Abstract
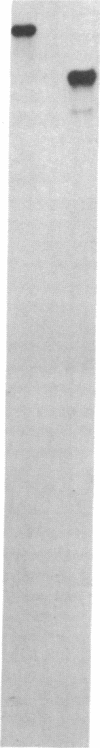
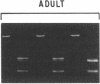
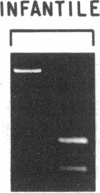
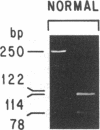
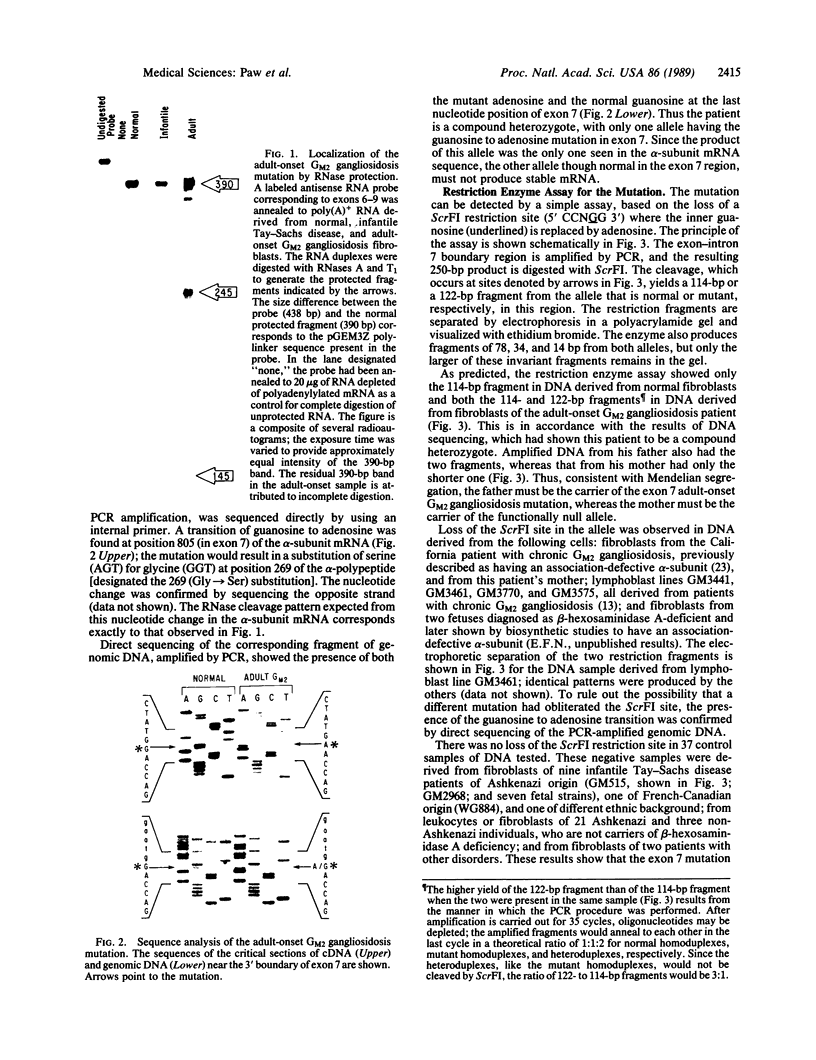
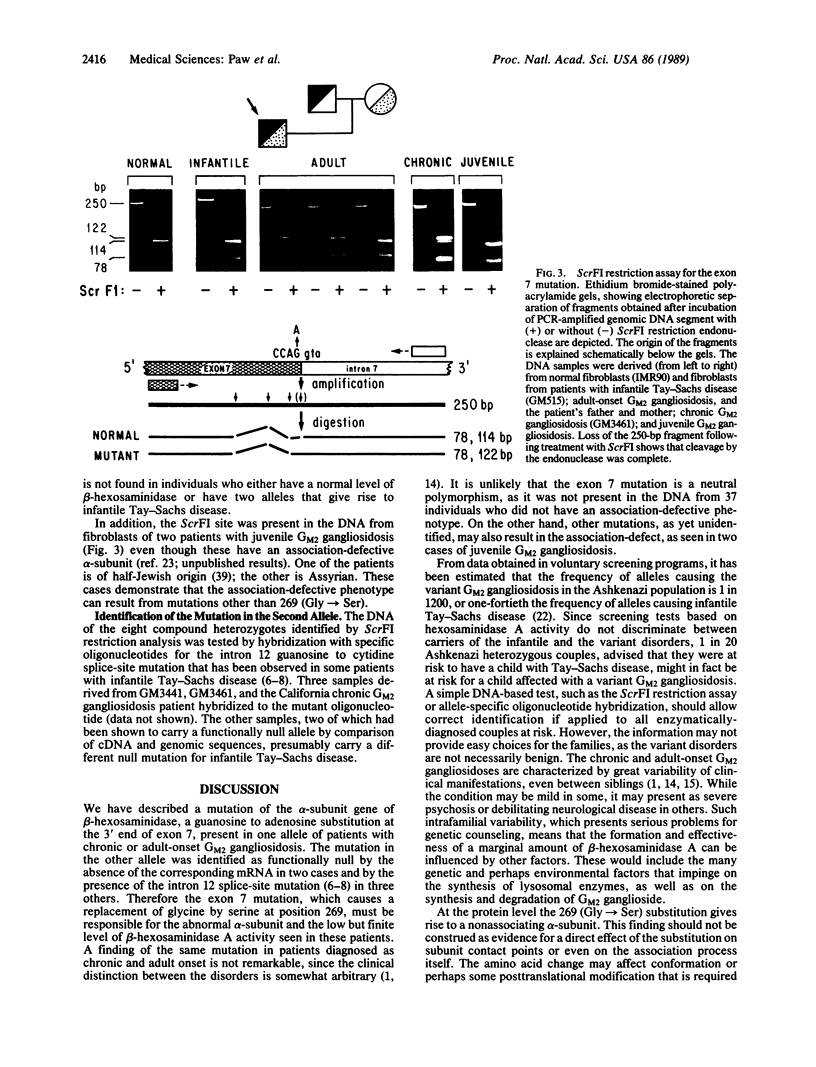
Chronic and adult-onset GM2 gangliosidoses are neurological disorders caused by marked deficiency of the A isoenzyme of beta-hexosaminidase; they occur in the Ashkenazi Jewish population, though less frequently than classic (infantile) Tay-Sachs disease. Earlier biosynthetic studies had identified a defective alpha-subunit that failed to associate with the beta-subunit. We have now found a guanosine to adenosine transition at the 3' end of exon 7, which causes substitution of serine for glycine at position 269 of the alpha-subunit [designated 269 (Gly----Ser) substitution]. An RNase protection assay was used to localize the mutation to a segment of mRNA from fibroblasts of a patient with the adult-onset disorder. That segment of mRNA (after reverse transcription) and a corresponding segment of genomic DNA were amplified by the polymerase chain reaction and sequenced by the dideoxy method. The sequence analysis, together with an assay based on the loss of a ScrFI restriction site, showed that the patient was a compound heterozygote who had inherited the 269 (Gly----Ser) mutation from his father and an allelic null mutation from his mother. The 269 (Gly----Ser) mutation, in compound heterozygosity with a presumed null allele, was also found in fetal fibroblasts with an association-defective phenotype and in cells from five patients with chronic GM2 gangliosidosis. It was not found in beta-hexosaminidase A-deficient cells obtained from patients with infantile Tay-Sachs disease nor in cells from individuals who do not have beta-hexosaminidase A deficiency. However, there must be additional mutations with similar consequences, since the 269 (Gly----Ser) substitution was not present in fibroblasts from two patients with juvenile GM2 gangliosidosis even though these had an association-defective alpha-subunit.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arpaia E., Dumbrille-Ross A., Maler T., Neote K., Tropak M., Troxel C., Stirling J. L., Pitts J. S., Bapat B., Lamhonwah A. M. Identification of an altered splice site in Ashkenazi Tay-Sachs disease. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):85–86. doi: 10.1038/333085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr C. J., Saiki R. K., Erlich H. A., McCormick F., Marshall C. J. Analysis of RAS gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia by polymerase chain reaction and oligonucleotide probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1629–1633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Kaback M. M. Estimation of the frequency of hexosaminidase a variant alleles in the American Jewish population. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 May;34(3):444–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. G., Wigger H. J., Karp H. R., Glaubiger L. M., Rowland L. P. Juvenile spinal muscular atrophy: a new hexosaminidase deficiency phenotype. Ann Neurol. 1982 Jan;11(1):11–16. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karni A., Navon R., Sadeh M. Hexosaminidase A deficiency manifesting as spinal muscular atrophy of late onset. Ann Neurol. 1988 Sep;24(3):451–453. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneluk R. G., Mahuran D. J., Neote K., Klavins M. H., O'Dowd B. F., Tropak M., Willard H. F., Anderson M. J., Lowden J. A., Gravel R. A. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the alpha-subunit of human beta-hexosaminidase. Extensive homology between the alpha- and beta-subunits and studies on Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8407–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Costigan F. C. The major defect in Ashkenazi Jews with Tay-Sachs disease is an insertion in the gene for the alpha-chain of beta-hexosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18587–18589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Hogikyan N. D. A deletion involving Alu sequences in the beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain gene of French Canadians with Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15396–15399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Piekarz R., Neufeld E. F., Shows T. B., Suzuki K. Human beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain: coding sequence and homology with the beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7830–7834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. Splice junction mutation in some Ashkenazi Jews with Tay-Sachs disease: evidence against a single defect within this ethnic group. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3955–3959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Larin Z., Maniatis T. Detection of single base substitutions by ribonuclease cleavage at mismatches in RNA:DNA duplexes. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1242–1246. doi: 10.1126/science.4071043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Muscillo M., Ohno K., Hoffman A. J., Suzuki K. A point mutation in the coding sequence of the beta-hexosaminidase alpha gene results in defective processing of the enzyme protein in an unusual GM2-gangliosidosis variant. J Neurochem. 1988 Sep;51(3):984–987. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon R., Argov Z., Brand N., Sandbank U. Adult GM2 gangliosidosis in association with Tay-Sachs disease: a new phenotype. Neurology. 1981 Nov;31(11):1397–1401. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.11.1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon R., Sandbank U., Frisch A., Baram D., Adam A. Adult-onset GM2 gangliosidosis diagnosed in a fetus. Prenat Diagn. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):169–176. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Tennant L., Veath M. L., Scott C. R., Bucknall W. E. Characterization of unusual hexosaminidase A (HEX A) deficient human mutants. Am J Hum Genet. 1978 Nov;30(6):602–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Suzuki K. A splicing defect due to an exon-intron junctional mutation results in abnormal beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain mRNAs in Ashkenazi Jewish patients with Tay-Sachs disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 31;153(1):463–469. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Suzuki K. Multiple abnormal beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain mRNAs in a compound-heterozygous Ashkenazi Jewish patient with Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18563–18567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Suzuki K. Mutation in GM2-gangliosidosis B1 variant. J Neurochem. 1988 Jan;50(1):316–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb13266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paw B. H., Neufeld E. F. Normal transcription of the beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain gene in the Ashkenazi Tay-Sachs mutation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):3012–3015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L. Gene encoding the human beta-hexosaminidase beta chain: extensive homology of intron placement in the alpha- and beta-chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1883–1887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Neufeld E. F. Synthesis of beta-hexosaminidase in cell-free translation and in intact fibroblasts: an insoluble precursor alpha chain in a rare form of Tay-Sachs disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6360–6364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Soravia E. Organization of the gene encoding the human beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5677–5681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., d'Azzo A., Neufeld E. F. Association of alpha- and beta-subunits during the biosynthesis of beta-hexosaminidase in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3350–3354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willner J. P., Grabowski G. A., Gordon R. E., Bender A. N., Desnick R. J. Chronic GM2 gangliosidosis masquerading as atypical Friedreich ataxia: clinical, morphologic, and biochemical studies of nine cases. Neurology. 1981 Jul;31(7):787–798. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.7.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter E., Yamamoto F., Almoguera C., Perucho M. A method to detect and characterize point mutations in transcribed genes: amplification and overexpression of the mutant c-Ki-ras allele in human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7575–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zokaeem G., Bayleran J., Kaplan P., Hechtman P., Neufeld E. F. A shortened beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain in an Italian patient with infantile Tay-Sachs disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Jun;40(6):537–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Azzo A., Proia R. L., Kolodny E. H., Kaback M. M., Neufeld E. F. Faulty association of alpha- and beta-subunits in some forms of beta-hexosaminidase A deficiency. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):11070–11074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]