier analysis method simultaneously quantifies for individual cells (i) temporal changes in cell shape represented by cell ruffling, undulation, and pseudopodal extension, (ii) cell translation, and (iii) average cell size and shape. This spatial-temporal Fourier analysis was tested on a series of well-characterized animal tumor cell lines of rat prostatic cancer to study in a quantitative manner the correlation of cell motility with increasing in vivo metastatic potential. Fourier motility coefficients measuring pseudopodal extension correlated best with metastatic potential in the cell lines studied. This study demonstrated that Fourier analysis provides quantitative measurement of cell motility that may be applied to the study of biological processes. This analysis should aid in the study of the motility of individual cells in various areas of cellular and tumor biology.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht-Buehler G. The phagokinetic tracks of 3T3 cells. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V. R., Chen L. B., Buchanan J. M. Surface ruffles as markers for studies of cell transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3144–3148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Induction of membrane ruffling and fluid-phase pinocytosis in quiescent fibroblasts by ras proteins. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1061–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.3090687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn G. A., Brown A. F. A unified approach to analysing cell motility. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;8:81–102. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_8.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn G. A., Brown A. F. Alignment of fibroblasts on grooved surfaces described by a simple geometric transformation. J Cell Sci. 1986 Jul;83:313–340. doi: 10.1242/jcs.83.1.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEY G. O. Some aspects of the constitution and behavior of normal and malignant cells maintained in continuous culture. Harvey Lect. 1954;50:154–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gail M. H., Boone C. W. The locomotion of mouse fibroblasts in tissue culture. Biophys J. 1970 Oct;10(10):980–993. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86347-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goshima K., Masuda A., Owaribe K. Insulin-induced formation of ruffling membranes of KB cells and its correlation with enhancement of amino acid transport. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):801–809. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirguis R., Margulies I., Taraboletti G., Schiffmann E., Liotta L. Cytokine-induced pseudopodial protrusion is coupled to tumour cell migration. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):261–263. doi: 10.1038/329261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine U. I., Keski-Oja J., Wetzel B. Rapid membrane changes in mouse epithelial cells after exposure to epidermal growth factor. J Ultrastruct Res. 1981 Dec;77(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(81)80029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs J. T., Isaacs W. B., Feitz W. F., Scheres J. Establishment and characterization of seven Dunning rat prostatic cancer cell lines and their use in developing methods for predicting metastatic abilities of prostatic cancers. Prostate. 1986;9(3):261–281. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990090306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mareel M. M. Recent aspects of tumor invasiveness. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1980;22:65–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohler J. L., Partin A. W., Isaacs W. B., Coffey D. S. Time lapse videomicroscopic identification of Dunning R-3327 adenocarcinoma and normal rat prostate cells. J Urol. 1987 Mar;137(3):544–547. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)44103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrdal S. E., Auersperg N. p21ras. Heterogeneous localization in transformed cells. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Aug;159(2):441–450. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myrdal S. E., Twardzik D. R., Auersperg N. Cell-mediated co-action of transforming growth factors: incubation of type beta with normal rat kidney cells produces a soluble activity that prolongs the ruffling response to type alpha. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1230–1234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K. R., Todaro G. J., Fonte V. A scanning electron microscope study of surface features of viral and spontaneous transformants of mouse Balb-3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):633–642. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sträuli P., Haemmerli G. The role of cancer cell motility in invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1984;3(2):127–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00047660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



