Abstract
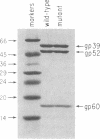
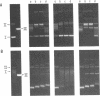
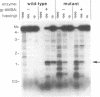
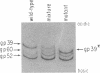
The mammalian type II DNA topoisomerase has been proposed to be the intracellular target of a variety of antitumor agents, including m-AMSA [4'-(9-acridinylamino)-methanesulfon-m-anisidide]. Because the bacteriophage T4-encoded topoisomerase resembles the mammalian enzyme, we are using T4 as a simple model system to investigate the mechanism of action of m-AMSA. A mutation that renders T4 growth m-AMSA-resistant is closely linked to an amber mutation in T4 gene 39, which encodes one of the topoisomerase subunits. In addition, the gene 39 subunit from the m-AMSA-resistant mutant phage has an altered net charge, strongly indicating that the drug-resistance mutation is within gene 39. Topoisomerase purified from mutant phage-infected Escherichia coli exhibits drug-insensitive DNA relaxation and DNA cleavage activities. Because a single mutation results in both drug-resistant phage growth and a drug-insensitive viral topoisomerase, we conclude that the T4-encoded type II DNA topoisomerase is the physiological target of m-AMSA in phage-infected E. coli.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakic M., Beran M., Andersson B. S., Silberman L., Estey E., Zwelling L. A. The production of topoisomerase II-mediated DNA cleavage in human leukemia cells predicts their susceptibility to 4'-(9-acridinylamino)methanesulfon-m-anisidide (m-AMSA). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):638–645. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80467-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Pedersen-Lane J., West D., Ehrenman K., Maley G., Chu F., Maley F. Processing of the intron-containing thymidylate synthase (td) gene of phage T4 is at the RNA level. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. L., Yang L., Rowe T. C., Halligan B. D., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Nonintercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage-reunion reaction of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13560–13566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny W. A., Wakelin L. P. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of the interaction of amsacrine and anilino ring-substituted analogues with DNA. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 1):1717–1721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estey E. H., Silberman L., Beran M., Andersson B. S., Zwelling L. A. The interaction between nuclear topoisomerase II activity from human leukemia cells, exogenous DNA, and 4'-(9-acridinylamino)methanesulfon-m-anisidide (m-AMSA) or 4-(4,6-O-ethylidene-beta-D-glucopyranoside) (VP-16) indicates the sensitivity of the cells to the drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):787–793. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsche H., Wähnert U., Chaires J. B., Dattagupta N., Schlessinger F. B., Crothers D. M. Anthracycline antibiotics. Interaction with DNA and nucleosomes and inhibition of DNA synthesis. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):1996–2000. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisson B. S., Ross W. E. DNA topoisomerase II: a primer on the enzyme and its unique role as a multidrug target in cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacol Ther. 1987;32(2):89–106. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(87)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisson B., Gupta R., Smallwood-Kentro S., Ross W. Characterization of acquired epipodophyllotoxin resistance in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line: loss of drug-stimulated DNA cleavage activity. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 2):1934–1938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gott J. M., Shub D. A., Belfort M. Multiple self-splicing introns in bacteriophage T4: evidence from autocatalytic GTP labeling of RNA in vitro. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90368-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Hertzberg R., Hecht S., Liu L. F. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14873–14878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. M. Nucleotide sequence of a type II DNA topoisomerase gene. Bacteriophage T4 gene 39. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7751–7765. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen E., Bonven B. J., Andoh T., Ishii K., Okada K., Bolund L., Westergaard O. Characterization of a camptothecin-resistant human DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3912–3916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Alberts B. M. Site-specific recognition of bacteriophage T4 DNA by T4 type II DNA topoisomerase and Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5339–5346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Jongeneel C. V. Escherichia coli phage T4 topoisomerase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:144–160. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Liu C. C., Alberts B. M. T4 DNA topoisomerase: a new ATP-dependent enzyme essential for initiation of T4 bacteriophage DNA replication. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):456–461. doi: 10.1038/281456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. M., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Mechanism of antitumor drug action: poisoning of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II on DNA by 4'-(9-acridinylamino)-methanesulfon-m-anisidide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1361–1365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. E. The vestibular apparatus. Sci Am. 1980 Nov;243(5):118–135. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1180-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier Y., Kerrigan D., Schwartz R. E., Swack J. A., McCurdy A. Altered DNA topoisomerase II activity in Chinese hamster cells resistant to topoisomerase II inhibitors. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):3075–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier Y., Schwartz R. E., Zwelling L. A., Kerrigan D., Mattern M. R., Charcosset J. Y., Jacquemin-Sablon A., Kohn K. W. Reduced formation of protein-associated DNA strand breaks in Chinese hamster cells resistant to topoisomerase II inhibitors. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripley L. S., Dubins J. S., deBoer J. G., DeMarini D. M., Bogerd A. M., Kreuzer K. N. Hotspot sites for acridine-induced frameshift mutations in bacteriophage T4 correspond to sites of action of the T4 type II topoisomerase. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):665–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90479-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbie M., Wilkins R. J. Identification of the specific sites of interaction between intercalating drugs and DNA. Chem Biol Interact. 1984 Apr;49(1-2):189–207. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(84)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. E., Glaubiger D., Kohn K. W. Qualitative and quantitative aspects of intercalator-induced DNA strand breaks. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 28;562(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe T. C., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Identification of the breakage-reunion subunit of T4 DNA topoisomerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9177–9181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt F. J. RNA splicing in prokaryotes: bacteriophage T4 leads the way. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):339–340. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by analogues of nalidixic acid: the target of the drugs is DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):307–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Pulleyblank D. E., Vinograd J. The problems of eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA packaging and in vivo conformation posed by superhelix density heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1183–1205. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Rush J., Fung C., Reha-Krantz L. J., Karam J. D., Konigsberg W. H. Primary structure of T4 DNA polymerase. Evolutionary relatedness to eucaryotic and other procaryotic DNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7478–7486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler G. L., King G. J., Huang W. M. T4 DNA-delay proteins, required for specific DNA replication, form a complex that has ATP-dependent DNA topoisomerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3737–3741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Peebles C. L., Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid: purification of Escherichia coli nalA gene product and its relationship to DNA gyrase and a novel nicking-closing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Dervan P. B. Chromomycin, mithramycin, and olivomycin binding sites on heterogeneous deoxyribonucleic acid. Footprinting with (methidiumpropyl-EDTA)iron(II). Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2373–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Map of distamycin, netropsin, and actinomycin binding sites on heterogeneous DNA: DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns with methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. DNA modification and cancer. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:159–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. DNA-binding characteristics of acridinylmethanesulphonanilide drugs: comparison with antitumour properties. Eur J Cancer. 1976 Dec;12(12):995–1001. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(76)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. W., Wahl A. F., Yuan P. M., Arai N., Pearson B. E., Arai K., Korn D., Hunkapiller M. W., Wang T. S. Human DNA polymerase alpha gene expression is cell proliferation dependent and its primary structure is similar to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic replicative DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):37–47. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi J., Yoshida H., Yamayoshi M., Nakamura S. Nalidixic acid-resistant mutations of the gyrB gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Sep;204(3):367–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00331012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwelling L. A., Michaels S., Erickson L. C., Ungerleider R. S., Nichols M., Kohn K. W. Protein-associated deoxyribonucleic acid strand breaks in L1210 cells treated with the deoxyribonucleic acid intercalating agents 4'-(9-acridinylamino) methanesulfon-m-anisidide and adriamycin. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 10;20(23):6553–6563. doi: 10.1021/bi00526a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]