Abstract
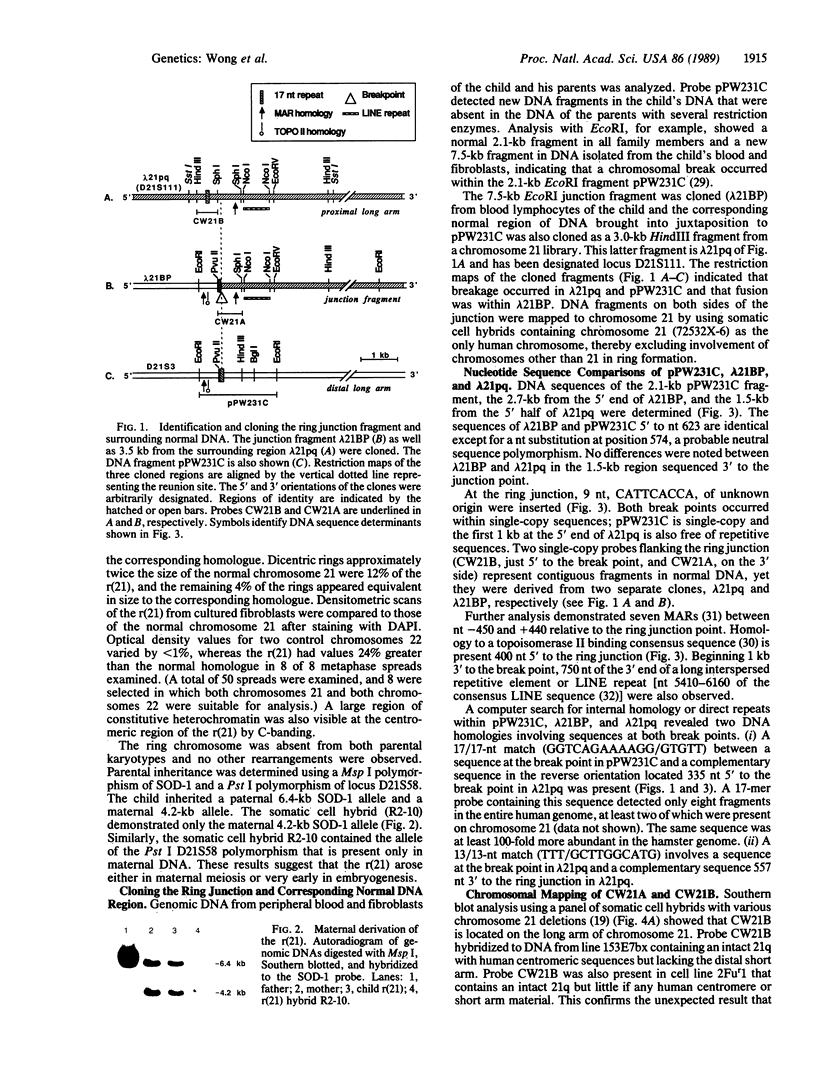
We have characterized the structural rearrangements of a chromosome 21 that led to the de novo formation of a human ring chromosome 21 [r(21)]. Molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of the DNA regions flanking the ring junction provide evidence for a long arm to long arm fusion in formation of the r(21). In addition, the centromere and proximal long arm region of a maternal chromosome 21 are duplicated in the r(21). Therefore, the mechanism in formation of the r(21) was complex involving two sequential chromosomal rearrangements. (i) Duplication of the centromere and long arm of one maternal chromosome 21 occurred forming a rearranged intermediate. (ii) Chromosomal breaks in both the proximal and telomeric long arm regions on opposite arms of this rearranged chromosome occurred with subsequent reunion producing the r(21).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Identification of a nuclear protein matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1410–1417. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chimera J. A., Musich P. R. The association of the interspersed repetitive KpnI sequences with the nuclear matrix. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9373–9379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallapiccola B., Bianco I., Brinchi V., Santulli B., Scarano G., Sicolo A., Stabile M., Ventruto V. t(21q21q)/r[t(21q21q)] mosaic in two unrelated patients with mild stigmata of Down's syndrome. Ann Genet. 1982;25(1):56–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Heck M. M. Localization of topoisomerase II in mitotic chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1716–1725. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Migeon B. R. Three related centromere proteins are absent from the inactive centromere of a stable isodicentric chromosome. Chromosoma. 1985;92(4):290–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00329812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Sullivan K. F., Machlin P. S., Cooke C. A., Kaiser D. A., Pollard T. D., Rothfield N. F., Cleveland D. W. Molecular cloning of cDNA for CENP-B, the major human centromere autoantigen. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):817–829. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Kleczkowska A. Ring chromosome 21 in the mother and 21/21 translocation in the fetus: karyotype: 45,XX,-21,-21,+t(21;21)(p11;q11). Ann Genet. 1987;30(2):109–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Van den Berghe H. Ring chromosome 22 in a mentally retarded child and mosaic 45,XX,-15,-22,+t(15;22)(p11;q11)/46,XX,r(22)/46,XX karyotype in the mother. Hum Genet. 1979 Mar 12;47(2):213–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00273205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P. S., Mager D. L., Huisman T. H., Smithies O. A gene deletion ending within a complex array of repeated sequences 3' to the human beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5194–5198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ieshima A., Ogasawara N., Yamamoto Y., Kuroki Y. A case of r(21) with stigmata of atypical Down syndrome. Hum Genet. 1980;55(1):65–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00329128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A. Mutation rates of structural chromosome rearrangements in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Jan;33(1):44–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Tuan D., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. A gene deletion ending at the midpoint of a repetitive DNA sequence in one form of hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):469–470. doi: 10.1038/296469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. W., Jones R. W., Wood W. G., Weatherall D. J. Analysis of an inversion within the human beta globin gene cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2897–2906. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao F. T., Puck T. T. Induction and isolation of auxotrophic mutants in mammalian cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1974;8(0):23–39. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Wong C., Trusko S. P., Stetten G., Oliver M., Potter M. J., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C. Ring chromosome 21: characterization of DNA sequences at sites of breakage and reunion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;450:33–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb21481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lejeune J. De la duplication de structures circulaires. Ann Genet. 1968 Jun;11(2):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieman-Hurwitz J., Dafni N., Lavie V., Groner Y. Human cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase cDNA clone: a probe for studying the molecular biology of Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2808–2811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Henthorn P. S., Smithies O. A Chinese G gamma + (A gamma delta beta)zero thalassemia deletion: comparison to other deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster and sequence analysis of the breakpoints. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6559–6575. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara T., Nakagome Y., Ogasawara N., Oka S., Yokochi T. Maternally transmitted extra ring (21) chromosome in a boy with Down's syndrome. Hum Genet. 1982;60(1):78–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00281270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mules E. H., Stamberg J., Jabs E. W., Leonard C. O. Two different structural abnormalities of chromosome 13 in offspring of chromosomally normal parents with two fragile sites. Clin Genet. 1983 May;23(5):380–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb00450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri G., Ricci R., Pelino A., Bova R., Tedeschi B., Serra A. A boy with ring chromosome 15 derived from a t(15q;15q) Robertsonian translocation in the mother: cytogenetic and biochemical findings. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Feb;14(2):307–314. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr E. Reexamination of a family with a t(13q14q) and a ring D(13) child. Ann Genet. 1973 Sep;16(3):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orye E., Craen M. A t(21q21q) ring chromosome. Hum Hered. 1974;24(3):253–258. doi: 10.1159/000152658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi S., Giglioni B. The deletion in a type of delta 0-beta 0-thalassaemia begins in an inverted AluI repeat. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):770–771. doi: 10.1038/300770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer C. G., Hodes M. E., Reed T., Kojetin J. Four new cases of ring 21 and 22 including familial transmission of ring 21. J Med Genet. 1977 Feb;14(1):54–60. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli S. P., Caimi P. G., Cole M. D. A conserved sequence at c-myc oncogene chromosomal translocation breakpoints in plasmacytomas. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):327–330. doi: 10.1038/310327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Wisniewski H. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the cerebrovascular and the neuritic plaque amyloid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Drosophila topoisomerase II double-strand DNA cleavage: analysis of DNA sequence homology at the cleavage site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1057–1072. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid W., Tenconi R., Baccichetti C., Caufin D., Schinzel A. Ring chromosome 21 in phenotypically apparently normal persons: report of two families from Switzerland and Italy. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Nov;16(3):323–329. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. F., Schmeckpeper B. J., Abdelrazik M., Comey C. T., O'Hara B., Rossiter J. P., Cooley T., Heath P., Smith K. D., Margolet L. Origin of the human L1 elements: proposed progenitor genes deduced from a consensus DNA sequence. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90003-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetten G., Sroka B., Corson V. L., Boehm C. D. Prenatal detection of an unstable ring 21 chromosome. Hum Genet. 1984;68(4):310–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00292590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Gorham J., Cossman J., Jaffe E., Croce C. M. The t(14;18) chromosome translocations involved in B-cell neoplasms result from mistakes in VDJ joining. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1390–1393. doi: 10.1126/science.3929382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Keuren M. L., Watkins P. C., Drabkin H. A., Jabs E. W., Gusella J. F., Patterson D. Regional localization of DNA sequences on chromosome 21 using somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;38(6):793–804. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. J., Rimoin D. L. The G deletion syndromes. J Pediatr. 1970 Oct;77(4):658–663. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. C., Tanzi R. E., Gibbons K. T., Tricoli J. V., Landes G., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Gusella J. F. Isolation of polymorphic DNA segments from human chromosome 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6075–6088. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Fennell D. J. The use of fluorescent DNA-binding agent for detecting and separating yeast mitochondrial DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:335–351. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60963-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdansky R., Bühler E. M., Vest M., Bühler U. K., Stalder G. Familiäres Mosaik mit G-Ring. Humangenetik. 1969;7(4):275–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00283550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida J. C., Llerena J. C., Jr, Gomes D. M., Martins R. R., Pereira E. T. Ring 13 in an adult male with a 13:13 translocation mother. Ann Genet. 1983;26(2):112–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








