Abstract
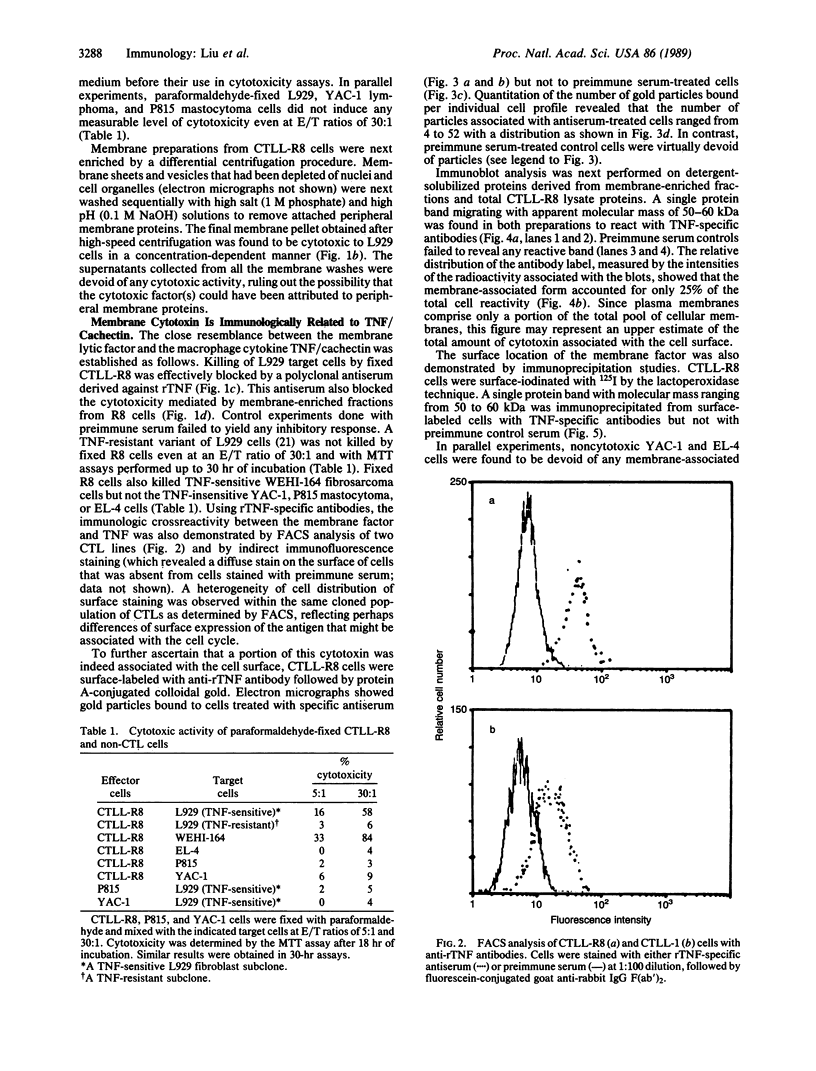
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) kill their targets by a contact-dependent mechanism. We investigated the possibility that the CTL membranes themselves could exert direct cytotoxic activity. Murine CTLs that had been fixed with paraformaldehyde retained a slow cytotoxic activity toward various target cells that are also sensitive to another cytokine, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)/cachectin. This cytotoxic activity was neutralized by antibodies specific for TNF. Membrane fractions obtained from CTLs were cytotoxic to TNF-sensitive targets but not to several TNF-resistant cell lines. Immunoblot analysis revealed a membrane protein band of 50-60 kDa from CTLs that reacts with anti-TNF antibodies. The surface localization of this cytokine was further ascertained by flow cytometry, indirect immunofluorescence, and immunoelectron microscopy studies using TNF-specific antibodies. Radioiodination of CTL surface proteins followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-TNF antibodies confirmed the presence of a TNF-related cytokine in the plasma membranes of CTLs that migrated with an apparent molecular mass of 50-60 kDa under disulfide-reducing conditions. This cytokine can be removed from membranes by treatment with detergents but not with high-salt buffers, suggesting that it may be an integral membrane protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Gifford G. E. Cell-associated tumor necrosis factor (TNF) as a killing mechanism of activated cytotoxic macrophages. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):957–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degliantoni G., Murphy M., Kobayashi M., Francis M. K., Perussia B., Trinchieri G. Natural killer (NK) cell-derived hematopoietic colony-inhibiting activity and NK cytotoxic factor. Relationship with tumor necrosis factor and synergism with immune interferon. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1512–1530. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Anderson C. G., Prochazka G. High activity of N-alpha-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine thiobenzyl ester serine esterase and cytolytic perforin in cloned cell lines is not demonstrable in in-vivo-induced cytotoxic effector cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5004–5008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detmers P. A., Wright S. D., Olsen E., Kimball B., Cohn Z. A. Aggregation of complement receptors on human neutrophils in the absence of ligand. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1137–1145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Chervenak R., Cohen J. J. Endogenous endonuclease-induced DNA fragmentation: an early event in cell-mediated cytolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. Tumour necrosis factor-like activity on paraformaldehyde-fixed monocyte monolayers. Immunology. 1987 Aug;61(4):443–448. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferluga J., Allison A. C. Cytotoxicity of isolated plasma membranes from lymph node cells. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):708–710. doi: 10.1038/255708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golstein P. Cytolytic T-cell melodrama. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):12–12. doi: 10.1038/327012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. M., Reade J. L., Ware C. F., Devlin P. E., Liang C. M., Devlin J. J. Cytotoxic lymphokines produced by cloned human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. II. A novel CTL-produced cytotoxin that is antigenically distinct from tumor necrosis factor and alpha-lymphotoxin. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3488–3493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. M., Reade J. L., Ware C. F. Rapid colorimetric assay for cell viability: application to the quantitation of cytotoxic and growth inhibitory lymphokines. J Immunol Methods. 1984 May 25;70(2):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90190-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gromkowski S. H., Brown T. C., Cerutti P. A., Cerottini J. C. DNA of human Raji target cells is damaged upon lymphocyte-mediated lysis. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):752–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell D. M., Martz E. Low calcium concentrations support killing by some but not all cytolytic T lymphocytes, and reveal inhibition of a postconjugation step by calcium antagonists. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1982–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V., Nedospasov S. A., Plaetinck G., Naquet P., Cerottini J. C. Expression of the tumor necrosis factor locus is not necessary for the cytolytic activity of T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1916–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn-Perles B., Golstein P. Cell membrane-mediated cytolysis by membranes from noncytolytic cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jan;8(1):71–75. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler M., Perez C., DeFay K., Albert I., Lu S. D. A novel form of TNF/cachectin is a cell surface cytotoxic transmembrane protein: ramifications for the complex physiology of TNF. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90486-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J. Are complement lysis and lymphocytotoxicity analogous? Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):473–474. doi: 10.1038/305473a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Steffen M., King F., Young J. D. Identification, isolation, and characterization of a novel cytotoxin in murine cytolytic lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Santer V. Enzymic iodination. A probe for accessible surface proteins of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj1240921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N., Watkins J. F. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. I. Mode of action, specificity and physicochemical properties. Br J Cancer. 1978 Aug;38(2):302–309. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Kane K. P., Mescher M. F., Clark W. R. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediated lysis without release of serine esterase. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):71–72. doi: 10.1038/330071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters P. M., Ortaldo J. R., Shalaby M. R., Svedersky L. P., Nedwin G. E., Bringman T. S., Hass P. E., Aggarwal B. B., Herberman R. B., Goeddel D. V. Natural killer-sensitive targets stimulate production of TNF-alpha but not TNF-beta (lymphotoxin) by highly purified human peripheral blood large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2592–2598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H. Internal disintegration model of cytotoxic lymphocyte-induced target damage. Immunol Rev. 1983;72:97–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutman O., Paige C. J., Figarella E. F. Natural cytotoxic cells against solid tumors in mice. I. Strain and age distribution and target cell susceptibility. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1819–1826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirosh R., Berke G. T-Lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis as an excitatory process of the target. I. Evidence that the target cell may be the site of Ca2+ action. Cell Immunol. 1985 Oct 1;95(1):113–123. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90300-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trenn G., Takayama H., Sitkovsky M. V. Exocytosis of cytolytic granules may not be required for target cell lysis by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):72–74. doi: 10.1038/330072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Jongeneel C. V. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediated cytolysis. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2641–2646. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto R. S., Ware C. F., Granger G. A. The human LT system. XI. Identification of LT and "TNF-like" forms from stimulated natural killers, specific and nonspecific cytotoxic human T cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1878–1884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Clark W. R., Liu C. C., Cohn Z. A. A calcium- and perforin-independent pathway of killing mediated by murine cytolytic lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1894–1899. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Cellular and humoral mechanisms of cytotoxicity: structural and functional analogies. Adv Immunol. 1987;41:269–332. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Leong L. G., Liu C. C., Damiano A., Wall D. A., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and characterization of a serine esterase from cytolytic T cell granules. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]