Abstract
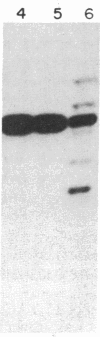
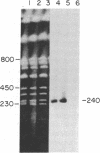
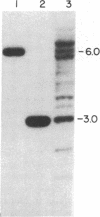
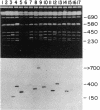
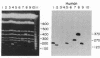
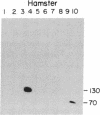
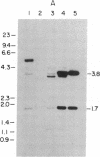
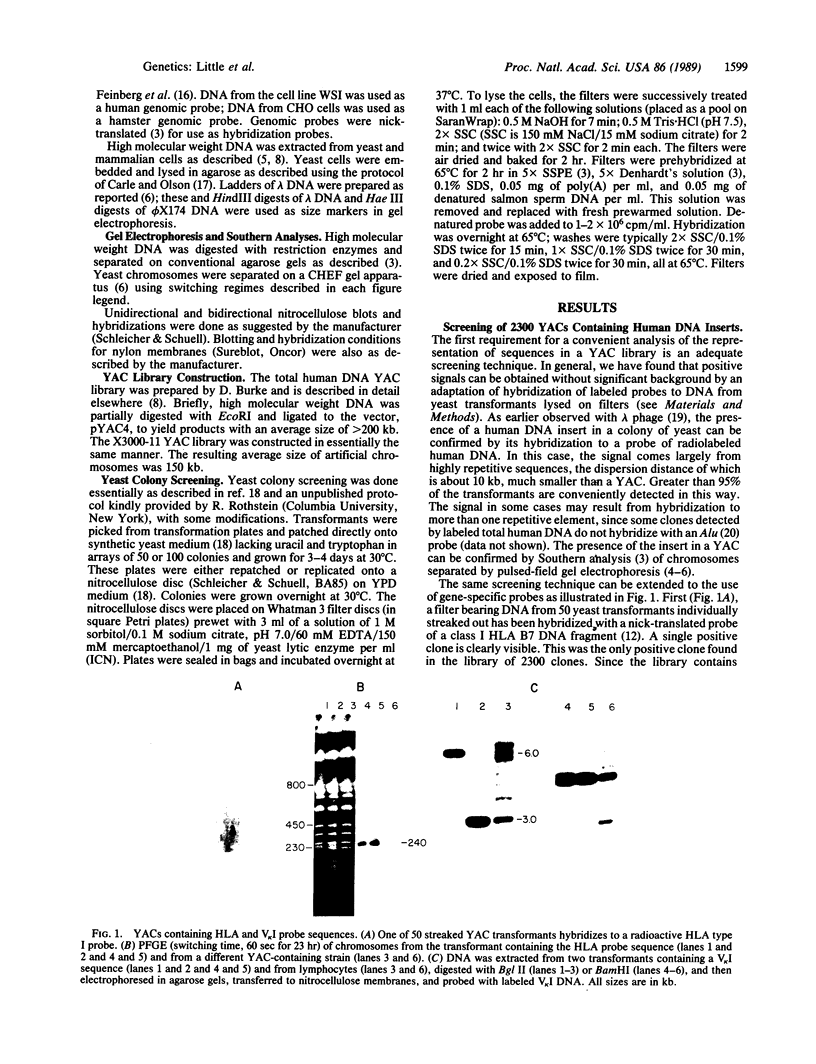
Sequences hybridizing to several human gene probes have been recovered as cloned inserts in yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs). Among 2300 YACs made from human leukocyte DNA (totaling about 0.1 genomic equivalent of human DNA) we have found two, 200 and 780 kilobases (kb), containing sequences of V kappa I immunoglobulin (V = variable); one, 240 kb, with class I HLA; and 11, 200-800 kb, with 5S rRNA-encoding DNA (rDNA). Fifty human YACs from a hamster-human cell hybrid with only the Xq24-Xq28 portion of the X chromosome include one that contains two anonymous probe sequences, DX13 and St14, previously inferred by indirect means to lie within about 70 kb of one another in Xq28. The YACs specific for human DNA arise at a frequency equivalent to the fraction of cellular DNA that is human-specific. Furthermore, the human YACs, formed in a 280-fold excess of hamster DNA, do not hybridize to a hamster DNA probe, indicating that individual YACs do not contain a combination of human and hamster DNA. To confirm that sequences are not scrambled, the YACs containing V kappa I or DX13 and St14 sequences were shown to produce restriction fragments identical in mobility to fragments detected by the same probes in total human DNA digested with the same enzymes. YACs may therefore provide large clones to bridge gene mapping at the chromosome level to molecular analyses of small fragments of genomic DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentley D. L., Rabbitts T. H. Human V kappa immunoglobulin gene number: implications for the origin of antibody diversity. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):613–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Waterston R., Kiff J., Sulston J., Kohara Y. Genome linking with yeast artificial chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):184–186. doi: 10.1038/335184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Green P., Helms C., Cartinhour S., Weiffenbach B., Stephens K., Keith T. P., Bowden D. W., Smith D. R., Lander E. S. A genetic linkage map of the human genome. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Davies K., Hartley D., Mandel J. L., Camerino G., Williamson R., White R. Genetic mapping of the human X chromosome by using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., Folk W. R. Structure and organization of a mammalian 5 S gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11706–11711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Arveiler B., Camerino G., Hanauer A., Heilig R., Koenig M., Oberlé I. Genetic mapping of the human X chromosome: linkage analysis of the q26-q28 region that includes the fragile X locus and isolation of expressed sequences. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):195–203. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. D., Ruddle F. H. Isolation and regional mapping of random X sequences from distal human X chromosome. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Sep;11(5):433–444. doi: 10.1007/BF01534837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Airhart S. D., Ledbetter D. H. A rodent-human hybrid containing Xq24-qter translocated to a hamster chromosome expresses the Xq27 folate-sensitive fragile site. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):457–466. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Drayna D., Camerino G., White R., Mandel J. L. The telomeric region of the human X chromosome long arm: presence of a highly polymorphic DNA marker and analysis of recombination frequency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr H. T., DeMars R. Class I-like HLA genes map telomeric to the HLA-A2 locus in human cells. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):534–536. doi: 10.1038/302534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Kenwrick S., Thibodeau S., Faulk K., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Davies K. E. Mapping of DNA markers close to the fragile site on the human X chromosome at Xq27.3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2639–2651. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Rothblum L., Busch H. Some gene variants for 5 S RNA are dispersed in the rat genome. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10618–10623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pereira D., Weissman S. M. Isolation and partial nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B by use of an oligodeoxynucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straubinger B., Thiebe R., Pech M., Zachau H. G. The Z family, a group of transposed human immunoglobulin V kappa genes. Gene. 1988 Sep 30;69(2):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90431-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7865–7876. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]