Abstract
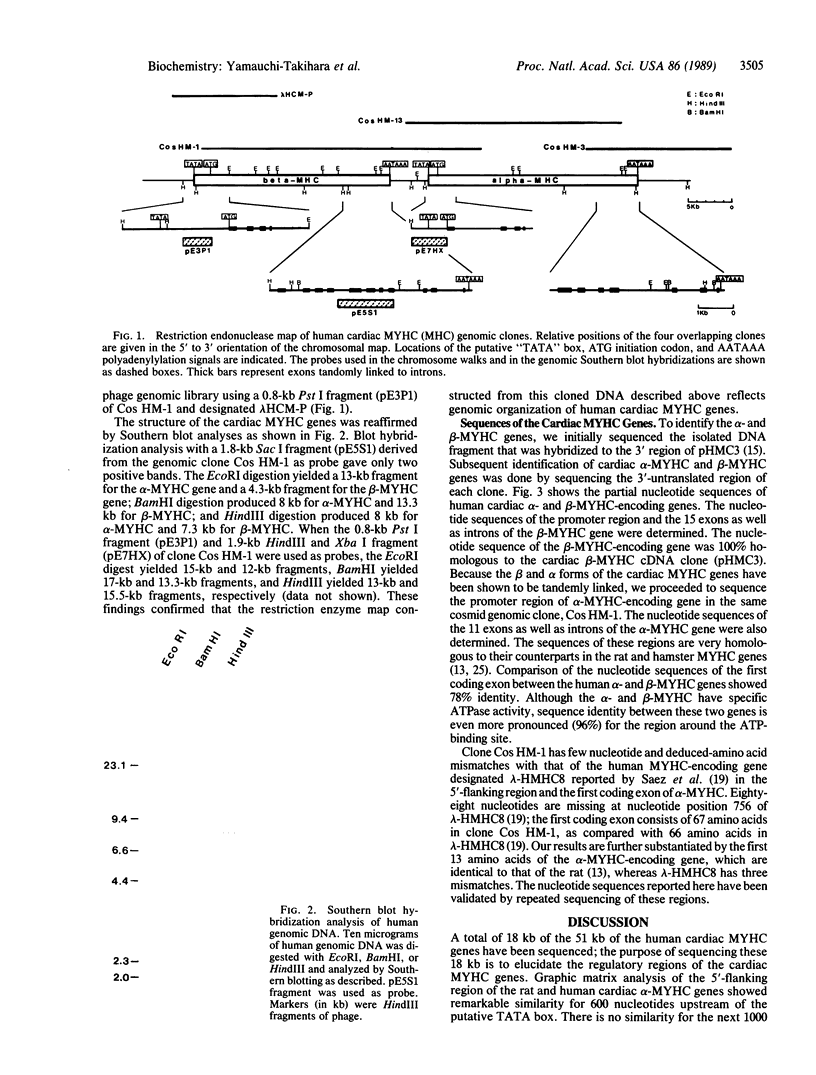
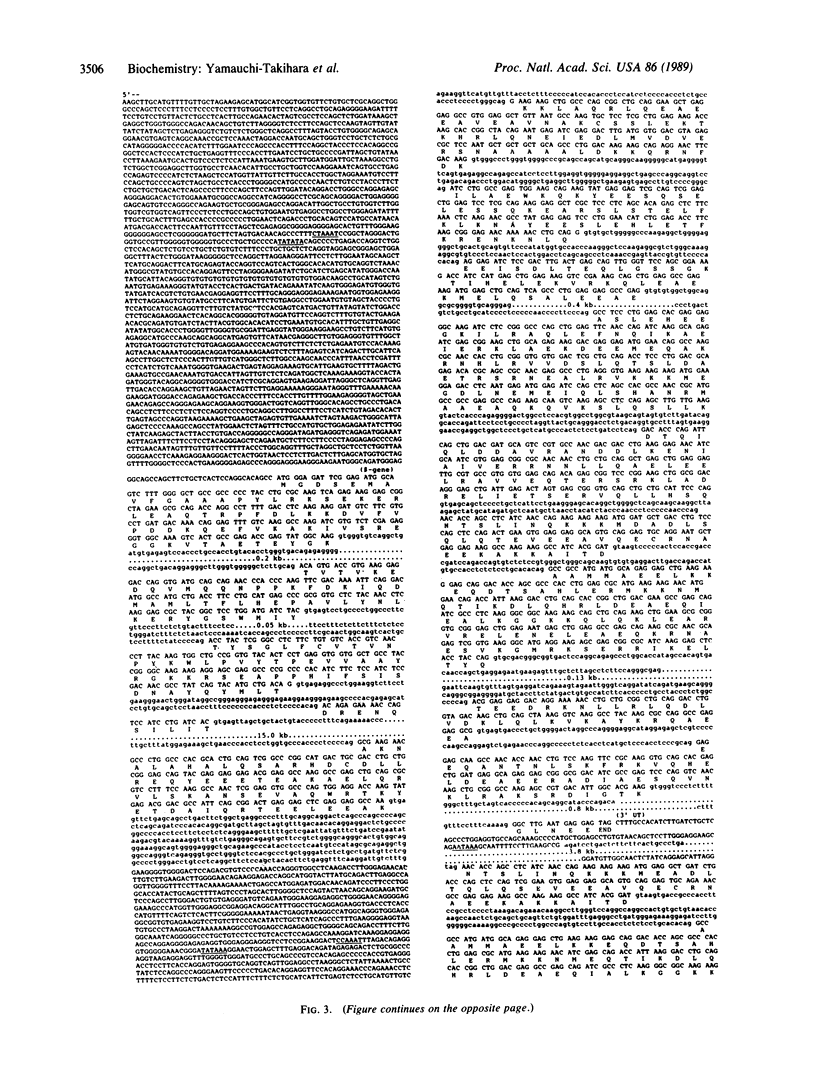
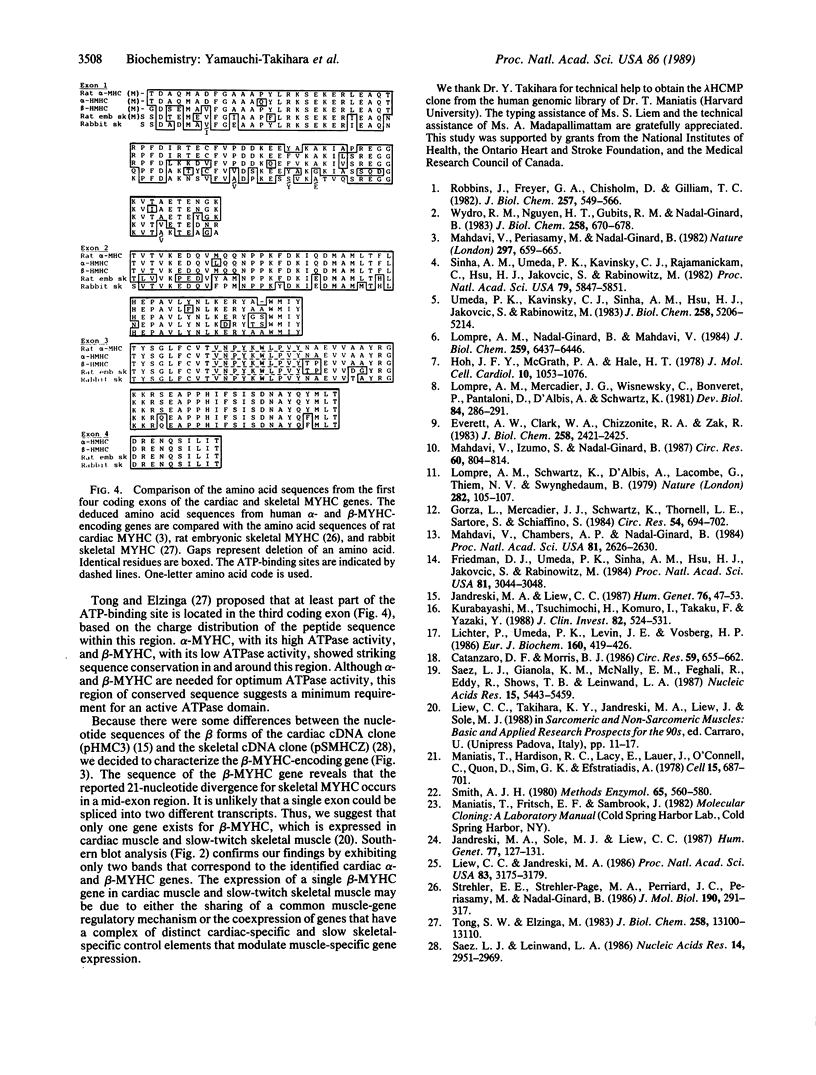
We have isolated and analyzed the structure of the genes coding for the alpha and beta forms of the human cardiac myosin heavy chain (MYHC). Detailed analysis of four overlapping MYHC genomic clones shows that the alpha-MYHC and beta-MYHC genes constitute a total length of 51 kilobases and are tandemly linked. The beta-MYHC-encoding gene, predominantly expressed in the normal human ventricle and also in slow-twitch skeletal muscle, is located 4.5 kilobases upstream of the alpha-MYHC-encoding gene, which is predominantly expressed in normal human atrium. We have determined the nucleotide sequences of the beta form of the MYHC gene, which is 100% homologous to the cardiac MYHC cDNA clone (pHMC3). It is unlikely that the divergence of a few nucleotide sequences from the cardiac beta-MYHC cDNA clone (pHMC3) reported in a MYHC cDNA clone (pSMHCZ) from skeletal muscle is due to a splicing mechanism. This finding suggests that the same beta form of the cardiac MYHC gene is expressed in both ventricular and slow-twitch skeletal muscle. The promoter regions of both alpha- and beta-MYHC genes, as well as the first four coding regions in the respective genes, have also been sequenced. The sequences in the 5'-flanking region of the alpha- and beta-MYHC-encoding genes diverge extensively from one another, suggesting that expression of the alpha- and beta-MYHC genes is independently regulated.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Catanzaro D. F., Morris B. J. Human cardiac myosin heavy chain genes. Isolation of a genomic DNA clone and its characterization and of a second unique clone also present in the human genome. Circ Res. 1986 Dec;59(6):655–662. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.6.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett A. W., Clark W. A., Chizzonite R. A., Zak R. Change in synthesis rates of alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chains in rabbit heart after treatment with thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2421–2425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. J., Umeda P. K., Sinha A. M., Hsu H. J., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M. Characterization of genomic clones specifying rabbit alpha- and beta-ventricular myosin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3044–3048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorza L., Mercadier J. J., Schwartz K., Thornell L. E., Sartore S., Schiaffino S. Myosin types in the human heart. An immunofluorescence study of normal and hypertrophied atrial and ventricular myocardium. Circ Res. 1984 Jun;54(6):694–702. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.6.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F., McGrath P. A., Hale P. T. Electrophoretic analysis of multiple forms of rat cardiac myosin: effects of hypophysectomy and thyroxine replacement. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1978 Nov;10(11):1053–1076. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(78)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandreski M. A., Liew C. C. Construction of a human ventricular cDNA library and characterization of a beta myosin heavy chain cDNA clone. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):47–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00283049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandreski M. A., Sole M. J., Liew C. C. Two different forms of beta myosin heavy chain are expressed in human striated muscle. Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;77(2):127–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00272378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurabayashi M., Tsuchimochi H., Komuro I., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of human cardiac alpha- and beta-form myosin heavy chain complementary DNA clones. Regulation of expression during development and pressure overload in human atrium. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):524–531. doi: 10.1172/JCI113627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Umeda P. K., Levin J. E., Vosberg H. P. Partial characterization of the human beta-myosin heavy-chain gene which is expressed in heart and skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):419–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew C. C., Jandreski M. A. Construction and characterization of the alpha form of a cardiac myosin heavy chain cDNA clone and its developmental expression in the Syrian hamster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3175–3179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lompre A. M., Schwartz K., d'Albis A., Lacombe G., Van Thiem N., Swynghedauw B. Myosin isoenzyme redistribution in chronic heart overload. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):105–107. doi: 10.1038/282105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lompré A. M., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Expression of the cardiac ventricular alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain genes is developmentally and hormonally regulated. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6437–6446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi V., Chambers A. P., Nadal-Ginard B. Cardiac alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain genes are organized in tandem. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi V., Izumo S., Nadal-Ginard B. Developmental and hormonal regulation of sarcomeric myosin heavy chain gene family. Circ Res. 1987 Jun;60(6):804–814. doi: 10.1161/01.res.60.6.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi V., Periasamy M., Nadal-Ginard B. Molecular characterization of two myosin heavy chain genes expressed in the adult heart. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):659–664. doi: 10.1038/297659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Freyer G. A., Chisholm D., Gilliam T. C. Isolation of multiple genomic sequences coding for chicken myosin heavy chain protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):549–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saez L. J., Gianola K. M., McNally E. M., Feghali R., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Leinwand L. A. Human cardiac myosin heavy chain genes and their linkage in the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5443–5459. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saez L., Leinwand L. A. Characterization of diverse forms of myosin heavy chain expressed in adult human skeletal muscle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2951–2969. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha A. M., Umeda P. K., Kavinsky C. J., Rajamanickam C., Hsu H. J., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M. Molecular cloning of mRNA sequences for cardiac alpha- and beta-form myosin heavy chains: expression in ventricles of normal, hypothyroid, and thyrotoxic rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5847–5851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J. DNA sequence analysis by primed synthesis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):560–580. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehler E. E., Strehler-Page M. A., Perriard J. C., Periasamy M., Nadal-Ginard B. Complete nucleotide and encoded amino acid sequence of a mammalian myosin heavy chain gene. Evidence against intron-dependent evolution of the rod. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):291–317. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. W., Elzinga M. The sequence of the NH2-terminal 204-residue fragment of the heavy chain of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13100–13110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda P. K., Kavinsky C. J., Sinha A. M., Hsu H. J., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M. Cloned mRNA sequences for two types of embryonic myosin heavy chains from chick skeletal muscle. II. Expression during development using S1 nuclease mapping. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5206–5214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wydro R. M., Nguyen H. T., Gubits R. M., Nadal-Ginard B. Characterization of sarcomeric myosin heavy chain genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):670–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



