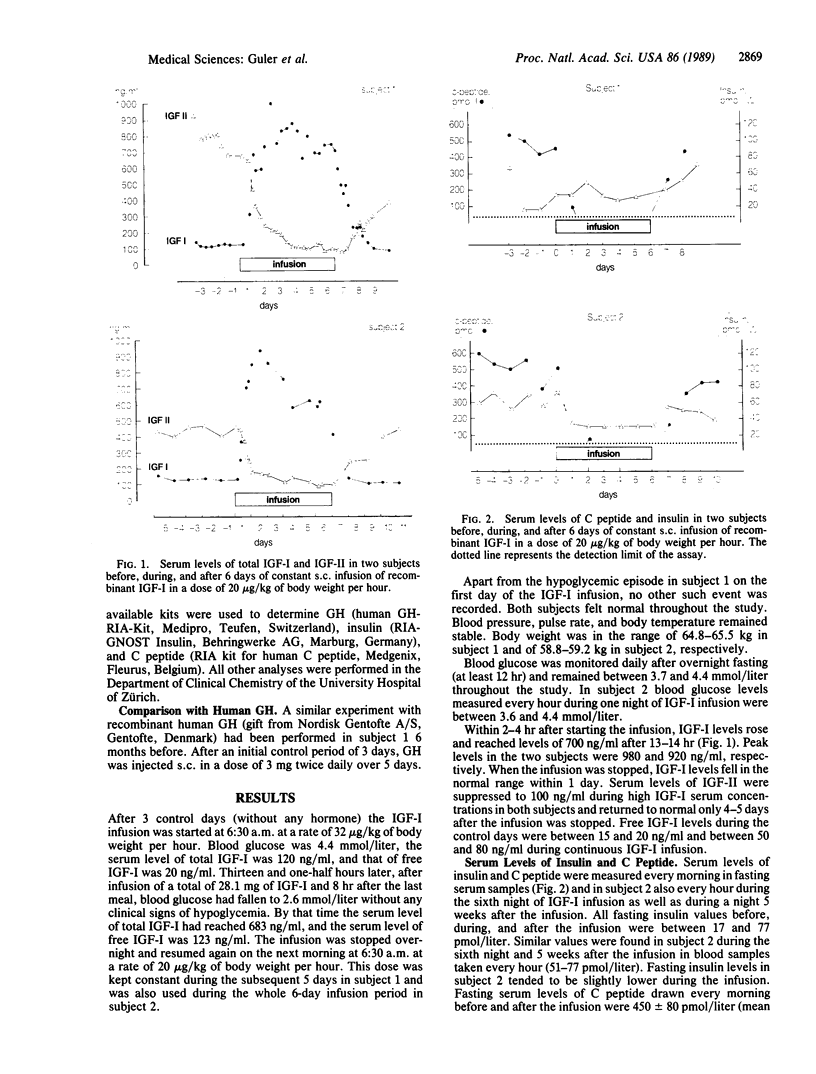
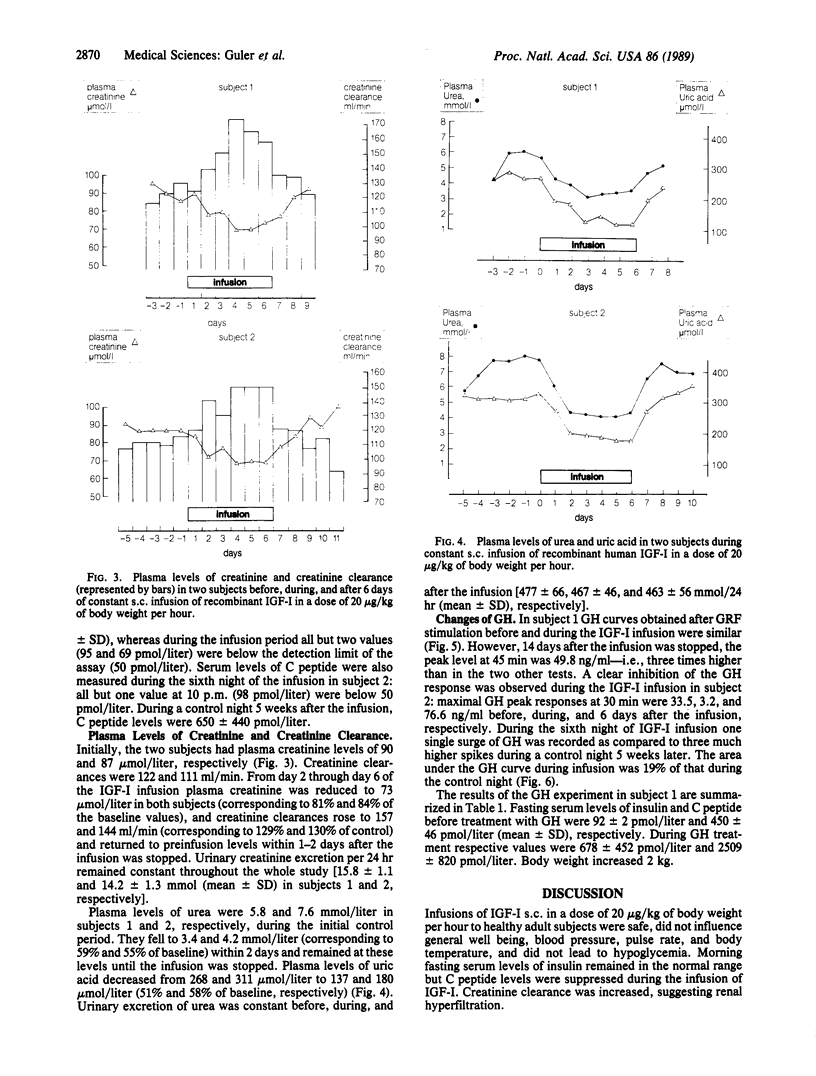
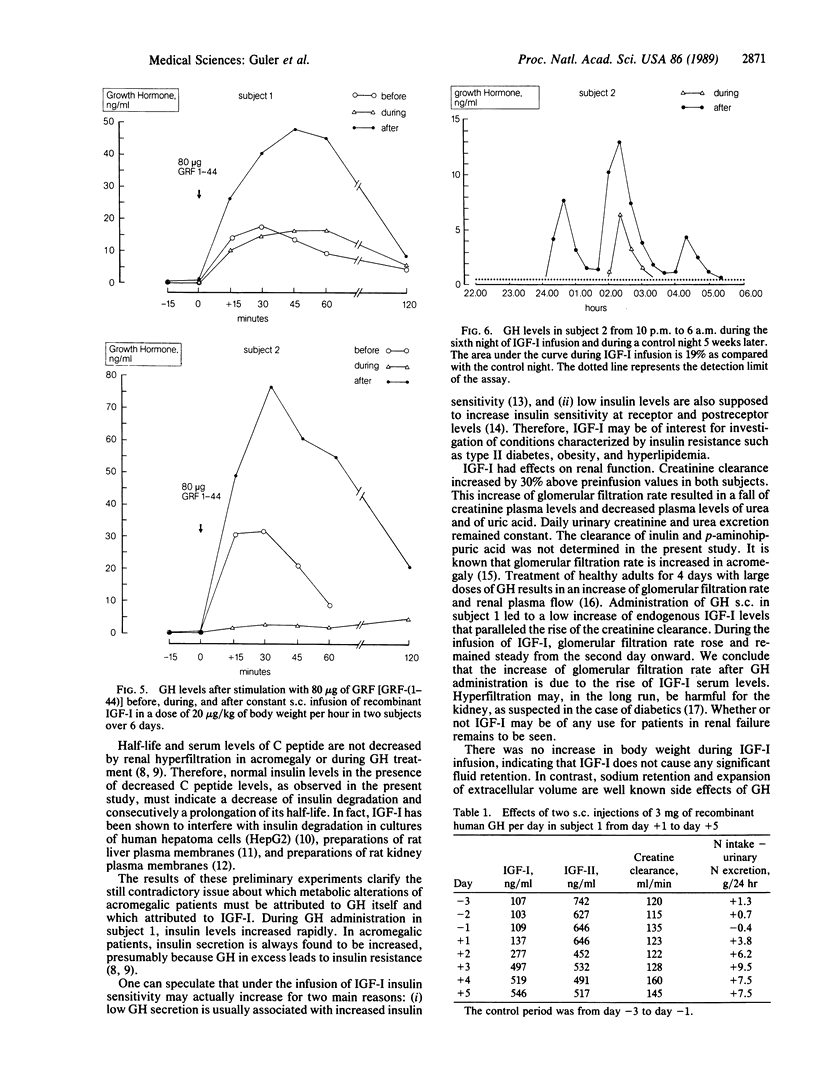
Abstract
Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is an important mediator of growth hormone (GH) action and it appeared tempting to evaluate possible clinical applications. Recombinant IGF-I was infused s.c. at a dose of 20 micrograms/kg of body weight per hour during 6 days in two healthy adult subjects. Blood glucose and fasting insulin levels remained within normal limits and IGF-II levels were suppressed. In contrast to insulin, fasting C peptide levels were decreased. GH secretion was also suppressed by IGF-I. Our preliminary data allow us to distinguish between the effects of GH per se and those of IGF-I: GH causes hyperinsulinism, whereas IGF-I leads to decreased insulin secretion. Glomerular filtration rate, as estimated by creatinine clearance, increased to 130% of preinfusion values during the IGF-I infusion. Total creatinine and urea excretion remained unchanged. We conclude that IGF-I influences kidney function and, in contrast to GH, exerts an insulin-sparing effect. It may be speculated that the therapeutic spectrum of IGF-I is quite different from that of GH.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe H., Molitch M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Underwood L. E. Human growth hormone and somatomedin C suppress the spontaneous release of growth hormone in unanesthetized rats. Endocrinology. 1983 Oct;113(4):1319–1324. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-4-1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berelowitz M., Szabo M., Frohman L. A., Firestone S., Chu L., Hintz R. L. Somatomedin-C mediates growth hormone negative feedback by effects on both the hypothalamus and the pituitary. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1279–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.6262917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORVILAIN J., ABRAMOW M., BERGANS A. Some effects of human growth hormone on renal hemodynamics and on tubular phosphate transport in man. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jun;41:1230–1235. doi: 10.1172/JCI104584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Decedue C. J., Furlanetto R. W., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Evidence that somatomedin-C is degraded by the kidney and inhibits insulin degradation. Endocrinology. 1977 Aug;101(2):577–586. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-2-577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Short-term metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in healthy adults. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):137–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Scheiwiller E., Froesch E. R. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth and has distinct effects on organ size in hypophysectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4889–4893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen I., Tsalikian E., Beaufrere B., Gerich J., Haymond M., Rizza R. Insulin resistance in acromegaly: defects in both hepatic and extrahepatic insulin action. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):E269–E273. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.3.E269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IKKOS D., LUFT R., GEMZELL C. A. The effect of human growth hormone in man. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1959 Nov;32:341–361. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.xxxii0341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Megyesi K., Roth J. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. A potent inhibitor of insulin degradation. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):526–529. doi: 10.1172/JCI108306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelfsema F., Frölich M., Geelhoed-Duyvestijn P. H., Nieuwenhuijzen Kruseman A. C., Looij B. J. Glucagon-stimulated plasma C-peptide and insulin levels in active and non-active acromegalics. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1985 Dec;23(6):627–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1985.tb01123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Kahn C. R., Lesniak M. A., Gorden P., De Meyts P., Megyesi K., Neville D. M., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Soll A. H., Freychet P. Receptors for insulin, NSILA-s, and growth hormone: applications to disease states in man. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1975;31:95–139. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571131-9.50007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheiwiller E., Guler H. P., Merryweather J., Scandella C., Maerki W., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Growth restoration of insulin-deficient diabetic rats by recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):169–171. doi: 10.1038/323169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth in hypophysectomized rats. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):252–253. doi: 10.1038/296252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. Enhanced sensitivity to insulin in rats treated with antibodies to rat growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1980 Oct;107(4):877–883. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-4-877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G., Keen H. The patterns of proteinuria in diabetes mellitus. Relevance to pathogenesis and prevention of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 1984 Jul;33(7):686–692. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.7.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita S., Melmed S. Insulin-like growth factor I action on rat anterior pituitary cells: suppression of growth hormone secretion and messenger ribonucleic acid levels. Endocrinology. 1986 Jan;118(1):176–182. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-1-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Hauri C., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Acute metabolic effects and half-lives of intravenously administered insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal and hypophysectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1768–1775. doi: 10.1172/JCI112500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Walter H., Froesch E. R. Radioimmunological determination of insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal subjects and in patients with growth disorders and extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1321–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI110379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Buul-Offers S., Ueda I., Van den Brande J. L. Biosynthetic somatomedin C (SM-C/IGF-I) increases the length and weight of Snell dwarf mice. Pediatr Res. 1986 Sep;20(9):825–827. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198609000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]