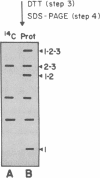
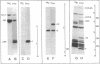
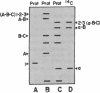
Abstract
We describe a general method to locate the positions of cysteine residues relative to the amino terminus of a protein, using a modified chemical cleavage of the polypeptide backbone at cysteine. The cleavage reaction introduces the carbon atom of 14CN into the carboxyl-terminal fragment produced at each cleavage of the polypeptide chain. Peptides containing the amino terminus of the intact protein are not labeled; all other peptides are labeled at their amino termini. Partial cleavage of a protein followed by gel electrophoresis and autoradiography identifies a ladder of unlabeled peptides that maps positions of the cysteine residues relative to the protein amino terminus. To map individual proteins present in a complex mixture, the polypeptides are cyanolated in solution with 14CN, and the modified proteins are separated by discontinuous SDS/PAGE. The gel is stained, and the desired protein is excised, cleaved at cysteine within the gel slice, and mapped in the second dimension by gel electrophoresis. These techniques are demonstrated with proteins of known sequence containing from zero to five cysteine residues. The cysteine "landmark map" should be particularly useful in locating protein modifications, in questions of protein similarity, and in mapping functional domains. A strategy is also presented for locating other residues in the polypeptide, for which specific cleavage methods exist.
Full text
PDF


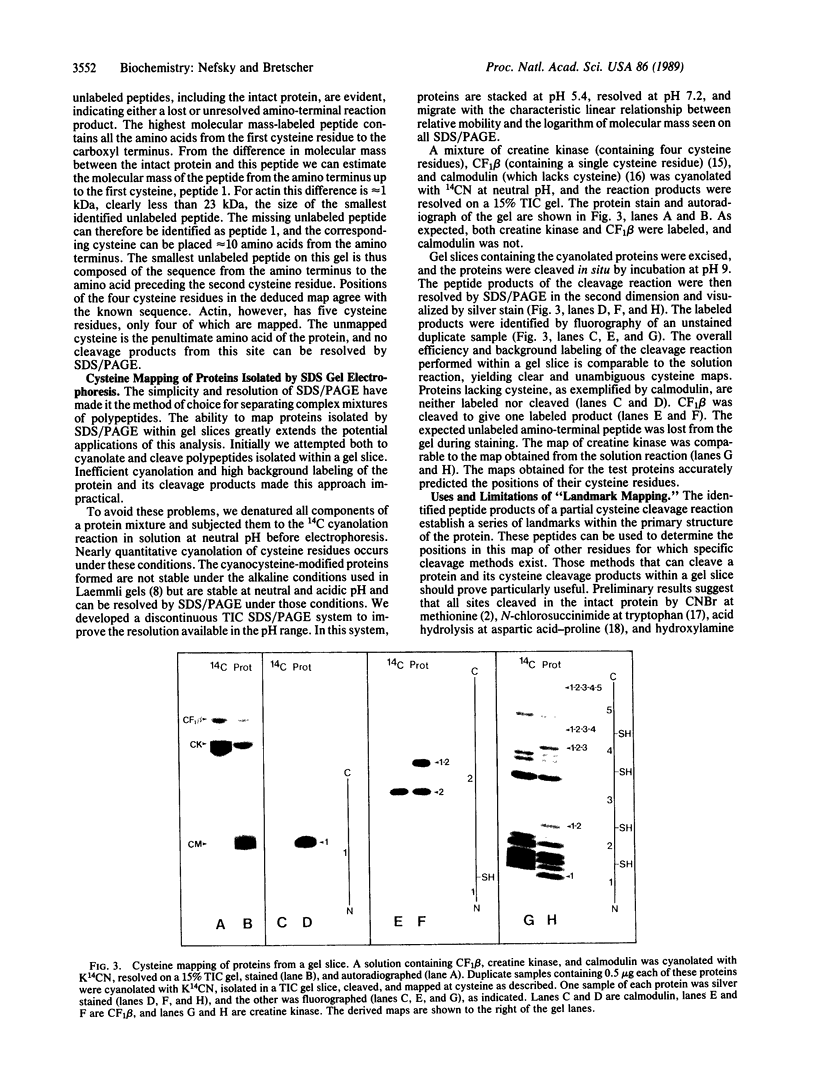
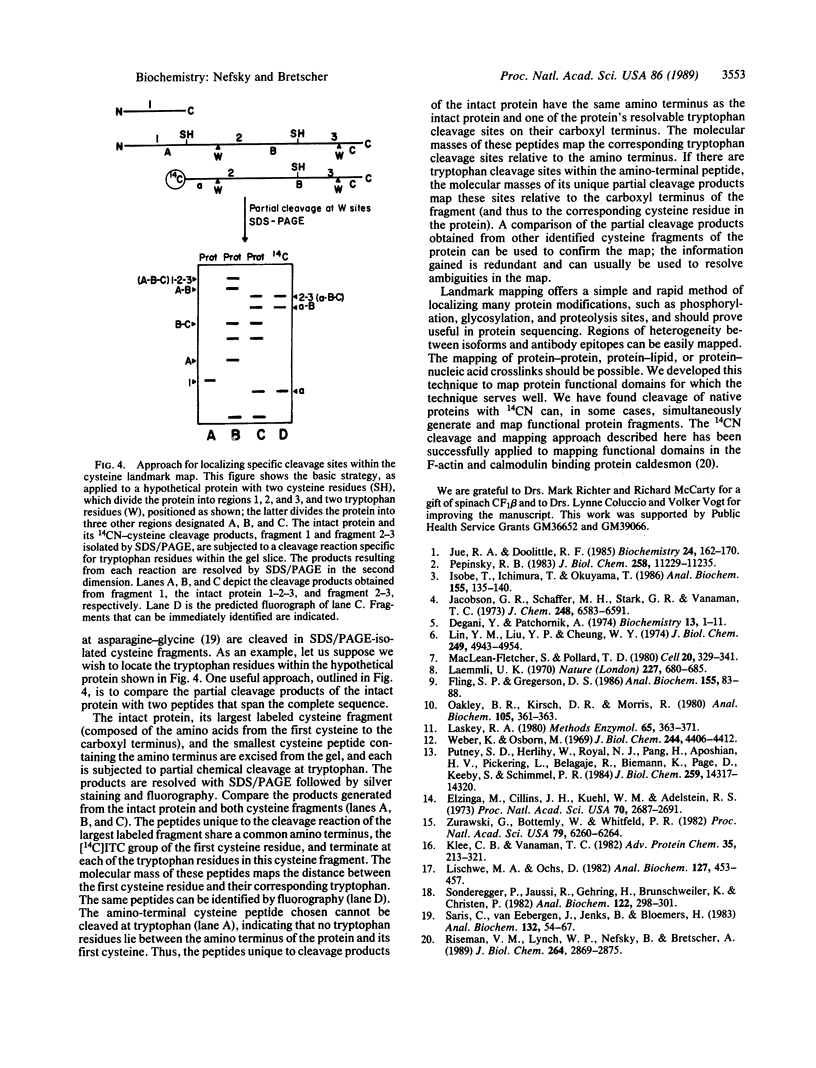
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Degani Y., Patchornik A. Cyanylation of sulfhydryl groups by 2-nitro-5-thiocyanobenzoic acid. High-yield modification and cleavage of peptides at cysteine residues. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):1–11. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzinga M., Collins J. H., Kuehl W. M., Adelstein R. S. Complete amino-acid sequence of actin of rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2687–2691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling S. P., Gregerson D. S. Peptide and protein molecular weight determination by electrophoresis using a high-molarity tris buffer system without urea. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe T., Ichimura T., Okuyama T. Identification of the C-terminal portion of a protein by comparative peptide mapping. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Schaffer M. H., Stark G. R., Vanaman T. C. Specific chemical cleavage in high yield at the amino peptide bonds of cysteine and cystine residues. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6583–6591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jue R. A., Doolittle R. F. Determination of the relative positions of amino acids by partial specific cleavages of end-labeled proteins. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):162–170. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Vanaman T. C. Calmodulin. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:213–321. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A. The use of intensifying screens or organic scintillators for visualizing radioactive molecules resolved by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):363–371. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. M., Liu Y. P., Cheung W. Y. Cyclic 3':5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Purification, characterization, and active form of the protein activator from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4943–4954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Ochs D. A new method for partial peptide mapping using N-chlorosuccinimide/urea and peptide silver staining in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):453–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean-Fletcher S., Pollard T. D. Mechanism of action of cytochalasin B on actin. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90619-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B. Localization of lipid-protein and protein-protein interactions within the murine retrovirus gag precursor by a novel peptide-mapping technique. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11229–11235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S., Herlihy W., Royal N., Pang H., Aposhian H. V., Pickering L., Belagaje R., Biemann K., Page D., Kuby S. Rabbit muscle creatine phosphokinase. CDNA cloning, primary structure and detection of human homologues. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14317–14320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riseman V. M., Lynch W. P., Nefsky B., Bretscher A. The calmodulin and F-actin binding sites of smooth muscle caldesmon lie in the carboxyl-terminal domain whereas the molecular weight heterogeneity lies in the middle of the molecule. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2869–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., van Eenbergen J., Jenks B. G., Bloemers H. P. Hydroxylamine cleavage of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):54–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonderegger P., Jaussi R., Gehring H., Brunschweiler K., Christen P. Peptide mapping of protein bands from polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis by chemical cleavage in gel pieces and re-electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1982 May 15;122(2):298–301. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. Structures of the genes for the beta and epsilon subunits of spinach chloroplast ATPase indicate a dicistronic mRNA and an overlapping translation stop/start signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6260–6264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]