Abstract
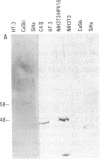
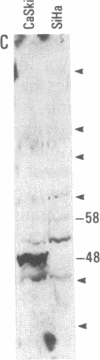
The growing awareness of the role of human papillomavirus (HPV) in cervical carcinoma has triggered a search for uncomplicated detection methods. To define a serologic response to HPV, we synthesized peptides based on sequences deduced from the genome of HPV type 16, the most common malignancy-associated type of HPV. One of these peptides reacted with IgA antibodies present in sera from 24 of 33 patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or cervical carcinoma, whereas this peptide reacted with only 6 of 27 sera from individuals without cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Immunoaffinity-purified human antipeptide IgA antibodies detected HPV-specific 58- and 48-kDa proteins in cervical carcinoma cell extracts and also detected a nuclear antigen in HPV-carrying cervical cancer cell lines and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia biopsied tissue. These antigens were also detected with mouse monoclonal and rabbit polyclonal antibodies to the same peptide. The results indicate that screening for infection with malignancy-associated types of HPV may be possible by simple synthetic peptide-based serology.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. F., Meanwell C. A., Maitland N. J., Blackledge G., Scully C., Jordan J. A. Human papillomavirus type-16 homologous DNA in normal human ectocervix. Lancet. 1986 Jul 19;2(8499):157–158. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Sternås L., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Jörnvall H., Klein G., Lerner R. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide identify the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4652–4656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Wendel-Hansen V., Kjellström G., Kallin B., Rosén A. Purification and characterization of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 using monoclonal antipeptide antibodies. Int J Cancer. 1988 Nov 15;42(5):721–727. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner L., Bekassy Z., Jonsson N., Moreno-Lopez J., Blomberg J. Detection of IgA antibodies against human papillomavirus in cervical secretions from patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jan 15;43(1):36–40. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doorbar J., Campbell D., Grand R. J., Gallimore P. H. Identification of the human papilloma virus-1a E4 gene products. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):355–362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04219.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzubai A., Anafi M., Masucci M. G., Dillner J., Lerner R. A., Klein G., Sulitzeanu D. Down-regulation of the EBV-encoded membrane protein (LMP) in Burkitt lymphomas. Int J Cancer. 1987 Sep 15;40(3):358–364. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgA serum antibodies as an outstanding feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenison S. A., Firzlaff J. M., Langenberg A., Galloway D. A. Identification of immunoreactive antigens of human papillomavirus type 6b by using Escherichia coli-expressed fusion proteins. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2115–2123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2115-2123.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jett M., Seed T. M., Jamieson G. A. Isolation and characterization of plasma membranes and intact nuclei from lymphoid cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2134–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B. C., Lindahl T., Fialkow P. J., Singh S., Stehlin J. S. Direct evidence for the presence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA and nuclear antigen in malignant epithelial cells from patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of the nasopharynx. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4737–4741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komly C. A., Breitburd F., Croissant O., Streeck R. E. The L2 open reading frame of human papillomavirus type 1a encodes a minor structural protein carrying type-specific antigens. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):813–816. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.813-816.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. C., Gilden R. V., Showalter S. D., Shah K. V. Identification of the human papillomavirus E2 protein in genital tract tissues. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):606–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.606-609.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. C., Shah K. V., Seth A., Gilden R. V. Identification of the human papillomavirus type 6b L1 open reading frame protein in condylomas and corresponding antibodies in human sera. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2684–2690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2684-2690.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisels A., Fortin R. Condylomatous lesions of the cervix and vagina. I. Cytologic patterns. Acta Cytol. 1976 Nov-Dec;20(6):505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty A. M., Alexander H., Lerner R. A., Thornton G. B. Antibodies to peptides detect new hepatitis B antigen: serological correlation with hepatocellular carcinoma. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):429–433. doi: 10.1126/science.2981434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Biberfeld G., Chiodi F., von Gegerfeldt A., Nauclér A., Parks E., Lerner R. Discrimination between antibodies to HIV and to related retroviruses using site-directed serology. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):248–250. doi: 10.1038/329248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Mufson M. A., Alexander H., Houghten R. A., Lerner R. A. Site-directed serology with synthetic peptides representing the large glycoprotein G of respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6572–6576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister H. Human papillomaviruses and genital cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1987;48:113–147. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60691-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Howley P. M. Transcriptional trans-activation by the human papillomavirus type 16 E2 gene product. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1630-1638.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Oltersdorf T., Krämmer G., Röwekamp W. Identification of early proteins of the human papilloma viruses type 16 (HPV 16) and type 18 (HPV 18) in cervical carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah K. V., Buscema J. Genital warts, papillomaviruses, and genital malignancies. Annu Rev Med. 1988;39:371–379. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.39.020188.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Naso R. B., Rosen J., Whalley A., Hom Y. L., Hoey K., Kennedy C. J., McCutchan J. A., Spector S. A., Richman D. D. Antibody to a synthetic oligopeptide in subjects at risk for human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1498–1504. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1498-1504.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M., Green N., Liu F. T., Niman H. L., Lerner R. A. Chemical synthesis of a polypeptide predicted from nucleotide sequence allows detection of a new retroviral gene product. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):801–805. doi: 10.1038/287801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjänen K. J. Current concepts of human papillomavirus infections in the genital tract and their relationship to intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1984 May;39(5):252–265. doi: 10.1097/00006254-198405000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. G., Singer A., Dyson J. L., Shah K. V., To A., Coleman D. V. The prevalence of human papillomavirus antigen in patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Br J Cancer. 1983 Jul;48(1):99–101. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1983.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto S., Burkhardt A. L., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA-induced malignant transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):572–577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.572-577.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C., Krishnan-Hewlett I., Baker C. C., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. Presence and expression of human papillomavirus sequences in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):361–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Human papillomaviruses and their possible role in squamous cell carcinomas. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;78:1–30. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66800-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]