Abstract
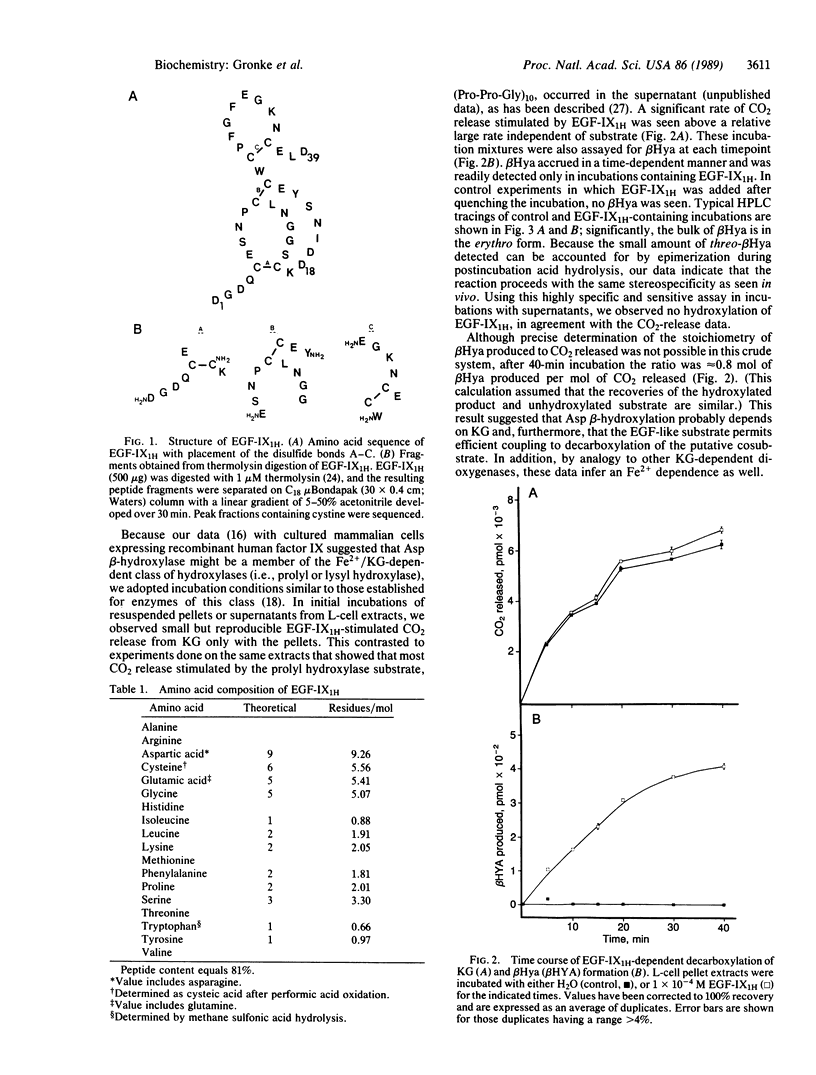
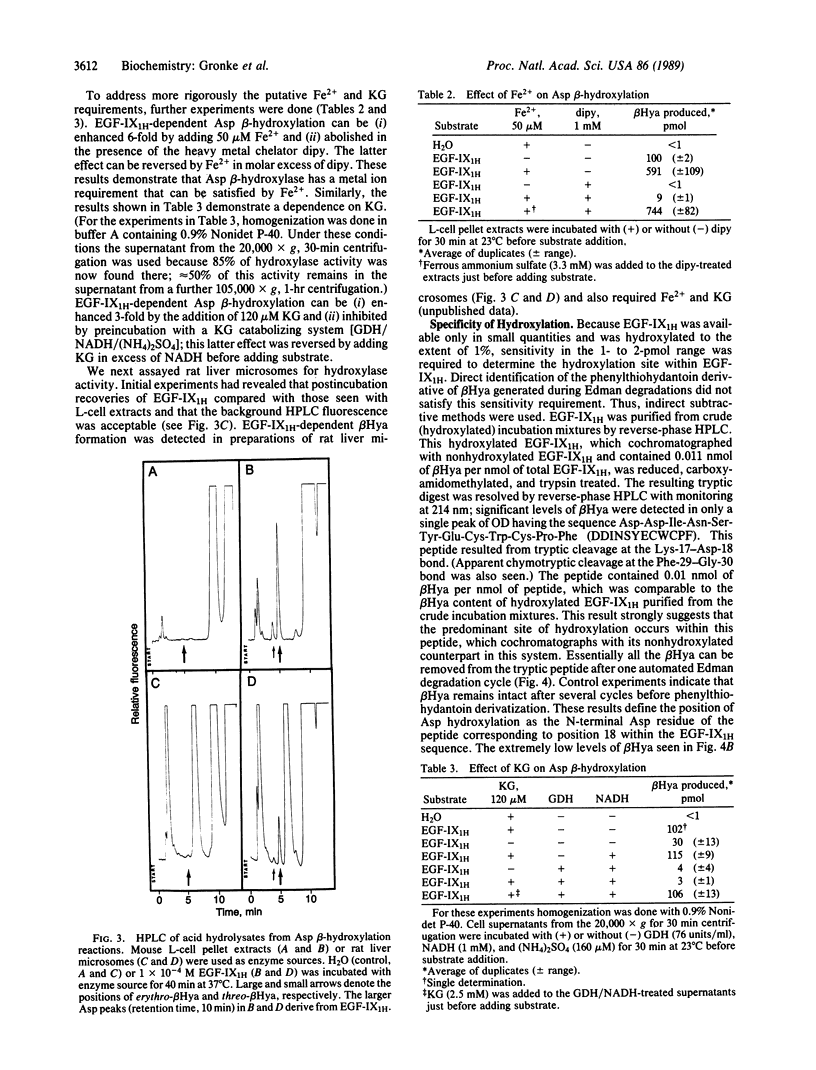
beta-Hydroxylation of aspartic acid is a post-translational modification that occurs in several vitamin K-dependent coagulation proteins. By use of a synthetic substrate comprised of the first epidermal growth factor-like domain in human factor IX and either mouse L-cell extracts or rat liver microsomes as the source of enzyme, in vitro aspartyl beta-hydroxylation was accomplished. Aspartyl beta-hydroxylase appears to require the same cofactors as known alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases. The hydroxylation reaction proceeds with the same stereospecificity and occurs only at the aspartate corresponding to the position seen in vivo. Further purification and characterization of this enzymatic activity should now be possible.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg R. A., Prockop D. J. Affinity column purification of protocollagen proline hydroxylase from chick embryos and further characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1175–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardinale G. J., Udenfriend S. Prolyl hydroxylase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):245–300. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Lundwall A., Stenflo J. Primary structure of bovine vitamin K-dependent protein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4199–4203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernlund P., Stenflo J. Beta-hydroxyaspartic acid in vitamin K-dependent proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12509–12512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Przysiecki C. T. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. Int J Biochem. 1987;19(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(87)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Shia M. Some characteristics of a vitamin K-dependent carboxylating system from rat liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):647–654. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Højrup P., Magnusson S. Disulphide bridges of bovine factor X. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):887–891. doi: 10.1042/bj2450887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao W. W., Berg R. A., Prockop D. J. Ascorbate increases the synthesis of procollagen hydroxyproline by cultured fibroblasts from chick embryo tendons without activation of prolyl hydroxyla. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 5;411(2):202–215. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90300-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majamaa K., Hanauske-Abel H. M., Günzler V., Kivirikko K. I. The 2-oxoglutarate binding site of prolyl 4-hydroxylase. Identification of distinct subsites and evidence for 2-oxoglutarate decarboxylation in a ligand reaction at the enzyme-bound ferrous ion. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):239–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen B. A., Fujikawa K., Kisiel W., Sasagawa T., Howald W. N., Kwa E. Y., Weinstein B. Complete amino acid sequence of the light chain of human blood coagulation factor X: evidence for identification of residue 63 as beta-hydroxyaspartic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2875–2884. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen B. A., Fujikawa K., Kisiel W. The occurrence of beta-hydroxyaspartic acid in the vitamin K-dependent blood coagulation zymogens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):8–14. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90961-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Isaacs B. S., Esmon C. T., Johnson A. E. Derivatives of blood coagulation factor IX contain a high affinity Ca2+-binding site that lacks gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5698–5704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlin A. K., Landes G., Bourdon P., Oppenheimer C., Wydro R., Stenflo J. Beta-hydroxyaspartic acid in the first epidermal growth factor-like domain of protein C. Its role in Ca2+ binding and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19240–19248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przysiecki C. T., Staggers J. E., Ramjit H. G., Musson D. G., Stern A. M., Bennett C. D., Friedman P. A. Occurrence of beta-hydroxylated asparagine residues in non-vitamin K-dependent proteins containing epidermal growth factor-like domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7856–7860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. J., Jones I. M., Handford P. A., Walter S. J., Esnouf M. P., Smith K. J., Brownlee G. G. The role of beta-hydroxyaspartate and adjacent carboxylate residues in the first EGF domain of human factor IX. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2053–2061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Hash J. H., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Location of disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7669–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Lundwall A., Dahlbäck B. beta-Hydroxyasparagine in domains homologous to the epidermal growth factor precursor in vitamin K-dependent protein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):368–372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent formation of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:157–172. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugo T., Björk I., Holmgren A., Stenflo J. Calcium-binding properties of bovine factor X lacking the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing region. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5705–5710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:459–477. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of glutamyl residues in proteins. Biofactors. 1988 Jan;1(1):55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


