Abstract
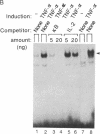
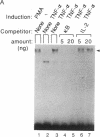
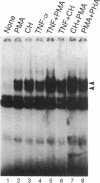
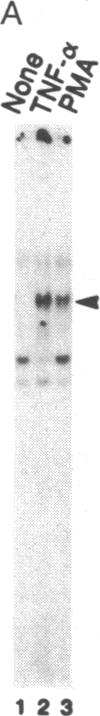
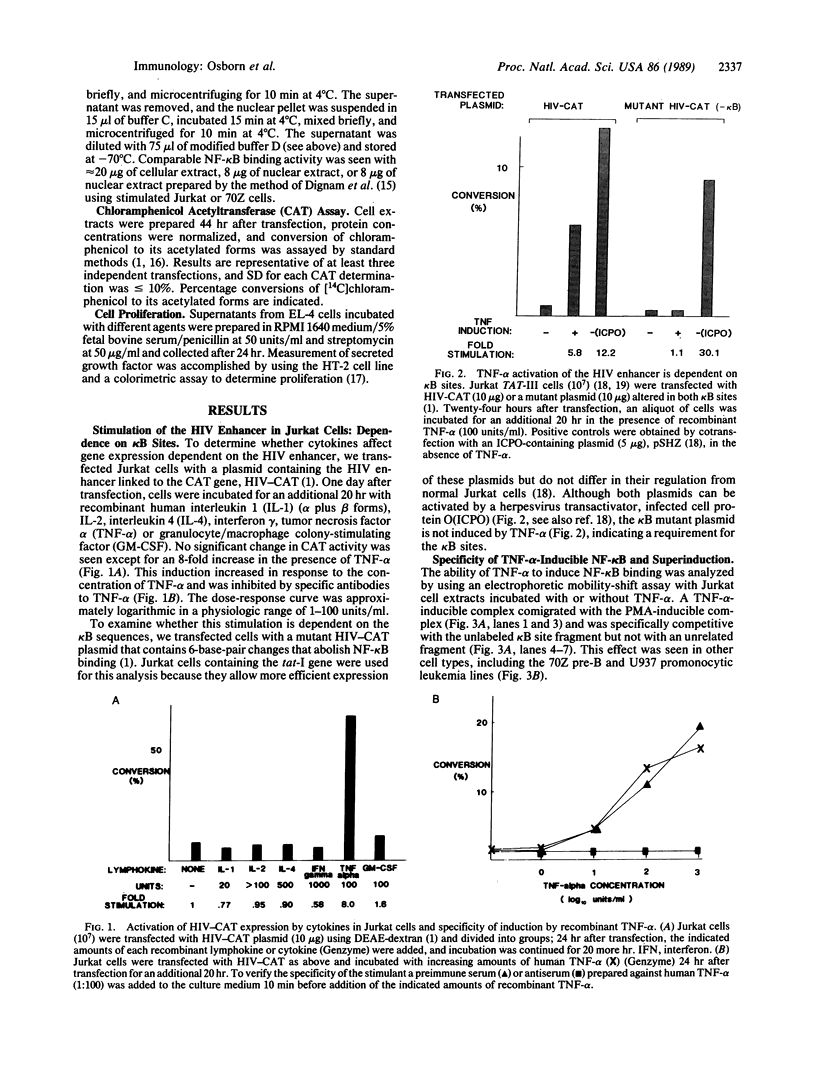
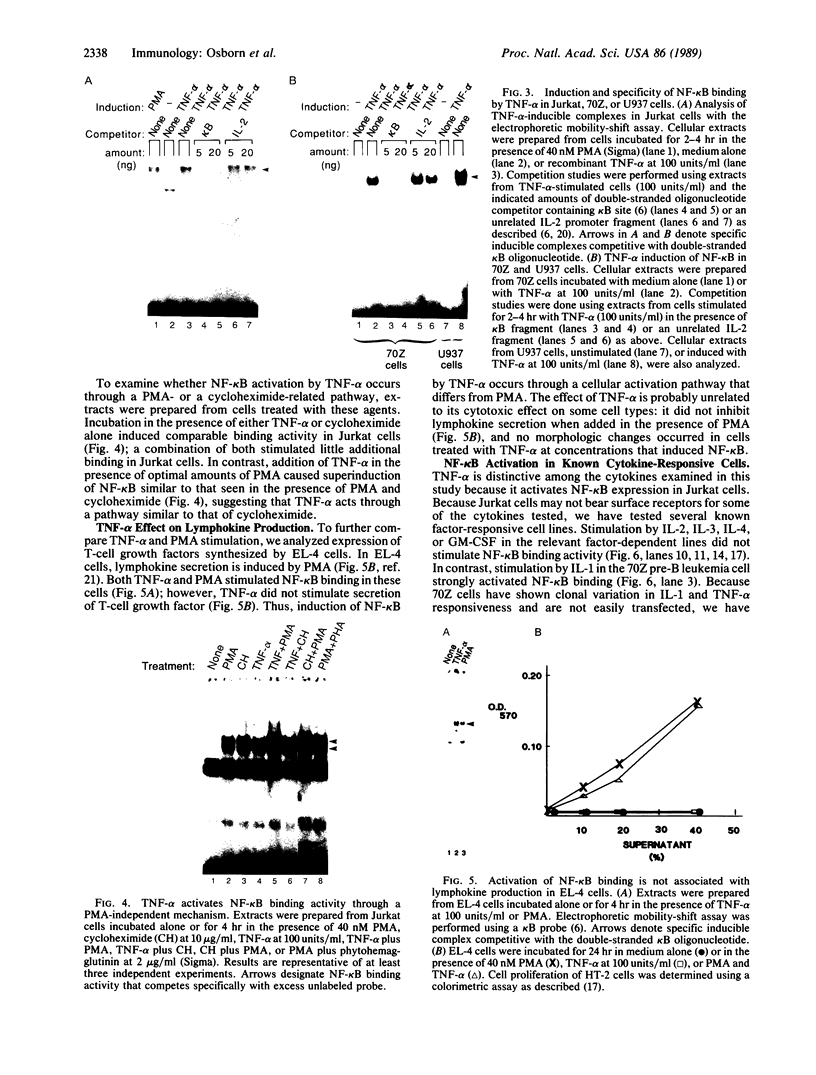
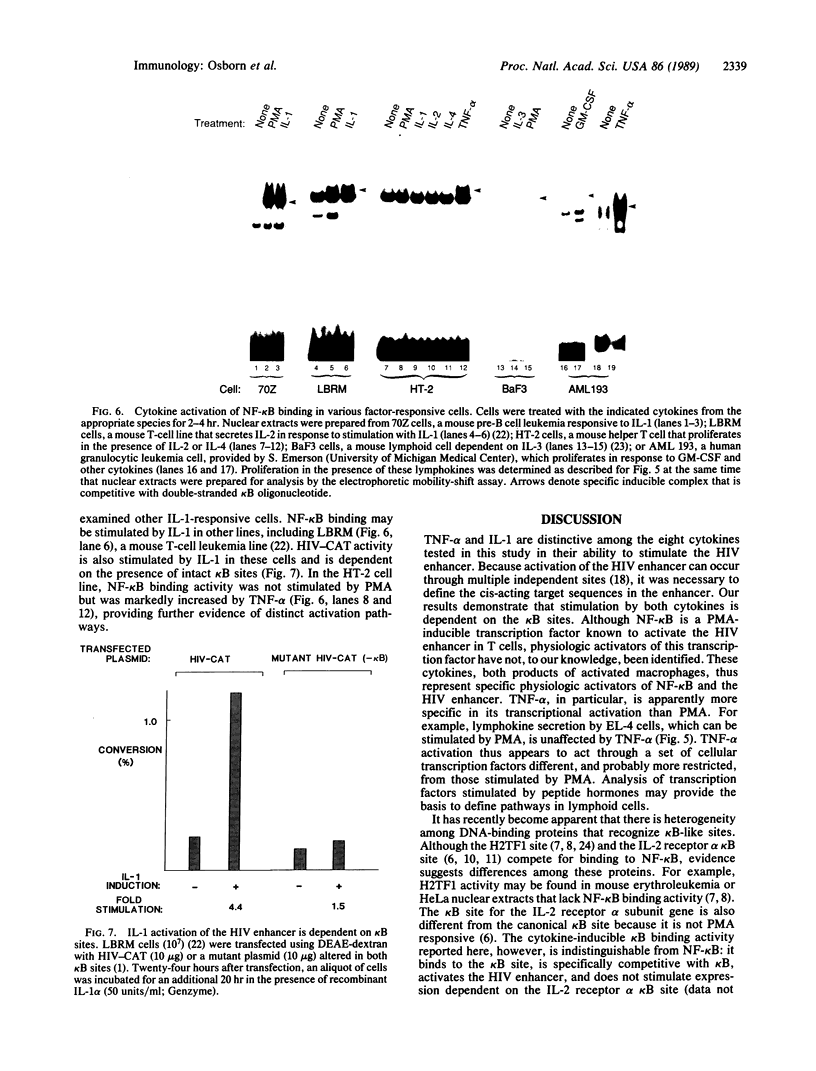
Binding of peptide hormones to surface membrane receptors leads to the transcription of specific genes within relevant target cells. How these signals are transduced to alter gene expression is largely unknown, but this mechanism probably involves a sequence of enzymatic steps that activate factors in the nucleus that modulate transcription. We now demonstrate that two different peptide hormones, or cytokines, stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer, and this effect is mediated by nuclear factor (NF) kappa B (nuclear factor that binds the kappa immunoglobulin light chain gene enhancer). These cytokines, tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1, act on multiple cell types and represent the only naturally occurring activators of this transcription factor among eight cytokines examined. Although NF-kappa B binding can be stimulated by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, tumor necrosis factor alpha acts through an independent mechanism, inducing NF-kappa B binding in HT-2 cells, which did not show increased binding in response to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, and causing superinduction in Jurkat T-lymphoma cells. Tumor necrosis factor alpha is also a more selective activator of T cells than phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, having no effect on lymphokine production in EL-4 cells at the same time it induces NF-kappa B. These findings suggest that human immunodeficiency virus gene expression can be induced in T cells without activating lymphokine secretion and that the role of these cytokines in the activation of latent human immunodeficiency virus infection deserves further clinical evaluation. Finally, this link between binding at the surface membrane and stimulation of a specific transcription factor should help define intermediates for these cytokine activation pathways.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Two transcription factors, NF-kappa B and H2TF1, interact with a single regulatory sequence in the class I major histocompatibility complex promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Siekevitz M., Ballard D. W., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. The same inducible nuclear proteins regulates mitogen activation of both the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and type 1 HIV. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Imagawa M., Imbra R. J., Bockoven J. R., Karin M. Multiple cis- and trans-acting elements mediate the transcriptional response to phorbol esters. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):648–651. doi: 10.1038/329648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Fuller-Farrar J., Simon P. L., Hilfiker M. L., Stadler B. M., Farrar W. L. Thymoma production of T cell growth factor (Interleukin 2). J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2555–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Justement J., Kinter A., Dinarello C. A., Fauci A. S. Cytokine-induced expression of HIV-1 in a chronically infected promonocyte cell line. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):800–802. doi: 10.1126/science.3313729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Scheid M., Watson J. Biochemical and biologic characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. III. The isolation and phenotypic characterization of Interleukin-2 producing T cell lymphomas. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2570–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Leonard W. J., Wano Y., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. Trans-activator gene of HTLV-II induces IL-2 receptor and IL-2 cellular gene expression. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3010456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Koyanagi Y., Nakashima H., Kobayashi N., Yamamoto N. Tumor promoter, TPA, enhances replication of HTLV-III/LAV. Virology. 1986 Oct 30;154(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Kimura A., Kieran M., Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. A common positive trans-acting factor binds to enhancer sequences in the promoters of mouse H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen O., Kabelitz D. Tumor necrosis factor selectively inhibits activation of human B cells by Epstein-Barr virus. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. Enhancement of human B cell proliferation and differentiation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2970–2976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Mitsuyasu R. T., Merrill J. E., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.3646751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathey-Prevot B., Nabel G., Palacios R., Baltimore D. Abelson virus abrogation of interleukin-3 dependence in a lymphoid cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4133–4135. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Gorka C., Baltimore D. T-cell-specific expression of interleukin 2: evidence for a negative regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Rice S. A., Knipe D. M., Baltimore D. Alternative mechanisms for activation of human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.2830675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S., Poteat H., Tan T. H., Kawakami K., Roeder R., Haseltine W., Rosen C. A. Cellular transcription factors and regulation of IL-2 receptor gene expression by HTLV-I tax gene product. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.2838905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi P., Sterling K. E., Lam K. S., Finley P. R., Ryan K. J., Ray C. G., Petersen E., Slymen D. J., Salmon S. E. Raised serum levels of tumour necrosis factor in parasitic infections. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1364–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Krowka J. F., Stites D. P., Goeddel D. V. In vitro anti-human immunodeficiency virus activities of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):120–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagury D., Bernard J., Leonard R., Cheynier R., Feldman M., Sarin P. S., Gallo R. C. Long-term cultures of HTLV-III--infected T cells: a model of cytopathology of T-cell depletion in AIDS. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):850–853. doi: 10.1126/science.2418502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]