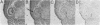Abstract
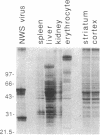
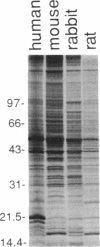
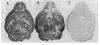
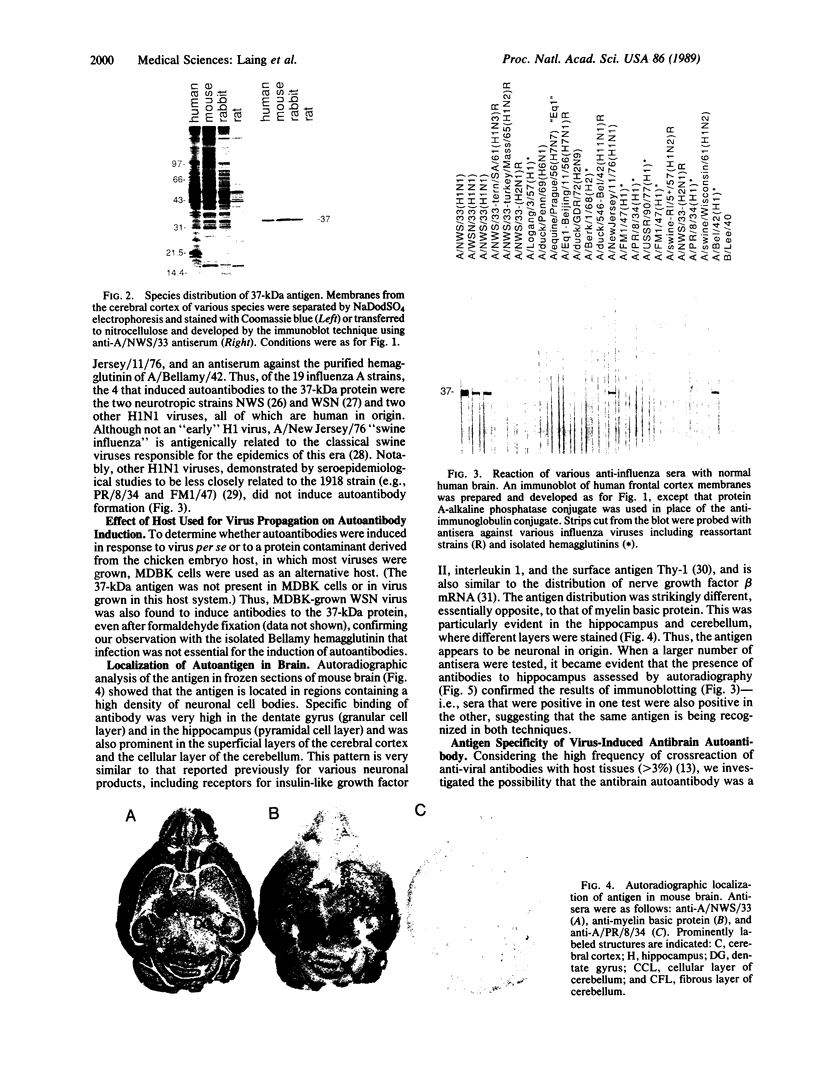
Immunization of rabbits with certain H1N1 influenza viruses, including the neurotropic strains NWS/33 and WSN/33 and the New Jersey/76 strain, resulted in the production of autoantibodies to a brain-specific protein of 37 kDa that is present in various species, including humans. Autoantibodies were produced to brain only; various other tissues tested were negative. These antibodies were not elicited by other influenza A or B viruses, including closely related recombinant strains, but were elicited by the isolated hemagglutinin of A/Bellamy/42 strain and by formaldehyde-fixed WSN virus--demonstrating that infection was not essential for the induction of autoantibodies. In histological studies, reaction with anti-viral antisera was specific to gray matter and was confined to sera that recognized the 37-kDa protein. Antibody binding was prominent in regions comprised of neuronal cell bodies in cellular layers of the dentate gyrus, hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and cerebellum and was undetectable in myelin-rich regions, such as the corpus callosum. The 37-kDa protein, therefore, appears to be a neuronal antigen. Antibodies directed against this protein may be involved in the pathogenesis of one or more of the neuropsychiatric disorders that occur after infection with influenza.
Full text
PDF

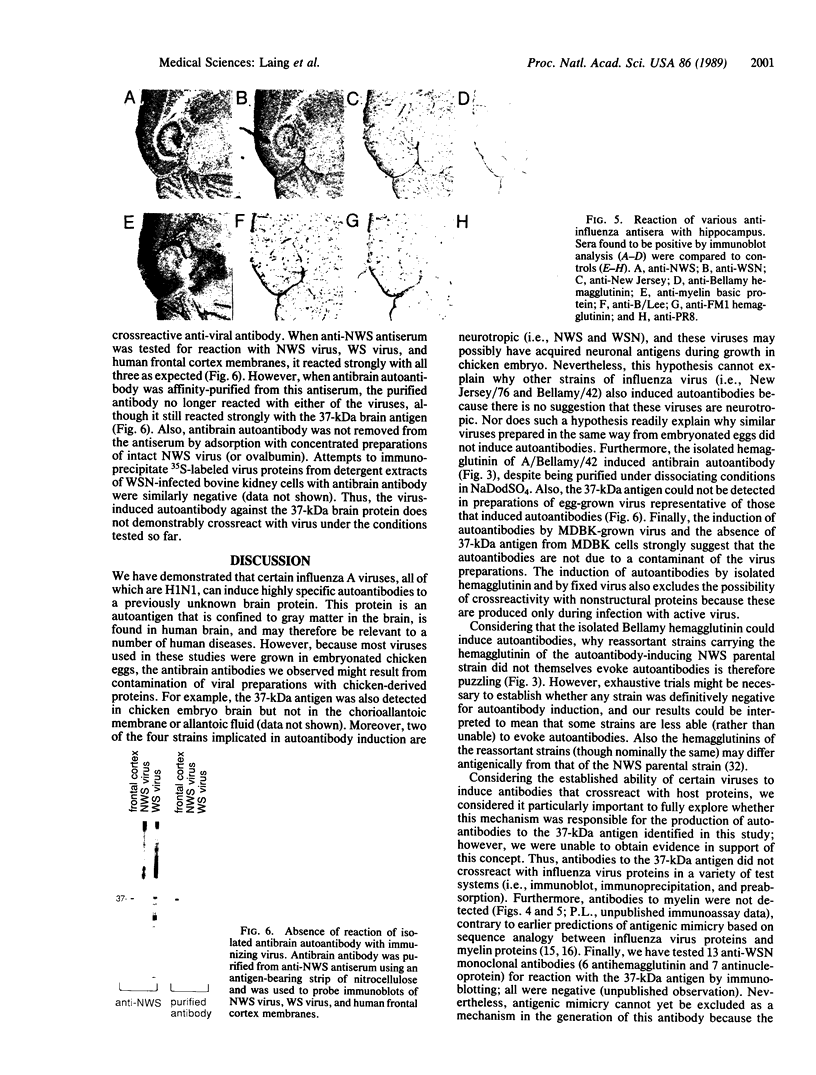

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramsky O., Litvin Y. Automimmune response to dopamine-receptor as a possible mechanism in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and schizophrenia. Perspect Biol Med. 1978 Autumn;22(1):104–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardman B., Khiroya R. H., Schwartz R. S. Recognition of a leukemia-related antigen by an antiidiotypic antiserum to an anti-gp70 monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):669–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer-LeLievre C., Olson L., Ebendal T., Seiger A., Persson H. Expression of the beta-nerve growth factor gene in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1339–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.2897715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENTAL E. Acute psychoses due to encephalitis following Asian influenza. Lancet. 1958 Jul 5;2(7036):18–20. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck S., Barrell B. G. Human cytomegalovirus encodes a glycoprotein homologous to MHC class-I antigens. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):269–272. doi: 10.1038/331269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyrberg T., Oldstone M. B. Peptides as probes to study molecular mimicry and virus-induced autoimmunity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;130:25–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71440-5_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein D. A., Marsh Y. V., Schreiber A. B., Newman S. R., Todaro G. J., Nestor J. J., Jr Epidermal growth factor receptor occupancy inhibits vaccinia virus infection. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):663–665. doi: 10.1038/318663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEWETT T. H., HOULT J. G. Influenzal encephalopathy and postinfluenzal encephalitis. Lancet. 1958 Jul 5;2(7036):11–15. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. E., Plescia O. J. An experimental model of autoimmune hemolytic anemia in mice. Immunol Commun. 1973;2(3):241–254. doi: 10.3109/08820137309022796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Nelson J. A., Walker L., Oldstone M. B. Sequence homology and immunologic cross-reactivity of human cytomegalovirus with HLA-DR beta chain: a means for graft rejection and immunosuppression. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.100-105.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Amino acid homology between the encephalitogenic site of myelin basic protein and virus: mechanism for autoimmunity. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1043–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.2414848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding H., Robey F. A., Gates F. T., 3rd, Linder W., Beining P. R., Hoffman T., Golding B. Identification of homologous regions in human immunodeficiency virus I gp41 and human MHC class II beta 1 domain. I. Monoclonal antibodies against the gp41-derived peptide and patients' sera react with native HLA class II antigens, suggesting a role for autoimmunity in the pathogenesis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):914–923. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G. M., Berek C., Kaartinen M., Milstein C. Somatic mutation and the maturation of immune response to 2-phenyl oxazolone. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):271–275. doi: 10.1038/312271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsey N. A., Hurwitz E. S., Meiklejohn G., Todd W. A., Edell T., Todd J. K., McIntosh K. An epidemic of Reye syndrome associated with influenza A (H1N1) in Colorado. J Pediatr. 1980 Oct;97(4):535–539. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. M., Ruff M. R., Weber R. J., Pert C. B. Transferrin receptors in rat brain: neuropeptide-like pattern and relationship to iron distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4553–4557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnke U., Fischer E. H., Alvord E. C., Jr Sequence homology between certain viral proteins and proteins related to encephalomyelitis and neuritis. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):282–284. doi: 10.1126/science.2409602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones I. H., Frei D. Seasonal births in schizophrenia. A southern hemisphere study using matched pairs. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1979 Feb;59(2):164–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1979.tb06958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krah D. L., Choppin P. W. Mice immunized with measles virus develop antibodies to a cell surface receptor for binding virus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1565–1572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1565-1572.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus W., Beachey E. H. Renal autoimmune epitope of group A streptococci specified by M protein tetrapeptide Ile-Arg-Leu-Arg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4516–4520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAVER W. G. STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE PROTEIN SUBUNITS FROM THREE STRAINS OF INFLUENZA VIRUS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jul;9:109–124. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz T. L., Benson R. J., Klimowicz D., Wilson P. T., Hawrot E. Binding of rabies virus to purified Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Brain Res. 1986 Dec;387(3):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz T. L., Hawrot E., Wilson P. T. Synthetic peptides corresponding to sequences of snake venom neurotoxins and rabies virus glycoprotein bind to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proteins. 1987;2(4):298–307. doi: 10.1002/prot.340020406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Protein-protein interactions within paramyxoviruses identified by native disulfide bonding or reversible chemical cross-linking. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):152–166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.152-166.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott S. J., Roeder D. J., Consigli R. A. Anti-idiotypic antibodies to a polyomavirus monoclonal antibody recognize cell surface components of mouse kidney cells and prevent polyomavirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2747–2753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2747-2753.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masurel N. Swine influenza virus and the recycling of influenza-A viruses in man. Lancet. 1976 Jul 31;2(7979):244–247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattock C., Marmot M., Stern G. Could Parkinson's disease follow intra-uterine influenza?: a speculative hypothesis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Jun;51(6):753–756. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.6.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mednick S. A., Machon R. A., Huttunen M. O., Bonett D. Adult schizophrenia following prenatal exposure to an influenza epidemic. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988 Feb;45(2):189–192. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1988.01800260109013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson K. G., Tyrrell D. A., Oxford J. S., Wood J., Schild G. C., Potter C. W., Jennings R., Michaels R. H., Appleyard G. Infectivity and reactogenicity of reassortant cold-adapted influenza A/Korea/1/82 vaccines obtained from the USA and USSR. Bull World Health Organ. 1987;65(3):295–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noseworthy J. H., Fields B. N., Dichter M. A., Sobotka C., Pizer E., Perry L. L., Nepom J. T., Greene M. I. Cell receptors for the mammalian reovirus. I. Syngeneic monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody identifies a cell surface receptor for reovirus. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2533–2538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POSKANZER D. C., SCHWAB R. S. COHORT ANALYSIS OF PARKINSON'S SYNDROME: EVIDENCE FOR A SINGLE ETIOLOGY RELATED TO SUBCLINICAL INFECTION ABOUT 1920. J Chronic Dis. 1963 Sep;16:961–973. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(63)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Hill J. M., Ruff M. R., Berman R. M., Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., Ruscetti F. W., Farrar W. L. Octapeptides deduced from the neuropeptide receptor-like pattern of antigen T4 in brain potently inhibit human immunodeficiency virus receptor binding and T-cell infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9254–9258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Knight J. G., Laing P., Markwell M. A. Scenarios for a viral etiology of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1988;14(2):243–247. doi: 10.1093/schbul/14.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotz P. H. Autoantibodies are anti-idiotype antibodies to antiviral antibodies. Lancet. 1983 Oct 8;2(8354):824–826. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Keene J. D. A human autoimmune protein associated with U1 RNA contains a region of homology that is cross-reactive with retroviral p30gag antigen. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravenholt R. T., Foege W. H. 1918 influenza, encephalitis lethargica, parkinsonism. Lancet. 1982 Oct 16;2(8303):860–864. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90820-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent S. J., Beachey E. H., Corbett C. E., Dale J. B. Sequence of protective epitopes of streptococcal M proteins shared with cardiac sarcolemmal membranes. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1285–1290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S. Y., Laursen R. A., Lees M. B. Analogous amino acid sequences in myelin proteolipid and viral proteins. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 27;207(2):266–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81502-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasappa J., Saegusa J., Prabhakar B. S., Gentry M. K., Buchmeier M. J., Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H., Oldstone M. B., Notkins A. L. Molecular mimicry: frequency of reactivity of monoclonal antiviral antibodies with normal tissues. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):397–401. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.397-401.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrey E. F., Rawlings R., Waldman I. N. Schizophrenic births and viral diseases in two states. Schizophr Res. 1988 Jan-Feb;1(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0920-9964(88)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson C. G., Kucala T., Tilleskjor C., Jacobs L. Schizophrenic birth seasonality in relation to the incidence of infectious diseases and temperature extremes. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Jan;41(1):85–90. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790120089011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G., Kilbourne E. D. Reactions of antibodies with surface antigens of influenza virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 Dec;3(3):315–326. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W., Brown J. H., Cusack S., Paulson J. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):426–431. doi: 10.1038/333426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]